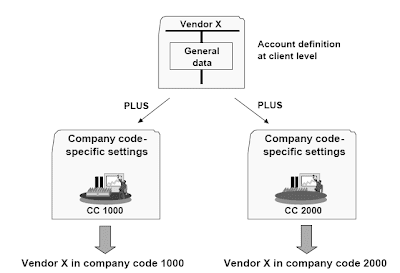
SAP Financial Master Data For General Ledger in the SAP software which has a separate module for financial and controlling part of the business.n Earlier than you ought to use an account in a company code, you want to preserve the account definition on the chart of accounts level. You then create firm code-specific settings, which are only valid within the company code. An example of an organization code-particular setting is defining the account currency. Most of the accounts in firm code 1000 use the UNI foreign money, whereas firm code 3000 uses USD for many of its accounts.
The IDES firm codes use the next charts of accounts:
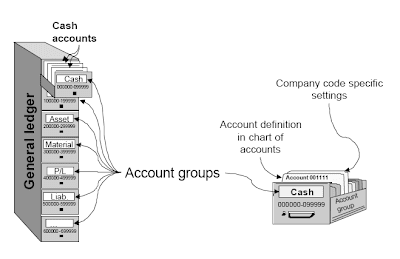
Account Groups
With the intention to set up and manage a lot of G/L accounts higher, they are arranged in account groups .The accounts of an account group usually have comparable business functions. You might possibly, for example,have an account group for money accounts, one for expense accounts, one for income accounts, and one for other balance sheet accounts, etc.
 Reconciliation accounts connect subsidiary ledgers with the overall ledger in real-time. This implies that a posting to a subsidiary ledger additionally posts to the corresponding reconciliation account within the general ledger on the same time. The subsidiary ledgers that are connected to the general ledger via reconciliation accounts are the A/P, A/R, and asset ledgers.
Reconciliation accounts connect subsidiary ledgers with the overall ledger in real-time. This implies that a posting to a subsidiary ledger additionally posts to the corresponding reconciliation account within the general ledger on the same time. The subsidiary ledgers that are connected to the general ledger via reconciliation accounts are the A/P, A/R, and asset ledgers.
A transaction determine is the total of all debit or credit score postings. Basically, the R/3 System retains one transaction determine for debits and one transaction figure for credits per account. The financial statements for the company code are calculated using these transaction figures.If using business areas, transaction figures are also kept per enterprise area. Should you create a financial assertion for the business space, the transaction figures for that particular business space are used to provide the data for the financial statements.
Organizational Structure of Cost Accounting
The controlling space identifies a self-contained organizational structure for which prices and revenues can be managed and allocated. It represents a separate unit of value accounting.A number of firm codes might be assigned to a controlling space, which lets you carry out cross-company code price accounting between the assigned company codes. Nevertheless, that is solely doable if the assigned firm codes and the controlling space all use the identical working chart of accounts.
It was notably necessary to the IDES board of directors that the European company codes,Germany, United Kingdom, Portugal, and Spain, all belong to the identical controlling area, since a great deal of exercise takes place between these firm codes. Subsequently, all four company codes needed to undertake the working chart of accounts (INT) of the controlling area. However, to guarantee that it to be attainable for exterior stories to comprise the account numbers usually used in the individual international locations, a rustic-specific chart of accounts was created for the corporate codes Germany, the United Kingdom, and Spain. These nation-particular charts of accounts meet the requirements of the separate countries.
For consolidation purposes, a gaggle chart of accounts was set up for the two operating charts of accounts.A controlling space comprises CO objects that take on varied capabilities within Controlling, comparable to:
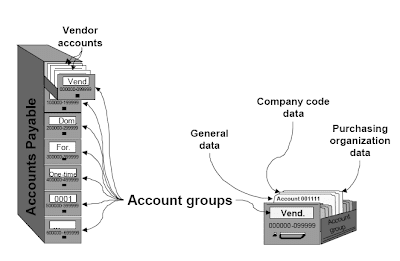
As with G/L accounts, vendor accounts are made up of two areas:
In the identical method as G/L accounts, vendor accounts can be combined in varied account groups , so that they are often organized and managed more easily. The accounts in an account group usually have similar characteristics. For instance, you could have one account group for domestic distributors, one for vendors abroad, one for affiliated distributors, and one for one-time accounts.
Integration with Materiel Management
Buying for the crops is completed by the buying organization. Every country, by which IDES vegetation function, has one purchasing organization. They purchase for all plants in the country and publish the purchases in the company code of that country.The purchasing organizations buy goods and services from suppliers, who are paid by accounts payable. The assorted purchasing organizations of the group must enter information particular to buying in the vendor master document earlier than the provider's master record could be used.
The three-step verification is the standard procedure for posting procurement transactions in FI.The procedure comprises the next three steps:
 Revenue Controlling
Revenue Controlling
An operating concern is the central organizational structure in profitability analysis. Every working concern represents an space by which a market (or customer-defined) section of a enterprise can be monitored and its profitability analyzed.A company group often solely requires one working concern. This operating concern is assigned to all existing controlling areas that assign their prices to that working concern. Revenues are assigned directly to the operating concern from FI.
IDES additionally uses just one working concern, to which all the controlling areas in the entire corporate group are assigned. This permits IDES to carry out international market and profitability analyses.The working concern is split into particular person market segments for which profitability analyses may be carried out. These market segments are generally identified as profitability segments . The profitability segments are defined using characteristics selected by the user.The IDES working concern makes use of the next traits to outline its profitability segments:
As with G/L accounts and vendor accounts, buyer accounts are additionally made up of two areas:
 Integration with Sales and Distribution
Integration with Sales and Distribution
The gross sales organizations are legally liable for sales in R/3. One firm code might comprise a number of gross sales organizations.Which means any accounting-related transactions in both of these sales organizations are posted in firm code 1000.Every gross sales group can use totally different distribution channels to promote goods. In precept, a distribution channel will also be used by two totally different gross sales organizations. Distribution channels used by IDES are:

Materials are divided into divisions in the R/3 System so that a large quantity of different materials might be managed and processed more efficiently. The IDES group uses the divisions bikes, paints, and foods, for example.The divisions are assigned to the distribution chain from which they are often sold. The mixture of distribution chain and division is a sales area.Customer-specific arrangements, regarding partial deliveries or terms of payment, for example, can be made for each gross sales area. Statistics will be created and separate advertising actions carried out within a sales area.
A sales area (combination of sales group, distribution channel, and division) should define gross sales area-particular settings for a customer earlier than it may possibly begin doing business with that customer. These could possibly be special situations and phrases of funds that the shopper has organized with the particular sales area.
Sales Process
The sales order forms the idea of the gross sales process. Once a customer has positioned an order, a sales order must be created at the start of the process. The sales order is generated on the distribution chain level. The ordered items could be from totally different divisions. The gross sales order is a document in SD and doesn't cause any postings in Monetary Accounting. When the gross sales order has been entered, the system carries out an availability examine for the required delivery date.On the day of shipping, an outbound delivery doc is created. Billing for the supply can solely happen when the goods have been taken from the warehouse inventory and posted as a goods issue.The warehouse administration perform is used for choosing . A switch order must be created, which generates the pick order. The requested items are taken from the warehouse and ready for delivery.The products to be delivered are posted as a items situation . A goods subject document is created in MM, and an accounting document is created in FI so that the goods issue is posted to the right G/L accounts.
The last stage within the sales process is billing. A billing document is created in SD, and a printed bill is shipped to the customer. At the similar time, a doc is created in FI so that the receivables and revenues might be posted to the proper accounts.
Credit Management
The organizational unit used for credit control is the credit management area. A credit management space could be assigned to particular person company codes (decentralized group) or to a group of firm codes (centralized group).A credit management space is usually managed by a separate credit division, which is split right into a variety of credit score representative teams, with every group consisting of several credit score representatives.Credit score control is carried out as follows at IDES:
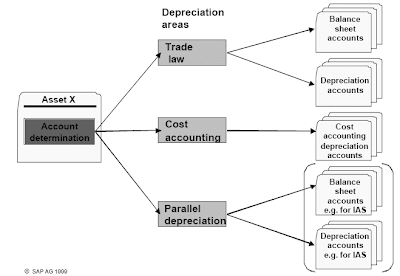
Each asset belongs to a company code and enterprise area. All postings made for the asset (acquisitions, retirements, depreciation, etc.) are utilized within the assigned company code and business area.Moreover, you'll have the option to assign the asset to various CO objects (price center, inside order, exercise type) and logistic organizational models (for selection functions solely).The asset class is the principle criteria for defining the asset. Every asset has to be assigned to an asset class. Within the asset class, you presumably can outline sure control parameters and default values for depreciation and different master data.
Assets that do not seem in the identical line merchandise of the stability sheet (equivalent to buildings and equipment) should be assigned to different asset classes. Moreover, there's at the very least one special asset class for belongings under development and one for low-worth assets. The asset lessons utilized by IDES for this are:
Because the depreciation areas in asset accounting do not exist within the basic ledger, these values have to be posted to numerous G/L accounts in the general ledger. The G/L accounts are then used in numerous financial statement variations (monetary statements per GAAP, monetary statements for tax authorities, group financial statements, and so forth).These G/L accounts are:
For reporting purposes, elements of an asset might be kept under asset sub-numbers, and assets could be combined in group assets.The primary asset is assigned the sub-quantity 0000, allowing the asset sub-numbers to be assigned as desired.A gaggle asset has its own grasp data. A number of foremost property will be assigned to a group. That is vital within the USA.
Master data in Travel Management
Worker information is saved as HR master data. For the rationale that HR grasp information may be fairly large, its information is stored in data groups which are organized based mostly on contents. One such information group is an infotype. For instance, metropolis, street, and number are a half of the handle of an employee and are thus saved (along with different information) within the infotype Addresses.IDES Group is using the HR software component and is thus capable of save and valuate a large amount of information within the infotypes of HR grasp data.Firms, which aren't utilizing HR, are also capable of create smaller HR master data, the so-known as mini grasp report in Journey Management. The FI-TV mini grasp report solely comprises the following infotypes:

A personnel motion consists of all infotypes to be processed as a half of a personal procedure, similar to hiring, organizational change, promotion, and so on. The relevant infotypes are made accessible for processing one after another, to ensure that no important info is forgotten. Every completed motion is entered within the ”motion" infotype, so that the ”actions" infotype has a log of all procedures completed for this person.Personnel actions are usually completed in HR. If HR is simply not implemented, FI-TV presents two actions for maintaining FI-TV mini master data:
Master Data in Accounting
The bank directory incorporates the addresses and valid management knowledge (similar to Swift code) of all banks used within the SAP System.The financial institution listing can both be:
Since the Enjoy Launch (4.6), SAP presents a transaction for managing money amounts. You can create money journals which can be uniquely identified by a four character name.Every cash journal must be assigned to at the very least one G/L account, which represents the cash journal within the common ledger. It is nonetheless doable, to connect multiple cash journals with one G/L account. Cash transactions are saved separately in the cash journal and are transferred periodically (for instance, day by day) to the final ledger.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Technology Overview
MySAP CRM Marketing IntroductionCRM Marketing and lead management
System Functions and user Profiles in SAP Financials
SAP Financial Accounting in Organizational Elements
The IDES firm codes use the next charts of accounts:
- INT is utilized by firm codes a thousand, 2000, 2100, 2300, and 6000.
- CAUS is used by company codes 3000 and 4000.
- CAFR is utilized by company code 2200.
- CAJP is used by firm code 5000.
Account Groups
With the intention to set up and manage a lot of G/L accounts higher, they are arranged in account groups .The accounts of an account group usually have comparable business functions. You might possibly, for example,have an account group for money accounts, one for expense accounts, one for income accounts, and one for other balance sheet accounts, etc.
 Reconciliation accounts connect subsidiary ledgers with the overall ledger in real-time. This implies that a posting to a subsidiary ledger additionally posts to the corresponding reconciliation account within the general ledger on the same time. The subsidiary ledgers that are connected to the general ledger via reconciliation accounts are the A/P, A/R, and asset ledgers.
Reconciliation accounts connect subsidiary ledgers with the overall ledger in real-time. This implies that a posting to a subsidiary ledger additionally posts to the corresponding reconciliation account within the general ledger on the same time. The subsidiary ledgers that are connected to the general ledger via reconciliation accounts are the A/P, A/R, and asset ledgers.A transaction determine is the total of all debit or credit score postings. Basically, the R/3 System retains one transaction determine for debits and one transaction figure for credits per account. The financial statements for the company code are calculated using these transaction figures.If using business areas, transaction figures are also kept per enterprise area. Should you create a financial assertion for the business space, the transaction figures for that particular business space are used to provide the data for the financial statements.
Organizational Structure of Cost Accounting
The controlling space identifies a self-contained organizational structure for which prices and revenues can be managed and allocated. It represents a separate unit of value accounting.A number of firm codes might be assigned to a controlling space, which lets you carry out cross-company code price accounting between the assigned company codes. Nevertheless, that is solely doable if the assigned firm codes and the controlling space all use the identical working chart of accounts.
It was notably necessary to the IDES board of directors that the European company codes,Germany, United Kingdom, Portugal, and Spain, all belong to the identical controlling area, since a great deal of exercise takes place between these firm codes. Subsequently, all four company codes needed to undertake the working chart of accounts (INT) of the controlling area. However, to guarantee that it to be attainable for exterior stories to comprise the account numbers usually used in the individual international locations, a rustic-specific chart of accounts was created for the corporate codes Germany, the United Kingdom, and Spain. These nation-particular charts of accounts meet the requirements of the separate countries.
For consolidation purposes, a gaggle chart of accounts was set up for the two operating charts of accounts.A controlling space comprises CO objects that take on varied capabilities within Controlling, comparable to:
- Inner orders
- Value objects
- Networks
- Initiatives
- Price facilities
- Make-to-order gross sales orders
- True objects can allocate their costs to other CO objects.
- Statistical objects cannot reallocate their prices and solely bear their costs for data purposes.
As with G/L accounts, vendor accounts are made up of two areas:
- A vendor account is outlined for all firm codes at consumer level. Basic data, such because the vendor's address, can also be saved here.
- Postings cannot be made to the account in an organization code until firm code-particular settings have been made, such as the agreed phrases of payment.

In the identical method as G/L accounts, vendor accounts can be combined in varied account groups , so that they are often organized and managed more easily. The accounts in an account group usually have similar characteristics. For instance, you could have one account group for domestic distributors, one for vendors abroad, one for affiliated distributors, and one for one-time accounts.

Integration with Materiel Management
Buying for the crops is completed by the buying organization. Every country, by which IDES vegetation function, has one purchasing organization. They purchase for all plants in the country and publish the purchases in the company code of that country.The purchasing organizations buy goods and services from suppliers, who are paid by accounts payable. The assorted purchasing organizations of the group must enter information particular to buying in the vendor master document earlier than the provider's master record could be used.
The three-step verification is the standard procedure for posting procurement transactions in FI.The procedure comprises the next three steps:
- Creating a buy order order: This transaction is completed in MM. No postings are made in FI.
- Items receipt:To replace the stock, a cloth doc is created in MM. On the identical time, a document is created in FI, with which the value of the products is posted to the supplies account (debit) and the goods receipt/bill receipt account (credit score) within the normal ledger.
- Invoice receipt: The vendor bill is posted in MM, which routinely creates a document in FI. The FI doc incorporates the bill quantity that is posted to the products receipt/bill receipt account (debit) and the seller account (credit score).
 Revenue Controlling
Revenue ControllingAn operating concern is the central organizational structure in profitability analysis. Every working concern represents an space by which a market (or customer-defined) section of a enterprise can be monitored and its profitability analyzed.A company group often solely requires one working concern. This operating concern is assigned to all existing controlling areas that assign their prices to that working concern. Revenues are assigned directly to the operating concern from FI.
IDES additionally uses just one working concern, to which all the controlling areas in the entire corporate group are assigned. This permits IDES to carry out international market and profitability analyses.The working concern is split into particular person market segments for which profitability analyses may be carried out. These market segments are generally identified as profitability segments . The profitability segments are defined using characteristics selected by the user.The IDES working concern makes use of the next traits to outline its profitability segments:
- Customer
- Gross sales organization
- Distribution channel
- Division
- Product
- Strategic enterprise unit
- Sales district
- Country
As with G/L accounts and vendor accounts, buyer accounts are additionally made up of two areas:
- A buyer account is defined for all firm codes as client level. Common information, such as the customer's deal with, can also be stored here.
- Postings cannot be made to the account in an organization code until firm code-specific settings have been made, such as the agreed terms of payment.
- Basic knowledge, which is relevant for all credit score control areas. This may very properly be the customer's deal with and communication knowledge, or the maximum total restrict that can be permitted for the sum of all granted credit score limits.
- Credit control are a data, which is just related for a particular credit management area. This could be the credit score limit at credit score management area stage, or a customer's danger category.
 Integration with Sales and Distribution
Integration with Sales and DistributionThe gross sales organizations are legally liable for sales in R/3. One firm code might comprise a number of gross sales organizations.Which means any accounting-related transactions in both of these sales organizations are posted in firm code 1000.Every gross sales group can use totally different distribution channels to promote goods. In precept, a distribution channel will also be used by two totally different gross sales organizations. Distribution channels used by IDES are:
- Closing buyer sales
- Resellers
- Service
- Manufacturing facility gross sales
- Store chains
- Industrial prospects
- Pharmaceutical clients

Materials are divided into divisions in the R/3 System so that a large quantity of different materials might be managed and processed more efficiently. The IDES group uses the divisions bikes, paints, and foods, for example.The divisions are assigned to the distribution chain from which they are often sold. The mixture of distribution chain and division is a sales area.Customer-specific arrangements, regarding partial deliveries or terms of payment, for example, can be made for each gross sales area. Statistics will be created and separate advertising actions carried out within a sales area.
A sales area (combination of sales group, distribution channel, and division) should define gross sales area-particular settings for a customer earlier than it may possibly begin doing business with that customer. These could possibly be special situations and phrases of funds that the shopper has organized with the particular sales area.
Sales Process
The sales order forms the idea of the gross sales process. Once a customer has positioned an order, a sales order must be created at the start of the process. The sales order is generated on the distribution chain level. The ordered items could be from totally different divisions. The gross sales order is a document in SD and doesn't cause any postings in Monetary Accounting. When the gross sales order has been entered, the system carries out an availability examine for the required delivery date.On the day of shipping, an outbound delivery doc is created. Billing for the supply can solely happen when the goods have been taken from the warehouse inventory and posted as a goods issue.The warehouse administration perform is used for choosing . A switch order must be created, which generates the pick order. The requested items are taken from the warehouse and ready for delivery.The products to be delivered are posted as a items situation . A goods subject document is created in MM, and an accounting document is created in FI so that the goods issue is posted to the right G/L accounts.
The last stage within the sales process is billing. A billing document is created in SD, and a printed bill is shipped to the customer. At the similar time, a doc is created in FI so that the receivables and revenues might be posted to the proper accounts.
Credit Management
The organizational unit used for credit control is the credit management area. A credit management space could be assigned to particular person company codes (decentralized group) or to a group of firm codes (centralized group).A credit management space is usually managed by a separate credit division, which is split right into a variety of credit score representative teams, with every group consisting of several credit score representatives.Credit score control is carried out as follows at IDES:
- When the order is placed, a check is run to see whether or not the customer's credit score limit could be exceeded if the order had been to be accepted. If this is not the case, the sales process could be carried out in the regular way.
- If the credit limit is exceeded, the order is blocked, and the credit department has to act. The responsible credit score representative can either be notified automatically by manner of distant mail, or can recurrently use a report again to examine an inventory of all blocked orders.
- The credit score representative then clarifies the state of affairs, either by using the credit data system, or by calling the customer.
- Once clarification has been made, the credit score consultant releases the order, and the transaction might be processed in SD within the normal way. If the credit score consultant decides to not release the order, the order is rejected.
Each asset belongs to a company code and enterprise area. All postings made for the asset (acquisitions, retirements, depreciation, etc.) are utilized within the assigned company code and business area.Moreover, you'll have the option to assign the asset to various CO objects (price center, inside order, exercise type) and logistic organizational models (for selection functions solely).The asset class is the principle criteria for defining the asset. Every asset has to be assigned to an asset class. Within the asset class, you presumably can outline sure control parameters and default values for depreciation and different master data.
Assets that do not seem in the identical line merchandise of the stability sheet (equivalent to buildings and equipment) should be assigned to different asset classes. Moreover, there's at the very least one special asset class for belongings under development and one for low-worth assets. The asset lessons utilized by IDES for this are:
- 4000 For assets under construction
- 5000 For low-value property
- Financial statements primarily based on regional requirements
- Financial statements for tax functions (if a special deprecation technique is allowed)
- Controlling (costing)
- Parallel accounting strategies for group monetary statements (per IAS, US-GAAP, etc.)
- per asset and depreciation area
- for individual worth elements such as balances, depreciation, remaining e book worth, etc.
Because the depreciation areas in asset accounting do not exist within the basic ledger, these values have to be posted to numerous G/L accounts in the general ledger. The G/L accounts are then used in numerous financial statement variations (monetary statements per GAAP, monetary statements for tax authorities, group financial statements, and so forth).These G/L accounts are:
- Stability sheet accounts, which document the changes to the asset's worth
- Depreciation accounts for depreciation and appreciation

For reporting purposes, elements of an asset might be kept under asset sub-numbers, and assets could be combined in group assets.The primary asset is assigned the sub-quantity 0000, allowing the asset sub-numbers to be assigned as desired.A gaggle asset has its own grasp data. A number of foremost property will be assigned to a group. That is vital within the USA.
Master data in Travel Management
Worker information is saved as HR master data. For the rationale that HR grasp information may be fairly large, its information is stored in data groups which are organized based mostly on contents. One such information group is an infotype. For instance, metropolis, street, and number are a half of the handle of an employee and are thus saved (along with different information) within the infotype Addresses.IDES Group is using the HR software component and is thus capable of save and valuate a large amount of information within the infotypes of HR grasp data.Firms, which aren't utilizing HR, are also capable of create smaller HR master data, the so-known as mini grasp report in Journey Management. The FI-TV mini grasp report solely comprises the following infotypes:
- Personnel actions (listing of all accomplished personnel actions)
- Organizational project (comparable to company code, enterprise space, and value heart)
- Personal info
- Addresses
- Financial institution Particulars
- Journey privileges (control parameters equivalent to task of travel restrictions for the worker and for determining travel reimbursement)
- Journey preferences (a row of infotypes for the assist of travel planning)

A personnel motion consists of all infotypes to be processed as a half of a personal procedure, similar to hiring, organizational change, promotion, and so on. The relevant infotypes are made accessible for processing one after another, to ensure that no important info is forgotten. Every completed motion is entered within the ”motion" infotype, so that the ”actions" infotype has a log of all procedures completed for this person.Personnel actions are usually completed in HR. If HR is simply not implemented, FI-TV presents two actions for maintaining FI-TV mini master data:
- Create TV mini grasp data
- Organizational change
Master Data in Accounting
The bank directory incorporates the addresses and valid management knowledge (similar to Swift code) of all banks used within the SAP System.The financial institution listing can both be:
- Mechanically imported, as lengthy as the bank directory is accessible on diskette and a import program exists for this data or
- manually created
- Checking account at home financial institution;
- combination home bank and account ID ;
- G/L account n The represented relationships ought to always be a one-to-one relationship.
Since the Enjoy Launch (4.6), SAP presents a transaction for managing money amounts. You can create money journals which can be uniquely identified by a four character name.Every cash journal must be assigned to at the very least one G/L account, which represents the cash journal within the common ledger. It is nonetheless doable, to connect multiple cash journals with one G/L account. Cash transactions are saved separately in the cash journal and are transferred periodically (for instance, day by day) to the final ledger.
Related Posts
SAP CRM Technology Overview
MySAP CRM Marketing IntroductionCRM Marketing and lead management
System Functions and user Profiles in SAP Financials
SAP Financial Accounting in Organizational Elements
No comments :
Post a Comment