SAP Financial Customer Vendor Accounts has G/L accounts, customer/vendor accounts have two segments one as phase with basic knowledge on the client level. This data will be accessed all through the entire organization and the other as a section with firm code particular information on the company code level. Any company code who wishes to do business with a particular customer or vendor has to create an organization code phase for him. By doing this, a buyer/vendor account is created.
Just as there's a gross sales space section for patrons, there are buying organization segments for
vendors.Any buying group which desires to do business with a vendor has to create a purchasing organization segment first. The buying organization segment incorporates purchasing group specific data. A complete vendor account consists of the following three segments:
If you would like to change or show an account, you can go straight to every page by selecting it on the initial show screen.Essential fields are:
The account group is used to manage the fields displayed on the grasp record. For example, to be certain that all correspondence has complete tackle data, alter the sector status so that all tackle fields are marked as “required entry”.When creating customer/vendor grasp information, the account group is entered on the preliminary create screen. In financial accounting, as soon as the shopper/vendor account is created, its account group cannot be changed. However, when using companion capabilities in sales and distribution, in some circumstances the account group can be modified from, for example, an ordering tackle to a ship-to address.
There are separate quantity ranges for buyer and vendor accounts. The vary of doable account numbers is divided into smaller number ranges. Quantity ranges should not allowed to overlap.For every number range you may set whether the numbering can be internally or externally assigned. Internal number assignment means that the numbers are assigned by R/3 in sequential order. With exterior quantity project, the numbers are entered manually by the person creating the master record. External numbers can be alphanumeric.With inner numbering for a new account the system always assigns the following number available in the range. Subsequently, it may possibly show the “present number” which informs you how many numbers are still left within a given quantity range.
With exterior numbering, the consumer chooses the account number. Numbers do not have to be assigned in sequence; therefore, a present number can't be displayed.Each quantity vary can be assigned to a number of account groups.For all customers or distributors with whom you hardly ever do business, a special customer and a special vendor master report should be created. Those master records are for “one-time accounts”. In distinction to other master records, no knowledge particular to a single customer/vendor is saved within the onetime grasp document, since this account is used for more than one buyer/vendor. Therefore, the buyer-particular fields should be suppressed.
The client/vendor specific information for one time prospects/distributors are entered into the document at the time of posting.The structure of buyer/vendor master information screens can be affected by a number of factors:
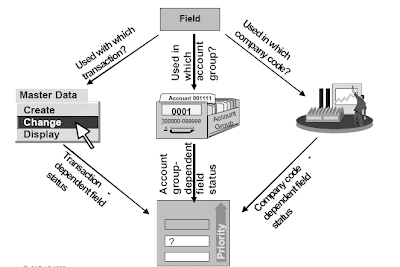
n Account group control : Often the field status is controlled only by the account group. This manner all accounts of one account group may have the same display layout.
When utilizing MM and/or SD, prospects and distributors must be maintained for all modules. It is best to create buyer/vendor grasp information centrally to be sure that that they are set up correctly.However, in some circumstances, MM/SD creates their segments of the master report after which FI creates their segments of the master record. On this case, there's the danger of making incomplete or duplicate master records. To find and proper these incomplete accounts, you'll have the opportunity to run report RFDKAG00,Buyer Master Knowledge Comparability, or RFKKAG00, Vendor Grasp Knowledge Comparability, and make the crucial corrections.Creation of duplicate accounts can be prevented by:
Alternative Payees
On the shopper and firm code stage, an alternative payer/payee can be entered. The enter into the company code segment has greater priority than on the consumer level.There are a quantity of options to make use of this performance within the grasp record. If you select the “Individual specification” subject, during invoice entry, you may enter particular person payee/payer info on a buyer/vendor that isn't created in R/3. If the alternative payee/payer is an current customer or vendor, the vendor/buyer quantity(s) might be entered on the master report as a permitted payee/payer. During bill entry, considered one of these payer(s)/payee(s) could be chosen using matchcodes.If an alternative payer is entered, the cash to clear the due open gadgets of the account is collected from the choice payer.If an alternate payee is entered, the money the corporate has to pay to clear the items due is distributed or transferred to the alternative payee.
 Dual Control
Dual Control
You now can have one particular person making changes to a customer or vendor while one other particular person is liable for validating the changes, normally for essential customer/vendor changes.First you need to define the fields for dual control within the buyer/vendor master data within the IMG.If you outline a discipline within the buyer/vendor grasp file as “delicate”, the corresponding customer/vendor is blocked for payment if the entry is changed. The block is removed when a second individual with authorization checks the change and confirms or rejects it.The affirmation for the modifications may be made for a single buyer/vendor or you may get a list. This record might be restricted by:
Related Posts
System Functions and user Profiles in SAP Financials
SAP Financial Accounting in Organizational Elements
SAP Financial Master Data for General Ledger
SAP Financial Document Control
SAP Financial Post ControlSAP Financial Posting Tips
Just as there's a gross sales space section for patrons, there are buying organization segments for
vendors.Any buying group which desires to do business with a vendor has to create a purchasing organization segment first. The buying organization segment incorporates purchasing group specific data. A complete vendor account consists of the following three segments:
- Basic knowledge at the consumer level
- Firm code phase
- Buying group section
If you would like to change or show an account, you can go straight to every page by selecting it on the initial show screen.Essential fields are:
- Search time period: ought to be stuffed with a brief version of the vendor identify in protecting with company guidelines/desires. New to 4.6 is an additional search field.
- Group key: Prospects or vendors who belong to 1 company group could be bundled together by a person-outlined group key. This group key can be used for working studies, transaction processing or for matchcodes.
- Accounting clerk: The accounting clerk's name needs to be stored under an ID and this ID will be entered in the customer/vendor grasp record of the account he or she is accountable for. The accounting clerk's title is then printed on correspondence and his ID is used to kind dunning and payment proposal lists.
The account group is used to manage the fields displayed on the grasp record. For example, to be certain that all correspondence has complete tackle data, alter the sector status so that all tackle fields are marked as “required entry”.When creating customer/vendor grasp information, the account group is entered on the preliminary create screen. In financial accounting, as soon as the shopper/vendor account is created, its account group cannot be changed. However, when using companion capabilities in sales and distribution, in some circumstances the account group can be modified from, for example, an ordering tackle to a ship-to address.
There are separate quantity ranges for buyer and vendor accounts. The vary of doable account numbers is divided into smaller number ranges. Quantity ranges should not allowed to overlap.For every number range you may set whether the numbering can be internally or externally assigned. Internal number assignment means that the numbers are assigned by R/3 in sequential order. With exterior quantity project, the numbers are entered manually by the person creating the master record. External numbers can be alphanumeric.With inner numbering for a new account the system always assigns the following number available in the range. Subsequently, it may possibly show the “present number” which informs you how many numbers are still left within a given quantity range.
With exterior numbering, the consumer chooses the account number. Numbers do not have to be assigned in sequence; therefore, a present number can't be displayed.Each quantity vary can be assigned to a number of account groups.For all customers or distributors with whom you hardly ever do business, a special customer and a special vendor master report should be created. Those master records are for “one-time accounts”. In distinction to other master records, no knowledge particular to a single customer/vendor is saved within the onetime grasp document, since this account is used for more than one buyer/vendor. Therefore, the buyer-particular fields should be suppressed.
The client/vendor specific information for one time prospects/distributors are entered into the document at the time of posting.The structure of buyer/vendor master information screens can be affected by a number of factors:
n Account group control : Often the field status is controlled only by the account group. This manner all accounts of one account group may have the same display layout.
- Transaction dependent control : If desired, the field status can even depend on the master data transaction “Create”, “Change”, and “Display”. The transaction dependent subject standing needs to be set on “display” for the transaction “change” if the field should not be changed after creation, e.g. the discipline “reconciliation account”.
- Company code dependent control : The sector standing may also be controlled per firm code.Fields which are not utilized in one company code might be suppressed while they're entry fields in others.
- Field status definitions of account groups, the transaction, and company code are combined and the one which has highest priority is used.
- Fields which are accessed with the transaction “show” are all the time both displayed or suppressed since you can not make an entry in a show transaction.
- If you do not want to make use of transaction dependent or firm code dependent discipline standing control, set all field standing definitions as optionally available entry since this has the lowest priority and can due to this fact not battle with the account group control.

When utilizing MM and/or SD, prospects and distributors must be maintained for all modules. It is best to create buyer/vendor grasp information centrally to be sure that that they are set up correctly.However, in some circumstances, MM/SD creates their segments of the master report after which FI creates their segments of the master record. On this case, there's the danger of making incomplete or duplicate master records. To find and proper these incomplete accounts, you'll have the opportunity to run report RFDKAG00,Buyer Master Knowledge Comparability, or RFKKAG00, Vendor Grasp Knowledge Comparability, and make the crucial corrections.Creation of duplicate accounts can be prevented by:
- using the matchcode before creating a model new account
- switching on automatic duplication verify
- The vendor account number should be entered into the shopper account and the client account number should be entered into the seller account
- Each company code can decide separately whether or not it desires to clear a buyer with a vendor. If clearing is for use, the sector ”Clrg with vend.” in the customer account must be marked and vice versa.
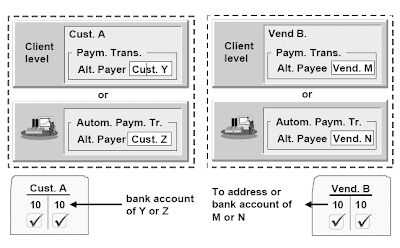
Alternative Payees
On the shopper and firm code stage, an alternative payer/payee can be entered. The enter into the company code segment has greater priority than on the consumer level.There are a quantity of options to make use of this performance within the grasp record. If you select the “Individual specification” subject, during invoice entry, you may enter particular person payee/payer info on a buyer/vendor that isn't created in R/3. If the alternative payee/payer is an current customer or vendor, the vendor/buyer quantity(s) might be entered on the master report as a permitted payee/payer. During bill entry, considered one of these payer(s)/payee(s) could be chosen using matchcodes.If an alternative payer is entered, the cash to clear the due open gadgets of the account is collected from the choice payer.If an alternate payee is entered, the money the corporate has to pay to clear the items due is distributed or transferred to the alternative payee.
 Dual Control
Dual ControlYou now can have one particular person making changes to a customer or vendor while one other particular person is liable for validating the changes, normally for essential customer/vendor changes.First you need to define the fields for dual control within the buyer/vendor master data within the IMG.If you outline a discipline within the buyer/vendor grasp file as “delicate”, the corresponding customer/vendor is blocked for payment if the entry is changed. The block is removed when a second individual with authorization checks the change and confirms or rejects it.The affirmation for the modifications may be made for a single buyer/vendor or you may get a list. This record might be restricted by:
- Buyer/Vendor
- Firm code
- Accounts not but confirmed
- Accounts refused
- Accounts to be confirmed by me.
Related Posts
System Functions and user Profiles in SAP Financials
SAP Financial Accounting in Organizational Elements
SAP Financial Master Data for General Ledger
SAP Financial Document Control
SAP Financial Post ControlSAP Financial Posting Tips
No comments :
Post a Comment