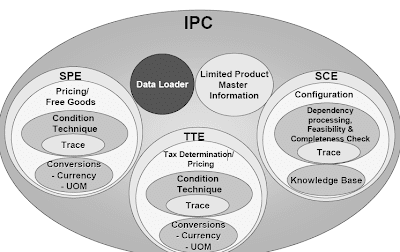
SAP CRM Pricing gives the overview of the product and how they are marketed.Sales Pricing and Configuration (SPC) accommodates a quantity of parts:
To carry out pricing, the Web Pricing and Configuration wants various types of data from the following sources:
The gross sales relevant master information will be extracted from the SAP SD system to the CRM system or IPC.The Web Pricing and Configurator makes use of the info saved in CRM or IPC databases. Related data that is needed for gross sales pricing includes the following:
SAP CRM pricing procedures can't be loaded into SAP R/3.
The willpower of pricing process have to be arrange manually. Unlike SAP R/3, no division setting is required.The next parts affect the determination of the pricing process:
Pricing makes the enter values gross sales area, accomplice procedure and document pricing process out there to condition technique.The system determines the pricing procedure depending on sales area, partner process and doc pricing procedure.The system reads the first situation sort of the pricing process and determines the assigned entry sequence. This step, along with the next steps, is repeated for each condition sort on the pricing procedure.The system reads the entry sequence with the situation tables. The sequence of the situation tables forms the search strategy for figuring out the person condition records. Each situation table comprises the field mixtures based on which the system ought to search in the condition data, for instance business companion - product - price.
The system searches for legitimate situation data for the condition tables. If the system doesn't discover a valid situation file for the first situation desk, it carries on and searches for a condition record for the subsequent condition table.As quickly as the system has discovered a legitimate situation file for a situation table, it makes the outcome obtainable to pricing in the form of prices and discounts.If the search procedure accommodates multiple situation sort, the system repeats the seek for condition records for every condition type.Data about conditions is stored in condition records.
You'll give you the chance to determine circumstances at any level you require.The levels on which pricing is most commonly carried out have been predefined in the usual version.You can simply add additional levels if required. A regular field catalog containing fields generally used in pricing is equipped with SAP R/3. However, you might make circumstances depending on any doc field(s), however you might need to add these fields to the sphere catalog. Knowledge about circumstances is saved in condition records.
You'll have the opportunity to limit a pricing agreement to a certain interval by specifying a validity period. This can be helpful whenever you wish to have completely different tariffs for different years or have discounts legitimate only for the period of a particular offer.The values in a situation file (price, surcharge, low cost) could be maintained according to a scale.You can specify a vast number of levels in a scale.You should utilize the worth group Prospects to group merchandise for which the same situations are to be valid.You assign the value group to the customers or to the merchandise when you maintain the business companions (buyer partner function) or the products. You probably can outline your own value groups.
The situations maintained in SAP CRM that start with a zero (0), for instance, 0PR0 for value, is
equal to the PR00 for the value from SAP R/3.In Customizing you'll have the ability to group the situation varieties / condition tables that you want using Condition Maintenance Group.By assigning the context GCM, you make the corresponding choice of situation sorts / condition tables possible for basic situation maintenance.
It is doable to carry out a condition evaluation, a log instrument that offers you an overview of the transactions in automated pricing.You need to use this info to check how the person pricing elements from the merchandise are calculated in the system.Not solely data for the last pricing transaction the system carried out is displayed, but for each of these transactions. This enables you to compare pricing transactions. This can be useful after failed searches or price changes. Consumer parameter PRC_TRACE = X needs to be set.
Condition analysis just isn't available in the People-Centric UI.SAP Pricing has a versatile infrastructure that enables complete pricing strategies.
SAP Pricing advantages include:
Situation varieties that aren't supported in SAP CRM: EK01, EK02, BO01 to BO05, AZWR, RL00,MW15, VRPS, EDI1, EDI2. Mass copying of situation records just isn't attainable in SAP CRM.
Change paperwork should not available in SAP CRM
Archiving of pricing circumstances is not possible in SAP CRM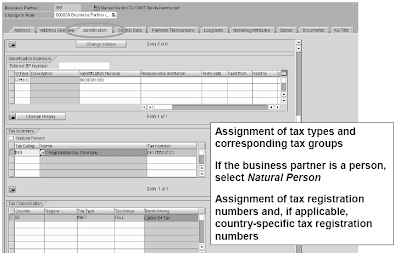
In pricing, more than one condition record may apply to a particular merchandise at anyone time. You can use situation exclusion to compare attainable situations with a view to determine things like the very best worth for a customer.Variant conditions can be utilized to influence the worth of a configurable materials depending on the attribute values assigned.You must use group situations if you need some conditions for use as the basis for determining scale values from a number of items. Example: Supplies have been assigned to a fabric pricing group.You desire a quantity-primarily based low cost to be assigned to those materials. You need the quantity scale to be learn cumulatively with the accumulated quantity of all supplies in the gross sales order which can be assigned to this material pricing group.
Hierarchical accesses are used to optimize pricing for hierarchical knowledge constellations such as a product hierarchy. Normal situation maintenance is offered within the basic person interface and within the Individuals-Centric Person Interface.Minimal and maximum limits permit you to restrict handbook processing of pricing conditions in transactions per condition type. At the moment this can be used just for condition data that were originally created in SAP R/3.
Tax calculation requires classification of business partners and products. The business accomplice and product tax classification is made by assigning tax teams to the tax varieties (for example, VAT, sales tax) that have to be determined in any given country. The tax teams point out whether or not a enterprise accomplice is answerable for or exempted from the respective tax sort that's imposed.In Customizing, the tax type specifies which taxes are decided for each country.Corresponding tax groups are defined for business companions and products for every tax type. The mixture of tax group, the nation (or area), and tax kind determines the tax condition record.
A default tax group could be defined for business partners and merchandise per nation and tax type. When a business partner or a product has not been assigned a tax classification, the default tax group is used.The product tax classification is made by assigning tax teams to the tax varieties that should be determined in any given country. The tax teams indicate whether a product is answerable for or exempted from a diminished fee of the respective tax type levied. This task can also be made on a regional basis.A prerequisite for business partner and product tax classification is the definition of country-specific tax varieties and tax teams in Customizing.
The tax sort specifies which taxes are determined for every country. The access sequence specifies the order by which situation information are accessed for a country when multiple tax sort has been outlined for it.The tax class is a distinct grouping of taxes to which tax sorts belong akin to sales tax, withholding tax or excise tax.Corresponding tax groups are outlined for enterprise companions and products for every tax type. The combination of tax group, the nation (or region), and tax kind determines the situation record.
A default tax group might be defined for business companions and merchandise per nation and tax type. When a business companion or a product has not been assigned a tax classification, the default tax group is used. The Transaction Tax Engine (TTE) is an integral a part of the Web and Pricing Configurator (IPC).The TTE determines and calculates tax primarily based on the condition data and tax exemption licenses. The TTE makes use of the transferred data to determine the tax event, tax type(s) and the corresponding tax record.As lengthy as the CRM bill is getting used for billing, CRM enterprise processes must use the Transaction Tax Engine (TTE) for tax determination. For CRM Billing the TTE points a tax document.SRM business processes can use the TTE for tax determination.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Business TransactionsSAP CRM marketing Management Campaign
SAP CRM Partner Processing
SAP ABAP All Topics Complete Courses
PERFORMANCE DURING TABLE ACCESS
ENHANCEMENTS TO DICTIONARY ELEMENTS
- Gross sales pricing engine
- Sales Configuration Engine (SCE)
- Product master data capabilities is learn from the database when an item is created.
- Simple doc functions
- The gross sales pricing engine incorporates the next components:
- Pricing features
- Normal situation technique
- A hint, which documents how the seek for condition information was done
- Forex and unit of measurement (UoM) conversions

To carry out pricing, the Web Pricing and Configuration wants various types of data from the following sources:
- Customizing accommodates information about currencies or pricing willpower procedures, for example.
- Grasp information data comprise info such as the gross worth of a product.
- Context-related data, for instance, about the product and buyer in a sure order, is gathered from the CRM database.
The gross sales relevant master information will be extracted from the SAP SD system to the CRM system or IPC.The Web Pricing and Configurator makes use of the info saved in CRM or IPC databases. Related data that is needed for gross sales pricing includes the following:
- Basic info on the supplies, business companions and gross sales organization
- Gross sales processes
- Pricing
- Which subtotals are shown on the pricing screens
- If a condition kind is mandatory
- If a situation sort is statistical
- If a condition can be entered manually solely
- Formulation for calculating prices
SAP CRM pricing procedures can't be loaded into SAP R/3.
The willpower of pricing process have to be arrange manually. Unlike SAP R/3, no division setting is required.The next parts affect the determination of the pricing process:
- Sales Organization
- Distribution Channel
- Doc Pricing Procedure (will be assigned to a gross sales transaction, on the third level)
- Buyer Pricing Procedure (assignment in enterprise accomplice grasp)
- optionally the Division.
Pricing makes the enter values gross sales area, accomplice procedure and document pricing process out there to condition technique.The system determines the pricing procedure depending on sales area, partner process and doc pricing procedure.The system reads the first situation sort of the pricing process and determines the assigned entry sequence. This step, along with the next steps, is repeated for each condition sort on the pricing procedure.The system reads the entry sequence with the situation tables. The sequence of the situation tables forms the search strategy for figuring out the person condition records. Each situation table comprises the field mixtures based on which the system ought to search in the condition data, for instance business companion - product - price.
The system searches for legitimate situation data for the condition tables. If the system doesn't discover a valid situation file for the first situation desk, it carries on and searches for a condition record for the subsequent condition table.As quickly as the system has discovered a legitimate situation file for a situation table, it makes the outcome obtainable to pricing in the form of prices and discounts.If the search procedure accommodates multiple situation sort, the system repeats the seek for condition records for every condition type.Data about conditions is stored in condition records.
You'll give you the chance to determine circumstances at any level you require.The levels on which pricing is most commonly carried out have been predefined in the usual version.You can simply add additional levels if required. A regular field catalog containing fields generally used in pricing is equipped with SAP R/3. However, you might make circumstances depending on any doc field(s), however you might need to add these fields to the sphere catalog. Knowledge about circumstances is saved in condition records.
You'll have the opportunity to limit a pricing agreement to a certain interval by specifying a validity period. This can be helpful whenever you wish to have completely different tariffs for different years or have discounts legitimate only for the period of a particular offer.The values in a situation file (price, surcharge, low cost) could be maintained according to a scale.You can specify a vast number of levels in a scale.You should utilize the worth group Prospects to group merchandise for which the same situations are to be valid.You assign the value group to the customers or to the merchandise when you maintain the business companions (buyer partner function) or the products. You probably can outline your own value groups.
The situations maintained in SAP CRM that start with a zero (0), for instance, 0PR0 for value, is
equal to the PR00 for the value from SAP R/3.In Customizing you'll have the ability to group the situation varieties / condition tables that you want using Condition Maintenance Group.By assigning the context GCM, you make the corresponding choice of situation sorts / condition tables possible for basic situation maintenance.
It is doable to carry out a condition evaluation, a log instrument that offers you an overview of the transactions in automated pricing.You need to use this info to check how the person pricing elements from the merchandise are calculated in the system.Not solely data for the last pricing transaction the system carried out is displayed, but for each of these transactions. This enables you to compare pricing transactions. This can be useful after failed searches or price changes. Consumer parameter PRC_TRACE = X needs to be set.
Condition analysis just isn't available in the People-Centric UI.SAP Pricing has a versatile infrastructure that enables complete pricing strategies.
SAP Pricing advantages include:
- Elevated profitability via economically sound response to any sort of buyer request
- Increased competitiveness
- Well timed reaction to any type of buyer request
- Enhanced selling effectiveness by providing product, pricing and discount info on the level of sale
Situation varieties that aren't supported in SAP CRM: EK01, EK02, BO01 to BO05, AZWR, RL00,MW15, VRPS, EDI1, EDI2. Mass copying of situation records just isn't attainable in SAP CRM.
Change paperwork should not available in SAP CRM
Archiving of pricing circumstances is not possible in SAP CRM

In pricing, more than one condition record may apply to a particular merchandise at anyone time. You can use situation exclusion to compare attainable situations with a view to determine things like the very best worth for a customer.Variant conditions can be utilized to influence the worth of a configurable materials depending on the attribute values assigned.You must use group situations if you need some conditions for use as the basis for determining scale values from a number of items. Example: Supplies have been assigned to a fabric pricing group.You desire a quantity-primarily based low cost to be assigned to those materials. You need the quantity scale to be learn cumulatively with the accumulated quantity of all supplies in the gross sales order which can be assigned to this material pricing group.
Hierarchical accesses are used to optimize pricing for hierarchical knowledge constellations such as a product hierarchy. Normal situation maintenance is offered within the basic person interface and within the Individuals-Centric Person Interface.Minimal and maximum limits permit you to restrict handbook processing of pricing conditions in transactions per condition type. At the moment this can be used just for condition data that were originally created in SAP R/3.
Tax calculation requires classification of business partners and products. The business accomplice and product tax classification is made by assigning tax teams to the tax varieties (for example, VAT, sales tax) that have to be determined in any given country. The tax teams point out whether or not a enterprise accomplice is answerable for or exempted from the respective tax sort that's imposed.In Customizing, the tax type specifies which taxes are decided for each country.Corresponding tax groups are defined for business companions and products for every tax type. The mixture of tax group, the nation (or area), and tax kind determines the tax condition record.
A default tax group could be defined for business partners and merchandise per nation and tax type. When a business partner or a product has not been assigned a tax classification, the default tax group is used.The product tax classification is made by assigning tax teams to the tax varieties that should be determined in any given country. The tax teams indicate whether a product is answerable for or exempted from a diminished fee of the respective tax type levied. This task can also be made on a regional basis.A prerequisite for business partner and product tax classification is the definition of country-specific tax varieties and tax teams in Customizing.
The tax sort specifies which taxes are determined for every country. The access sequence specifies the order by which situation information are accessed for a country when multiple tax sort has been outlined for it.The tax class is a distinct grouping of taxes to which tax sorts belong akin to sales tax, withholding tax or excise tax.Corresponding tax groups are outlined for enterprise companions and products for every tax type. The combination of tax group, the nation (or region), and tax kind determines the situation record.
A default tax group might be defined for business companions and merchandise per nation and tax type. When a business companion or a product has not been assigned a tax classification, the default tax group is used. The Transaction Tax Engine (TTE) is an integral a part of the Web and Pricing Configurator (IPC).The TTE determines and calculates tax primarily based on the condition data and tax exemption licenses. The TTE makes use of the transferred data to determine the tax event, tax type(s) and the corresponding tax record.As lengthy as the CRM bill is getting used for billing, CRM enterprise processes must use the Transaction Tax Engine (TTE) for tax determination. For CRM Billing the TTE points a tax document.SRM business processes can use the TTE for tax determination.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Business TransactionsSAP CRM marketing Management Campaign
SAP CRM Partner Processing
SAP ABAP All Topics Complete Courses
PERFORMANCE DURING TABLE ACCESS
ENHANCEMENTS TO DICTIONARY ELEMENTS
No comments :
Post a Comment