The concept of CRM Business Transactions in SAP has the meanings of a uniform construction for all business transactions.Different transaction varieties have the identical structure.A enterprise transaction can cover a quantity of business circumstances, for instance, sales order and business activity.There's a comparable interface for processing all sorts of business transactions. There is a strict break up between the consumer interface and the processing of transactions. Similar capabilities can be found in all types of business transactions.
Depending on the Leading Transaction Category (e.g. Alternative, Gross sales, Task, Business Exercise), a business transaction has a sure structure.Tasks have a construction that is composes only of one Header level. Alternatives have a structure that is composed of two ranges:
Management attributes (such as the main business transaction class, text willpower procedure, associate willpower process, standing profile, the organizational data profile and the number range assignment) may be defined at header level. Various settings can be made, depending on the business transaction category.
First you outline the overall settings, that are the identical attributes for all sorts of merchandise
categories like General knowledge: merchandise object sort, calculation of weights and quantity for freight and Profiles: textual content determination, accomplice determination, status profile, ATP profile, organizational information profile, action profile, BOM explosion, configuration data.
Next you outline the business context in which the item class is used. Settings differ depending on the assigned business transaction category (billing data, pricing data, or citation information). Actions do not have items. Customizing item categories and item class determination shouldn't be obligatory in this case.
The procedure for willpower of merchandise categories needs to be set up in the same way as within the SAP R/3 system. In every other case, problems can occur through the upload to SAP R/3. SAP delivers the commonest item classes for gross sales transactions (TAN, TAM, TAC and TAE) and the suitable determination. Other customized-made merchandise classes and their dedication should be arrange manually. No customizing obtain from SAP R/three is supported.
Examples for merchandise category willpower:
A normal merchandise (NORM) in a typical gross sales order (TA) will lead to item category TAN.A typical item (NORM) in a typical sales order (TA) that belongs to the next-level merchandise (handbook enter) will result in merchandise class TANN (free good), because the principle merchandise class is taken into account.
A typical item (NORM) in a regular gross sales order (TA) that belongs to the next-level item of item class TAN will lead to merchandise class TANN, once free items willpower takes place (item
category utilization is FREE).
Prerequisite: Related organizational knowledge within the source and target transactions ought to match.For processing follow-up documents, you could carry out three customizing steps:
You want copying management for processing observe-up documents.
In SAPGUI doc movement
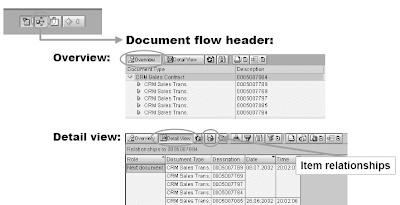
In the Individuals-Centric UI tab pages are used to show the doc flow.Document move tab pages are available on header and merchandise level. Navigation to linked CRM business transactions is possible.
Text objects and textual content sorts are defined in Customizing:
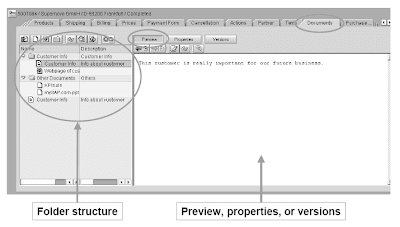
Additionally, you'll give you the chance to create ArchiveLink documents from Content Management.The exchange of Content Administration documents with CRM Mobile is possible. Usage of filter profiles means that you simply can specify which paperwork are to be transferred to the Mobile Client.
Functions for Content Management are on the Paperwork tab page.Special capabilities in SAP GUI: Sending paperwork: You can ship business partners documents linked to a enterprise transaction, for instance, by e-mail or fax.Creation of non-public- and customarily seen notes at doc degree
System status: Status that may be a status set by the system, which informs the consumer that the system has executed a particular business transaction on an object. You'll find a way to only influence this standing when you execute a business transaction that changes the system status.
?? Nevertheless, there are additionally some system statuses in CRM that the person can set or reset as he needs, for example, Do not distribute. These statuses are outlined in the CRMC_STATUS_PROC table.Standing that you set, that you would give you the chance to create as additional info to the present system status. You outline a consumer status in a Status Profile that's created in Customizing for business transactions. You probably can outline and activate as many person statuses as you wish. A standing profile can then be assigned to a transaction kind (header status) and/or merchandise category (merchandise status).
Person statuses let you prolong the control of business processes managed by the system status. You can set and delete person statuses manually throughout enterprise processes.The header status is impartial of the item status. One exception is the standing Completed. If all gadgets have the standing Accomplished, the header standing can also be set to Accomplished .Depending on the enterprise transaction there could be R/three Transfer and R/3 Status data available (e.g. in a sales order).Setting a consumer status can affect the system status.
In SAP GUI you'll have the opportunity to show a standing analysis. If you need to investigate an issue individually, and would like to know for instance why the system does not show a selected status for setting, you'll have the option to use the standing analysis to call up a technical analysis function.User statuses are outlined in standing procedures or standing profiles. In standing profiles you can do the following:
The scope of the examine can differ for every object. For example, the system checks completely different fields in a sales order than it checks in an opportunity.You may arrange incompleteness in Customizing.
To arrange the incompleteness examine, carry out these steps:
Related Posts
SAP CRM Business Transactions
SAP CRM marketing Management Campaign
DATA CONSISTENCY IN ABAP DAY 14
DEPENDENCIES IN ABAP DICTIONARY DAY 15
CHANGING DATA BASE TABLES IN SAP DAY 16
Depending on the Leading Transaction Category (e.g. Alternative, Gross sales, Task, Business Exercise), a business transaction has a sure structure.Tasks have a construction that is composes only of one Header level. Alternatives have a structure that is composed of two ranges:
- Header knowledge
- Merchandise knowledge
- Sales transactions have a structure that's composed of three ranges:
- Header information
- Merchandise data
- Schedule strains
- There are not any schedule line categories out there inside SAP CRM Customizing.
Management attributes (such as the main business transaction class, text willpower procedure, associate willpower process, standing profile, the organizational data profile and the number range assignment) may be defined at header level. Various settings can be made, depending on the business transaction category.
First you outline the overall settings, that are the identical attributes for all sorts of merchandise
categories like General knowledge: merchandise object sort, calculation of weights and quantity for freight and Profiles: textual content determination, accomplice determination, status profile, ATP profile, organizational information profile, action profile, BOM explosion, configuration data.
Next you outline the business context in which the item class is used. Settings differ depending on the assigned business transaction category (billing data, pricing data, or citation information). Actions do not have items. Customizing item categories and item class determination shouldn't be obligatory in this case.
The procedure for willpower of merchandise categories needs to be set up in the same way as within the SAP R/3 system. In every other case, problems can occur through the upload to SAP R/3. SAP delivers the commonest item classes for gross sales transactions (TAN, TAM, TAC and TAE) and the suitable determination. Other customized-made merchandise classes and their dedication should be arrange manually. No customizing obtain from SAP R/three is supported.
Examples for merchandise category willpower:
A normal merchandise (NORM) in a typical gross sales order (TA) will lead to item category TAN.A typical item (NORM) in a typical sales order (TA) that belongs to the next-level merchandise (handbook enter) will result in merchandise class TANN (free good), because the principle merchandise class is taken into account.
A typical item (NORM) in a regular gross sales order (TA) that belongs to the next-level item of item class TAN will lead to merchandise class TANN, once free items willpower takes place (item
category utilization is FREE).
- Not all capabilities are available in every transaction type.
- A collection of fundamental functions are:
- Partner Processing
- Pricing
- Incompleteness Verify
- Text Management
- Date Management
- Product substitution
- Free items
- Credit-check
- ATP-verify
Prerequisite: Related organizational knowledge within the source and target transactions ought to match.For processing follow-up documents, you could carry out three customizing steps:
- Copy management for transaction sorts
- Copy management for item categories
- Decide item category when copying
You want copying management for processing observe-up documents.
- Copying control for transaction types is mandatory
- Copying management for item categories is mandatory while you wish to copy products (objects) right into a observe-up document.
- The „definition of item category determination when copying“ is optionally available and can be used underneath particular circumstances.
- SAP Implementation Guide
- Buyer Relationship Management
- Transactions
- Basic Settings
- Copying Control for Business Transactions
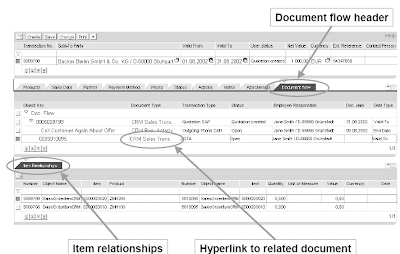
In SAPGUI doc movement
- the Detail View only reveals the quick preceding/succeeding paperwork
- the Overview exhibits all paperwork that are linked

In the Individuals-Centric UI tab pages are used to show the doc flow.Document move tab pages are available on header and merchandise level. Navigation to linked CRM business transactions is possible.

- In SAP CRM it is potential to take care of textual information for a quantity of objects, e.g. Business Partner
- Product
- Product Catalog
- Enterprise transaction (header and merchandise)
- Billing paperwork (header and merchandise)
- Texts could be maintained language-dependent
Text objects and textual content sorts are defined in Customizing:
- SAP Implementation Information
- Customer Relationship Administration
- Primary Functions
- Textual content Management
- Define Text Objects and Textual content Sorts
- Textual content willpower procedures and entry sequences are defined in Customizing: SAP Implementation Information
- Buyer Relationship Management
- Fundamental Functions
- Text Administration
- Outline
- Text Determination Process
Additionally, you'll give you the chance to create ArchiveLink documents from Content Management.The exchange of Content Administration documents with CRM Mobile is possible. Usage of filter profiles means that you simply can specify which paperwork are to be transferred to the Mobile Client.
Functions for Content Management are on the Paperwork tab page.Special capabilities in SAP GUI: Sending paperwork: You can ship business partners documents linked to a enterprise transaction, for instance, by e-mail or fax.Creation of non-public- and customarily seen notes at doc degree

System status: Status that may be a status set by the system, which informs the consumer that the system has executed a particular business transaction on an object. You'll find a way to only influence this standing when you execute a business transaction that changes the system status.
?? Nevertheless, there are additionally some system statuses in CRM that the person can set or reset as he needs, for example, Do not distribute. These statuses are outlined in the CRMC_STATUS_PROC table.Standing that you set, that you would give you the chance to create as additional info to the present system status. You outline a consumer status in a Status Profile that's created in Customizing for business transactions. You probably can outline and activate as many person statuses as you wish. A standing profile can then be assigned to a transaction kind (header status) and/or merchandise category (merchandise status).
Person statuses let you prolong the control of business processes managed by the system status. You can set and delete person statuses manually throughout enterprise processes.The header status is impartial of the item status. One exception is the standing Completed. If all gadgets have the standing Accomplished, the header standing can also be set to Accomplished .Depending on the enterprise transaction there could be R/three Transfer and R/3 Status data available (e.g. in a sales order).Setting a consumer status can affect the system status.
In SAP GUI you'll have the opportunity to show a standing analysis. If you need to investigate an issue individually, and would like to know for instance why the system does not show a selected status for setting, you'll have the option to use the standing analysis to call up a technical analysis function.User statuses are outlined in standing procedures or standing profiles. In standing profiles you can do the following:
- Define the sequence in which user statuses could be activated
- Outline initial statuses
- Permit or prohibit sure business transactions
- You have to assign not much less than one object sort, reminiscent of CRM Order Header, to the status procedure.
The scope of the examine can differ for every object. For example, the system checks completely different fields in a sales order than it checks in an opportunity.You may arrange incompleteness in Customizing.
To arrange the incompleteness examine, carry out these steps:
- Outline an incompleteness group for business transactions and items.
- Define an incompleteness verify for enterprise partners. In the business partner grasp knowledge, assign the required business companions to the incompleteness group within the Gross sales Area Knowledge on the Sales tab.
- Assign transaction varieties to the incompleteness groups. In the incompleteness check, the same conditions are valid for all transaction types with the same incompleteness group assigned.
- Assign item categories to the incompleteness groups. In the incompleteness check, the same circumstances are valid for all merchandise classes with the same incompleteness group assigned.
- Outline the incompleteness procedures which would possibly be valid for the various sub objects of a transaction, for instance, SALES for sales information or PRODUCT_I for product information at merchandise level. In an incompleteness procedure, you'll have the ability to group fields that you simply wish to test for completeness. If you don't enter knowledge in any of those fields in the business transaction, the transaction is taken into account incomplete. For every discipline in the process, you could also outline whether or not the message issued to the applying log during data processing needs to be a warning or an error message.
- Assign the incompleteness teams to the incompleteness procedures. This specifies the enterprise transactions during which checks are carried out. If you happen to assign an incompleteness group for business companions to an incompleteness procedure, the system carries out the check only for these enterprise partners to whom the incompleteness group was assigned. If you happen to create a transaction utilizing that transaction sort and enterprise associate, however, the incompleteness process is legitimate solely the business accomplice, that is, the system doesn't display a mixture of each procedures as incomplete.Only the fields from the incompleteness process for the business associate are displayed as incomplete.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Business Transactions
SAP CRM marketing Management Campaign
DATA CONSISTENCY IN ABAP DAY 14
DEPENDENCIES IN ABAP DICTIONARY DAY 15
CHANGING DATA BASE TABLES IN SAP DAY 16
No comments :
Post a Comment