SAP Financial Planning is used to set organizational goals. The comparison of precise operating results with the plan can determine variances that serve as signals to take corrective measures within the business operations.There are a quantity of fundamental objectives in planning:
Versions in Controlling
The definition of a model applies for the whole of Controlling. This ensures that your knowledge stays constant for those who use the model in different applications, for instance in each Overhead Price Controlling and in Profitability Anaylsis (built-in planning).You define Controlling versions centrally and add application-specific settings for Profitability Evaluation, Profit Middle Accounting, and Overhead Cost Controlling.You may plan your value centers in as many CO versions as you wish. Each model within the R/3 System is tailor-made to explicit planning requirements.Once you create a controlling area, the R/three System mechanically creates version zero, valid for 5 fiscal years. It's also attainable to create different versions for, for example, constructive or unfavorable scenarios.When referring to actual postings , the R/3 System always makes use of version 0. Different versions can relate only to saving planning data in Price Center Accounting.
Copy Plan and Actual Data
You should utilize the tool Copy Planning if you want to reuse large parts of your manual value heart planning from a previous 12 months on your current planning, or to repeat plan values inside a fiscal year to a unique period, or to generate alternate plan versions.Equally, the instrument Copy Precise to Plan lets you utilize previous actual cost center information as the reference for creating new plan data.To make use of the Copy Planning operate, select a reference model and a goal version.You'll give you the chance to copy plan data:
producing best-case and worst-case situations within a year. Plan line objects are recorded throughout revaluation execution.You could undertake as many revaluations of value middle and price ingredient deliberate values as required.The chances within a revaluation may be modified as usually as desired. Repeated executions with changed percentages cancel the previous plan line gadgets and always use the original initial value.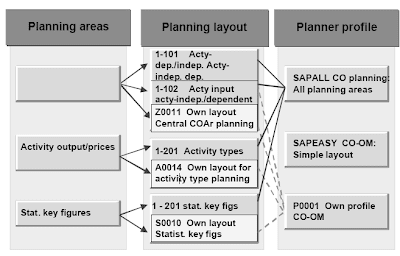
Overview of Planning
You enter planning data in Controlling using entry screens, the structure of which you'll define in
Customizing. These screens are often recognized as planning layouts .There are three planning areas in Price Middle Accounting:
values, and set up the suitable value columns. SAP provides numerous predefined standard layouts.You utilize planner profiles to control the planning process. In a given planner profile, you'll have the option to assign any number of planning layouts to any number of planning areas.The R/3 System comprises customary planner profiles and standard planning layouts that cover virtually every conceivable planning situation. You can use the SAPALL planner profile to plan for the three planning areas utilizing a quantity of SAP customary layouts. SAP offers the planner profile SAPEASY for conditions where a easy planner profile is required. You can also outline your personal planner profiles.You can perform both centralized (planning of a single cost factor for all value facilities for example) and decentralized planning (for example, planning of all cost components on a single cost center). The kind of planning depends upon manner your organization is organized. You may mix both methods, enabling you for example to plan your personnel prices centrally, and have all other prices deliberate regionally by the fee heart managers.
Planning Statical Key Figures
You may plan statistical key figures to be able to:
Primary Cost Planning
Activity-unbiased primary costs, labeled by price components, are planned on price facilities by plan version.If you happen to plan activity-unbiased main prices, you can only plan fastened costs. For price facilities using activity types, these deliberate fastened costs are assigned to the activity sorts of the related fee middle primarily based on the equivalence numbers within the plan, or based mostly on the plan splitting structure. In activity worth calculation these fastened prices are taken into account to calculate the fixed portion of the exercise price.You have to use the Customary-Structure 1-one zero one included in the Profile SAPALL to plan activity independent main costs.
Activity Type Planning
Activity sorts function a measurement of cost middle performance. They describe the amount output of a price heart and can be utilized to discover out an operating rate and target costs. Exercise types are allotted below a secondary value aspect, which is stored as a default value within the exercise kind master record.The activity price is determined per value middle/activity sort both manually or in automated activity value calculation:
Cost Allocation Planning
Periodic re postings are used purely as a posting aid.Major postings (equivalent to telephone costs) are collected on an allocation controlling object to reduce the variety of postings to FI. These prices are then allocated to the suitable controlling objects at period-finish closing in accordance with a person-defined key (fastened quantities or tracing components). The sender controlling object generally is a cost center, inside order, or different object. You can specify the allowed sender and receiver objects for periodic reposting in customizing.Only primary prices may be reposted. The unique value elements are retained on the postings to the receivers. Distribution is meant for the switch of main costs from a sender cost middle to receiver controlling objects. Solely price facilities might serve as senders in a distribution.Primary postings (resembling energy prices) are collected on a service cost center and allocated in accordance to consumer-defined keys.Only primary prices will be distributed. The original value elements are retained on the postings to the receivers.Assessment is designed for the allocation of major and secondary costs from a sender price center to receiver controlling objects. Only cost centers might serve as senders in an assessment.
Primary and secondary postings are allocated in keeping with person-defined keys.Within the evaluation framework, the unique value elements are grouped collectively into evaluation price elements (secondary cost ingredient class = 42). The connection between unique and evaluation price components is defined in an allocation structure.
Plan Activity Price Calculation
Deliberate costs could be calculated for every price heart activity type. The R/3 system takes all plan exercise flows between cost centers under consideration and calculates the activity worth in an iterative course of by dividing the plan prices by the plan activity.Alternatively, you can calculate the mounted worth portion from the connection between the plan costs and capacity. This is useful when the availability costs for the maximum exercise amount are not to affect costing of a product. For example, an power-supplying value center must always be capable of supplying the utmost stage of exercise, even if this activity quantity isn't all the time used. On this case, the fixed provision prices should remain on the supplying value center, because the full quantity cannot be assigned on to the product costs.In the plan model, you'll give you the option to arrange the willpower technique for the plan exercise value calculation.You presumably can choose between average activity price and periodic activity price.In case you have prices which can be set each iteratively as well as manually, you can set the indicator "purely iterative" in the version. This ensures that the costs calculated from your planning (a mix of iterative and manual costs) are calculated utilizing purely iterative methods. Which means that an extra purely iterative value is calculated for all exercise types on all value centers, as if no costs have been set manually. You probably can thus see the impact of your manually deliberate costs on activity prices overall.
Related Posts
ABAP BADI PART TWO
ABAP BADI PART THREE
ABAP BADI PART FOUR
BADI PART FIVE
ABAP BADI PART SIX CALLING BADI AND ITS USES
BADI INTRODUCTION
- Plan the structure of the company's future operations for explicit intervals
- Create benchmarks for controlling the business transactions within an accounting period
- Monitor efficiency after completion of the accounting interval by way of plan/precise and goal/precise comparisons
- Give a foundation for valuation of organizational actions, via estimating the unit cost of performing a given exercise in a given interval
Versions in Controlling
The definition of a model applies for the whole of Controlling. This ensures that your knowledge stays constant for those who use the model in different applications, for instance in each Overhead Price Controlling and in Profitability Anaylsis (built-in planning).You define Controlling versions centrally and add application-specific settings for Profitability Evaluation, Profit Middle Accounting, and Overhead Cost Controlling.You may plan your value centers in as many CO versions as you wish. Each model within the R/3 System is tailor-made to explicit planning requirements.Once you create a controlling area, the R/three System mechanically creates version zero, valid for 5 fiscal years. It's also attainable to create different versions for, for example, constructive or unfavorable scenarios.When referring to actual postings , the R/3 System always makes use of version 0. Different versions can relate only to saving planning data in Price Center Accounting.
Copy Plan and Actual Data
You should utilize the tool Copy Planning if you want to reuse large parts of your manual value heart planning from a previous 12 months on your current planning, or to repeat plan values inside a fiscal year to a unique period, or to generate alternate plan versions.Equally, the instrument Copy Precise to Plan lets you utilize previous actual cost center information as the reference for creating new plan data.To make use of the Copy Planning operate, select a reference model and a goal version.You'll give you the chance to copy plan data:
- Inside fiscal years, intervals, variations, and cost facilities
- Between totally different price facilities, fiscal years, durations, and versions
producing best-case and worst-case situations within a year. Plan line objects are recorded throughout revaluation execution.You could undertake as many revaluations of value middle and price ingredient deliberate values as required.The chances within a revaluation may be modified as usually as desired. Repeated executions with changed percentages cancel the previous plan line gadgets and always use the original initial value.

Overview of Planning
You enter planning data in Controlling using entry screens, the structure of which you'll define in
Customizing. These screens are often recognized as planning layouts .There are three planning areas in Price Middle Accounting:
- Value elements/exercise enter
- Exercise output/costs
- Statistical key figures
values, and set up the suitable value columns. SAP provides numerous predefined standard layouts.You utilize planner profiles to control the planning process. In a given planner profile, you'll have the option to assign any number of planning layouts to any number of planning areas.The R/3 System comprises customary planner profiles and standard planning layouts that cover virtually every conceivable planning situation. You can use the SAPALL planner profile to plan for the three planning areas utilizing a quantity of SAP customary layouts. SAP offers the planner profile SAPEASY for conditions where a easy planner profile is required. You can also outline your personal planner profiles.You can perform both centralized (planning of a single cost factor for all value facilities for example) and decentralized planning (for example, planning of all cost components on a single cost center). The kind of planning depends upon manner your organization is organized. You may mix both methods, enabling you for example to plan your personnel prices centrally, and have all other prices deliberate regionally by the fee heart managers.
Planning Statical Key Figures
You may plan statistical key figures to be able to:
- Calculate ratios in cost centers, comparable to cost per employee
- Create receiver tracing components (allocation elements) for periodic allocations (e.g. assessment, distribution)
Primary Cost Planning
Activity-unbiased primary costs, labeled by price components, are planned on price facilities by plan version.If you happen to plan activity-unbiased main prices, you can only plan fastened costs. For price facilities using activity types, these deliberate fastened costs are assigned to the activity sorts of the related fee middle primarily based on the equivalence numbers within the plan, or based mostly on the plan splitting structure. In activity worth calculation these fastened prices are taken into account to calculate the fixed portion of the exercise price.You have to use the Customary-Structure 1-one zero one included in the Profile SAPALL to plan activity independent main costs.
Activity Type Planning
Activity sorts function a measurement of cost middle performance. They describe the amount output of a price heart and can be utilized to discover out an operating rate and target costs. Exercise types are allotted below a secondary value aspect, which is stored as a default value within the exercise kind master record.The activity price is determined per value middle/activity sort both manually or in automated activity value calculation:
- You probably can set manual exercise costs in your price heart/exercise kind combination if the exercise price is mounted within your company and unaffected by any internal exchange of activities.
- In automated exercise price calculation, all major and secondary prices planned as activity dependent or exercise-unbiased for the appropriate cost facilities are included within the activity price.
- If a quantity of activity varieties are planned on a cost center, the exercise-unbiased plan prices are broken down (break up) onto these exercise varieties for activity price calculation. You can accomplish this by entering equivalence numbers along with each deliberate activity kind, or with plan price splitting.
- The unit value for an exercise type is calculated by dividing planned costs for an activity by the deliberate quantity of activity sort units. Alternatively, the capacity of a price heart to provide a given exercise kind can be used in calculating the fastened portion of the exercise price.
Cost Allocation Planning
Periodic re postings are used purely as a posting aid.Major postings (equivalent to telephone costs) are collected on an allocation controlling object to reduce the variety of postings to FI. These prices are then allocated to the suitable controlling objects at period-finish closing in accordance with a person-defined key (fastened quantities or tracing components). The sender controlling object generally is a cost center, inside order, or different object. You can specify the allowed sender and receiver objects for periodic reposting in customizing.Only primary prices may be reposted. The unique value elements are retained on the postings to the receivers. Distribution is meant for the switch of main costs from a sender cost middle to receiver controlling objects. Solely price facilities might serve as senders in a distribution.Primary postings (resembling energy prices) are collected on a service cost center and allocated in accordance to consumer-defined keys.Only primary prices will be distributed. The original value elements are retained on the postings to the receivers.Assessment is designed for the allocation of major and secondary costs from a sender price center to receiver controlling objects. Only cost centers might serve as senders in an assessment.
Primary and secondary postings are allocated in keeping with person-defined keys.Within the evaluation framework, the unique value elements are grouped collectively into evaluation price elements (secondary cost ingredient class = 42). The connection between unique and evaluation price components is defined in an allocation structure.
Plan Activity Price Calculation
Deliberate costs could be calculated for every price heart activity type. The R/3 system takes all plan exercise flows between cost centers under consideration and calculates the activity worth in an iterative course of by dividing the plan prices by the plan activity.Alternatively, you can calculate the mounted worth portion from the connection between the plan costs and capacity. This is useful when the availability costs for the maximum exercise amount are not to affect costing of a product. For example, an power-supplying value center must always be capable of supplying the utmost stage of exercise, even if this activity quantity isn't all the time used. On this case, the fixed provision prices should remain on the supplying value center, because the full quantity cannot be assigned on to the product costs.In the plan model, you'll give you the option to arrange the willpower technique for the plan exercise value calculation.You presumably can choose between average activity price and periodic activity price.In case you have prices which can be set each iteratively as well as manually, you can set the indicator "purely iterative" in the version. This ensures that the costs calculated from your planning (a mix of iterative and manual costs) are calculated utilizing purely iterative methods. Which means that an extra purely iterative value is calculated for all exercise types on all value centers, as if no costs have been set manually. You probably can thus see the impact of your manually deliberate costs on activity prices overall.
Related Posts
ABAP BADI PART TWO
ABAP BADI PART THREE
ABAP BADI PART FOUR
BADI PART FIVE
ABAP BADI PART SIX CALLING BADI AND ITS USES
BADI INTRODUCTION
No comments :
Post a Comment