SAP CRM Solution Monitoring a system landscape is a complex and very important subject for every firm running one or more SAP systems. The complexity will increase with each new system, add-on or component. One of the main issues is to have a fast and dependable risk to regulate the complete landscape.Using the Monitoring Structure of the Computing Heart Management System (CCMS), SAP supplies a versatile and universally relevant infrastructure, with which you can monitor the entire IT landscape centrally and which shortly and reliable studies problems that occur.The Monitoring Structure is delivered with every SAP Internet Software Server with no additional prices and can be utilized instantly after installation. The structure runs on all SAP Web Software Servers and might easily be extended with SAP and non-SAP components.The intention of the monitoring idea is to assemble all required data in one system to scale back the workload of an administrator and let him see issues, as soon as they appear. Moreover all logs are reachable from a single point, which reduces the required time to verify a certain log file for an error. This means higher efficiency in downside solving and lower costs.Additional configuration and optimization will permit using enhanced companies like notification, which can change the need to verify the system for any alerts.
CCMS Monitoring
The essential concept of the central system monitoring (for SAP instances ? 4.X) is that the monitoring data is stored in a shared reminiscence phase of the own occasion and transferred periodically via RFC into the shared memory of the central system.Parts with SAP Basis Methods or SAP Internet Utility Server can instantly be included into a central monitoring atmosphere using the CCMS alert monitoring architecture.Elements with out SAP Foundation are connected using CCMS agents.All components with SAP Basis Programs will be monitored by their own. In all parts detailed commonplace monitoring transactions are available. However, in a posh server landscape it's more useful to get a central overview first (e.g. system availability, transaction particular response times ...). and to make use of the system particular evaluation transactions afterwards in case of troubles.With CRM 4.0, SAP continues to focus to the SAP SOLUTION MANAGER as central monitoring system. This instrument is dedicated for being the CEN of the SAP landscape. In fact, you can even use any other SAP system, working on SAP WEB AS 6.20 foundation as CEN. The SAP Answer Manager has a additional benefit, as it's possible for SAP to attach remotely to this technique and to get all required data within the disagreeable case of errors, where help from SAP is required to unravel the issue.
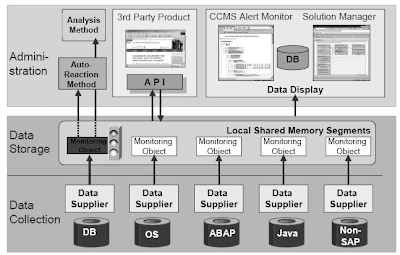
The CCMS Alert Monitoring Structure consists of three layers:
 CCMS brokers push monitoring information to the central monitoring component. They supply an alternate to the information pull triggered when the Alert Monitor is refreshed. Parts without SAP Basis have to be connected utilizing a CCMS agent (CCMSR).Alerts are displayed within the Alert Monitor. Alert notifications are triggered, if configured.
CCMS brokers push monitoring information to the central monitoring component. They supply an alternate to the information pull triggered when the Alert Monitor is refreshed. Parts without SAP Basis have to be connected utilizing a CCMS agent (CCMSR).Alerts are displayed within the Alert Monitor. Alert notifications are triggered, if configured.
Instance scenario:
An availability test experiences the breakdown of one component.An alert is displayed as a purple node within the Availability Monitor of the central monitoring system.An alert notification (e-mail, pager, or SMS) has been configured for this explicit alert.The administrator is notified accordingly and can immediately examine the error scenario of the corresponding system.
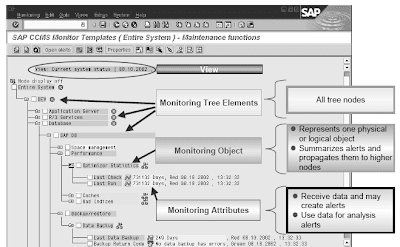
The monitoring data is displayed in a tree-based mostly structure. You'll give you the option to show two completely different views,the present system view and the alert view. The nodes of the tree-based construction are referred to as Monitoring Tree Element (MTE).The data measured is mixed with monitoring attributes. Monitoring attributes are the leaf nodes of the tree. They represent physical traits or messages related to a monitoring object.for example, the monitoring object Optimizer Statistics has the monitoring attributes Final Examine and Last run. All nodes above the extent of Monitor Attributes solely assist to search out the right "leaf node".For every monitoring attribute, alerts are displayed (in yellow and red) if configurable threshold conditions are exceeded.Alerts are propagated upwards in the hierarchy. Alerts within the upward MTE hierarchy also change into red.
J2EE Monitoring
The task of the Java Monitoring and Management is to supply developers, supporters and prospects with information about.Detailed statistics on exercise and useful resource consumption for accounting and auditing, SLA reporting and drawback analysis.The J2EE monitoring infrastructure can be used both with out being connected to a CCMS system (if the client makes use of the SAP J2EE Server standalone) or with CCMS connection.For connecting to CCMS, The sapccmsr agent should run on every host that runs a SAP J2EE Engine.The sapccmsr agent is also required if the J2EE Engine runs on the identical host as the SAP system which you're reporting to.The monitoring information is sent to different locations: Visual Administrator, CCMS, or text files.
JMX Interface
JMX is used to manage and monitor all server parts (providers, interfaces, libraries).Although functions can access the JMX APIs as nicely, more advanced administration and monitoring capabilities for purposes will be added within the following release.The JMX monitoring structure uses MBeans to characterize a J2EE useful resource (supervisor, service). In order to collect monitoring data at runtime this data will be either pulled periodically by a JMX monitor from the underlying useful resource (passive instrumentation) or alternatively the resource pushes the monitoring data to the JMX monitor using an occasion mechanism (energetic instrumentation).
Most JMX monitors are static: the instrumenter of the resource offers XML based mostly configuration data. At startup of the server the monitor service creates the JMX displays in maintaining with this configuration data. In some circumstances you could dynamically generate displays, which will doubtless be potential with the ultimate 6.30 release.For the storage of monitoring data the JMX displays use corresponding monitor nodes. Depending on the monitoring knowledge sort you can choose JMX screens and corresponding monitor nodes for text data, integer numbers or more complexe information like tables, swimming pools, caches, frequencies and so on.
The logic of the monitor nodes allows them to construct up data, maintain historical past or generate alerts, when a crucial state has occurred.For the visualization of the monitoring data the Swing based Visual Administrator of the SAP J2EE Server can be used.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Technology Overview
CRM Data Exchange with SAP R/3 CRM
CRM E commerce Introduction
CRM Interaction Center System Architecture
CRM Field Sales
People Centric SAP CRM
CCMS Monitoring
The essential concept of the central system monitoring (for SAP instances ? 4.X) is that the monitoring data is stored in a shared reminiscence phase of the own occasion and transferred periodically via RFC into the shared memory of the central system.Parts with SAP Basis Methods or SAP Internet Utility Server can instantly be included into a central monitoring atmosphere using the CCMS alert monitoring architecture.Elements with out SAP Foundation are connected using CCMS agents.All components with SAP Basis Programs will be monitored by their own. In all parts detailed commonplace monitoring transactions are available. However, in a posh server landscape it's more useful to get a central overview first (e.g. system availability, transaction particular response times ...). and to make use of the system particular evaluation transactions afterwards in case of troubles.With CRM 4.0, SAP continues to focus to the SAP SOLUTION MANAGER as central monitoring system. This instrument is dedicated for being the CEN of the SAP landscape. In fact, you can even use any other SAP system, working on SAP WEB AS 6.20 foundation as CEN. The SAP Answer Manager has a additional benefit, as it's possible for SAP to attach remotely to this technique and to get all required data within the disagreeable case of errors, where help from SAP is required to unravel the issue.
The CCMS Alert Monitoring Structure consists of three layers:
- Information collection :SAP parts are monitored by particular programs called data suppliers. Information suppliers could be ABAP, C, or Java programs. SAP delivers over a hundred information suppliers in ABAP alone. Each data supplier checks its component at regular intervals and shops the collected monitoring information in the main memory of its host.
- Information storage : The realm of the main reminiscence that contains the monitoring knowledge from the information supplier is named a monitoring segment. As the primary reminiscence data is always overwritten, monitoring segments may be permanently copied to database tables. You may then analyze the information later. The information collection and storage parts should be current domestically on each part to be centrally monitored.
- Administration: Knowledge from the monitoring segments are displayed and evaluated within the central monitoring system.SAP provides an professional software, the CCMS Alert Monitor (transaction RZ20). Alternatively, you'll find a way to use the Answer Supervisor to show the information in a business course of-oriented context. If the system identifies an issue, it may execute an auto reaction, equivalent to informing the accountable person. The analysis methodology then helps the administrator to investigate the problem.
- The CCMS Alert Monitoring Infrastructure will be extended. Customers can integrate their own components utilizing knowledge suppliers that they've written themselves. Third-get together distributors and partners can export the monitoring information from the monitoring segment utilizing numerous interfaces.
 CCMS brokers push monitoring information to the central monitoring component. They supply an alternate to the information pull triggered when the Alert Monitor is refreshed. Parts without SAP Basis have to be connected utilizing a CCMS agent (CCMSR).Alerts are displayed within the Alert Monitor. Alert notifications are triggered, if configured.
CCMS brokers push monitoring information to the central monitoring component. They supply an alternate to the information pull triggered when the Alert Monitor is refreshed. Parts without SAP Basis have to be connected utilizing a CCMS agent (CCMSR).Alerts are displayed within the Alert Monitor. Alert notifications are triggered, if configured.Instance scenario:
An availability test experiences the breakdown of one component.An alert is displayed as a purple node within the Availability Monitor of the central monitoring system.An alert notification (e-mail, pager, or SMS) has been configured for this explicit alert.The administrator is notified accordingly and can immediately examine the error scenario of the corresponding system.

The monitoring data is displayed in a tree-based mostly structure. You'll give you the option to show two completely different views,the present system view and the alert view. The nodes of the tree-based construction are referred to as Monitoring Tree Element (MTE).The data measured is mixed with monitoring attributes. Monitoring attributes are the leaf nodes of the tree. They represent physical traits or messages related to a monitoring object.for example, the monitoring object Optimizer Statistics has the monitoring attributes Final Examine and Last run. All nodes above the extent of Monitor Attributes solely assist to search out the right "leaf node".For every monitoring attribute, alerts are displayed (in yellow and red) if configurable threshold conditions are exceeded.Alerts are propagated upwards in the hierarchy. Alerts within the upward MTE hierarchy also change into red.

J2EE Monitoring
The task of the Java Monitoring and Management is to supply developers, supporters and prospects with information about.Detailed statistics on exercise and useful resource consumption for accounting and auditing, SLA reporting and drawback analysis.The J2EE monitoring infrastructure can be used both with out being connected to a CCMS system (if the client makes use of the SAP J2EE Server standalone) or with CCMS connection.For connecting to CCMS, The sapccmsr agent should run on every host that runs a SAP J2EE Engine.The sapccmsr agent is also required if the J2EE Engine runs on the identical host as the SAP system which you're reporting to.The monitoring information is sent to different locations: Visual Administrator, CCMS, or text files.
JMX Interface
JMX is used to manage and monitor all server parts (providers, interfaces, libraries).Although functions can access the JMX APIs as nicely, more advanced administration and monitoring capabilities for purposes will be added within the following release.The JMX monitoring structure uses MBeans to characterize a J2EE useful resource (supervisor, service). In order to collect monitoring data at runtime this data will be either pulled periodically by a JMX monitor from the underlying useful resource (passive instrumentation) or alternatively the resource pushes the monitoring data to the JMX monitor using an occasion mechanism (energetic instrumentation).
Most JMX monitors are static: the instrumenter of the resource offers XML based mostly configuration data. At startup of the server the monitor service creates the JMX displays in maintaining with this configuration data. In some circumstances you could dynamically generate displays, which will doubtless be potential with the ultimate 6.30 release.For the storage of monitoring data the JMX displays use corresponding monitor nodes. Depending on the monitoring knowledge sort you can choose JMX screens and corresponding monitor nodes for text data, integer numbers or more complexe information like tables, swimming pools, caches, frequencies and so on.
The logic of the monitor nodes allows them to construct up data, maintain historical past or generate alerts, when a crucial state has occurred.For the visualization of the monitoring data the Swing based Visual Administrator of the SAP J2EE Server can be used.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Technology Overview
CRM Data Exchange with SAP R/3 CRM
CRM E commerce Introduction
CRM Interaction Center System Architecture
CRM Field Sales
People Centric SAP CRM
No comments :
Post a Comment