The CRM product master represents products (for example, a hard disk), services (for example, PC warranty, PC maintenance), warranties and financing (e.g. leasing) ?? Products can be service packages, bills of material or a combination.Configurable products, such as personal computers, are only given attributes and attribute values when the product is sold.Warranty information for individual objects is created with reference to product, for example, product registration via e-service.A separate number range can be maintained for each product type. Product type IP (Intellectual Property) is available for the Media industry.
- The CRM product master is a collection or arrangement of various set types that contain specific data.Set types, which correspond to database tables, are displayed on various views (tab pages). Predefined set types (for example, basic data, short texts, conversion of unit of measure) are delivered with the standard product. You can enhance the product master with user-defined set types.For SAP GUI views (tab pages) can be defined in Customizing: SAP Implementation Guide
- Cross-Application Components
- SAP Products
- Settings for Product Maintenance
- Define Views
With inconsistent product data, the application log contains serious errors, for example, base unit of measure = XY. In this case, it is not possible to save the product data actively, only inactively. After the errors are corrected, it is then possible to save the inactive product data actively. Only then is the product available in the CRM applications.Mass maintenance of inactive products is possible. Through collective processing, you can activate and delete several products at a time. Inactive product data can also be created, if, for example, product data from product catalogs is imported into the CRM system by suppliers. The imported data can be processed subsequently; the data can be activated only after post-processing.
To use this option, you need to carry out Customizing:
- SAP Implementation Guide ?
- Cross-Application Components ?
- SAP Products ?
- Basic Settings ?
- Allow Inactive Products.
The relationship has accessories plays a large role in the CRM product catalog, which is used in the Internet sales scenario. If a customer adds a product to her shopping cart, additional products can be suggested to the customer via the relationship has accessories.The following are additional relationship types:
- Customers (a customer material number can be assigned)
- Financed by
- Content Provider
- Indemnity Payment
- Manufacturer
- Vendors (a vendor material number can be assigned)
- Components
- Warranty
Hierarchies can be imported with COM_HIERARCHY_CREATE_API. Categories and hierarchies can be transported.If SAP CRM is implemented without SAP R/3 system as the back-end system, preparatory steps are necessary before product master data can be created in the SAP CRM system. These preparatory steps are documented in Customizing: SAP Implementation Guide ? Customer Relationship Management ? Master Data ? Products ? CRM Standalone .
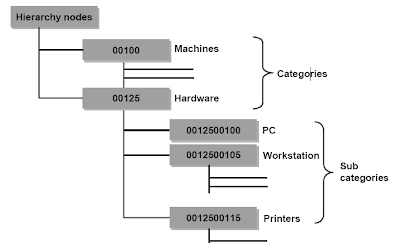
Product categories are used to group products together according to various criteria. Categories inherit the product category and the set types of all superordinate categories. For example, the base hierarchy R3PRODSTYP contains the category MAT_. This contains various set types, such as basic product data and conversion of units of measure. The sub-category MAT_HAWA inherits the set types from MAT_ and has additional set types, for example, sales set types.
The assignment of a product can be changed or deleted. An employee responsible at category level can be stored. Because a hierarchy can consist of many different categories, responsibilities can be mapped through these categories.You can import categories with the API function module, COM_PROD_CATEGORY_MAINTAIN.Hierarchies and categories are part of the transport system since release 3.0.
Creation of attributes results in the creation of data elements and domains on the database. Creation of settypes results in the creation of database tables and other data dictionary objects (e.g. function groups, function modules, dynpros, …)Set types can be assigned to categories. It is also possible to assign a view (tab page) on which set type information will be displayed.The upload cannot be automated. It must be carried out manually and individually for each product.Upload can be permitted or prohibited for each product type in Customizing:
SAP Implementation Guide
Customer Relationship Management
Master Data
Products
Settings for Product Type
Allow Upload for a Product Type.
The default basic unit of measure can be maintained in Customizing. Because this is a required entry field in SAP R/3, the product type Financing (which has no default base unit of measure in SAP CRM) must have a default base unit of measure.After a product has been uploaded from SAP CRM to OLTP, changes are updated via a delta transfer.An initial download is performed at the start, when SAP CRM is set up. Existing Customizing data is a prerequisite for a successful initial download. The middleware settings act as a filter to control which data should be loaded.During the initial download, a distinction is made between the object types business object, customizing object and condition object.
The delta download ensures that transaction data and master data are permanently exchanged between the CRM and a back-end system. Customizing changes are not updated via delta download.During the initial download, product hierarchies are loaded from SAP R/3 into SAP CRM. The Material group and Product hierarchy fields are compared.In the Customizing download example, the product hierarchy in SAP R/3:
Used to group materials by combining different characteristics, similar to the UN/SPSC principle.Used in SD for pricing.View Basic Data 1 in R/3 material master, MARA-PRDHA field with check table T179. The numbers in the category hierarchy R3PRODHIER are derived from the Customizing table T179 in SAP R/3.
At present, there must be a suitable numbering scheme in the SAP CRM system so that product hierarchies can be downloaded from SAP R/3. A competitive product has a lean product master. This is controlled by the product category.Competitive products can be created on the portal and can be integrated into business processes for Activity Management or Opportunity Management.
Competitive product information is exchanged with the mobile client in both directions.The following are standard delivered relationships:
- Competitor – competitor product
- Customer – competitor product
- Own product – competitor product
- Competitor products are only available in the People-Centric UI.
SAP CRM Business TransactionsSAP CRM marketing Management Campaign
SAP CRM Internet sales FeaturesSAP CRM interaction center overview
SAP CRM Mobile sales and serviceRoles in SAP CRMSAP CRM Organizational Model
No comments :
Post a Comment