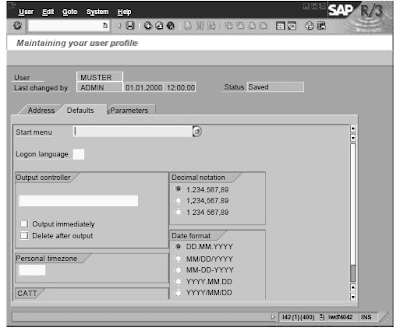
In creating and developing SAP Financial Accounting System Functions and User Profile you can use the menu option System Consumer profile Own data to set your own personal profile.You may select between the Address, Defaults and Parameters tabs.Deal with: You may create and preserve private information right here, for instance, title,function, room quantity, telephone number, e-mail addresses and so on.Defaults: Defaults embrace the date display format, the decimal notation format, the default printer, the logon language, and so on.
Parameters: Use this to assign entries to generally-used fields. This is solely accessible for input fields that have been allocated a parameter ID.Procedure for finding out a discipline’s Parameter ID: Go to the enter field to which you want to assign a value. Select F1, then the “Technical info” push button. This opens a window that shows the corresponding parameter ID (if one has been allocated to the field) in the “Area knowledge” section.The User profile menu additionally comprises, amongst others, the following option of Maintain knowledge, Set information, Delete data. Use Maintain data to maintain data values that you've got entered in fields in an utility at some stage in a consumer session. When you name up the appliance once more, you can overwrite these values. Once you have Set data , you'll have the opportunity to no longer overwrite these values and have to make use of Delete data if you need to enter different values.
System Wide Concepts
Business State of affairs: Business-related grouping of enterprise processes localized in a specific organizational space that share some related objectives in an enterprise, reminiscent of purchasing, companies, steadiness sheet preparation, production, personnel administration, and so on.Organizational Unit: Organizational grouping of enterprise areas which, for legal reasons or for other specific business-associated causes or functions, are grouped together. Organizational units embody authorized firm entities, sales places of work, and revenue centers.Grasp Data: Data which is used lengthy-time period within the R/3 System for a quantity of enterprise processes.Examples embody clients, supplies, and vendors.Transactions: Application programs which execute enterprise processes in the R/3 System corresponding to creating a buyer order, posting an incoming fee, or approving a depart request.
An enterprise structure is mapped to SAP functions utilizing organizational units. Organizational
models deal with specific business functions.Organizational items may be assigned to a single software (corresponding to a gross sales group assigned to Gross sales and Distribution, or to several functions (reminiscent of a plant assigned to Materials Administration and Production Planning).
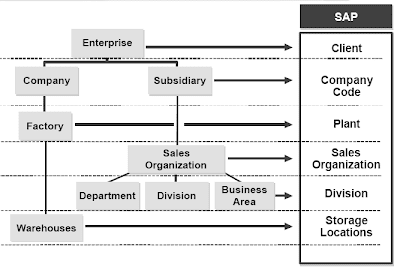 The best-stage factor of all organizational units is the client. The shopper could be an enterprise group with several subsidiaries. All the enterprise knowledge in an R/3 System implementation is split into not much less than the shopper area, and often into lower level organizational constructions as well.Flexible organizational units within the R/three System allow extra complex enterprise buildings to be represented. If there are many organizational models, the legal and organizational construction of an enterprise may be presented in different views.By linking the organizational models, the separate enterprise areas might be integrated and the structure of the entire enterprise represented within the R/3 System.An enterprise is structured within the SAP R/three System in keeping with enterprise capabilities that should correspond to the performance assigned to the organizational units.
The best-stage factor of all organizational units is the client. The shopper could be an enterprise group with several subsidiaries. All the enterprise knowledge in an R/3 System implementation is split into not much less than the shopper area, and often into lower level organizational constructions as well.Flexible organizational units within the R/three System allow extra complex enterprise buildings to be represented. If there are many organizational models, the legal and organizational construction of an enterprise may be presented in different views.By linking the organizational models, the separate enterprise areas might be integrated and the structure of the entire enterprise represented within the R/3 System.An enterprise is structured within the SAP R/three System in keeping with enterprise capabilities that should correspond to the performance assigned to the organizational units.Examples:
- A Company Code is a unit included in the steadiness sheet of a legally-independent enterprise. It is the central organizational factor of Financial Accounting.
- The Controlling Area is the enterprise unit where Cost Accounting is carrie d out. Often there's a 1:1 relationship between the controlling space and the corporate code. For the aim of company wide value accounting, one controlling area can deal with cost accounting for several firm codes in one enterprise.
- Within the context of Sales and Distribution, the Gross sales Group is central organizational ingredient that controls the terms of sale to the customer. Distribution Channel is the component that describes by means of what channel goods and/or companies might be distributed to the customer.
- In the context of Production Planning and Management, the Plant is the central organizational unit. A plant is the place of production or just a collection of several locations of fabric stocks in close bodily proximity.
- A Storage Location is a storage area comprising warehouses in shut proximity. Materials shares might be differentiated within one plant according to storage location (inventory administration).
Data records that stay in the database for an extended period of time are known as master data. Master data consists of collectors, distributors, supplies, accounts, and so on. Master knowledge is created centrally and can be utilized in all applications.
Instance: A buyer is master knowledge that can be used in buyer requests, deliveries, invoices, and payments.Grasp information additionally has an organizational side as it's assigned to organizational units.
Grasp knowledge has cross-part usage
Examples:
- Buyer grasp data uses the identical data for financial accounting and sales
- Buyer master data will be assigned to the next organizational units:firm code sales group distribution channel division .When creating a buyer master document, you enter:
- Shared data on the client degree
- Company code-particular data for every company code
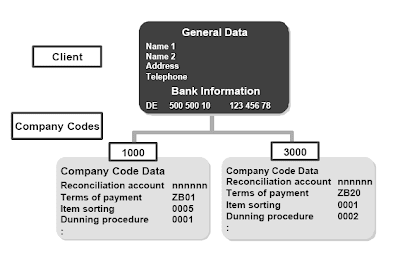 When you even have SAP Gross sales and Distribution carried out, there are extra fields you can maintain. These fields include data and management knowledge which are necessary for processing the enterprise actions in the Gross sales area.Fields for customer grasp knowledge are divided into Accounting and Gross sales areas. Tackle knowledge is used from each areas. In the Gross sales space, information recorded will be accessed by Financial Accounting and vice versa.The structural logic for buyer grasp records/accounts receivable can additionally be valid for vendor master data/accounts payable.
When you even have SAP Gross sales and Distribution carried out, there are extra fields you can maintain. These fields include data and management knowledge which are necessary for processing the enterprise actions in the Gross sales area.Fields for customer grasp knowledge are divided into Accounting and Gross sales areas. Tackle knowledge is used from each areas. In the Gross sales space, information recorded will be accessed by Financial Accounting and vice versa.The structural logic for buyer grasp records/accounts receivable can additionally be valid for vendor master data/accounts payable.Material Master Data
The material master represents the central source for releasing materials-specific data. It is used by all of the SAP Logistics parts within the R/3 System.Integrating the entire material data in one single database object signifies that the problem of knowledge redundancy isn't an issue. The saved information can be utilized by all areas, comparable to buying, inventory management, materials planning, bill verification, and so on.The information contained in the materials master is required, for example, by the following functions within the SAP Logistics element:
- Ordering in Purchasing
- Updating motion of products and managing the physical stock in Inventory Administration
- Posting invoices in Invoice Verification
- Processing gross sales orders in Gross sales
- Planning requirements, scheduling work in Manufacturing Planning and Control
Documents and Analysis
Paperwork are captured and saved on R/three with numerous quantities of information.You can generate experiences immediately from the online transactions or from the other sources of summarized knowledge such as the Business Data Warehouse, Government Data System or the
various module Information Systems.Element Transaction info is stored on the R/3 system and summarized data is typically saved on the BW, EIS or Info System for detailed summarized evaluation using the tools offered by those systems.
Online Transactions
Reviews will be run at any time within the R/3 System. Present data is processed on-line at the time the report is run. Reviews can be requested in several methods: they are often accessed from the initial R/3 System screen, by choosing Data systems.For frequent reporting, it makes sense to retailer report selection parameters as report “variants”. The stored report variants might be built-in in a “job.” The job is notified of the time when one or more report variants are to be run.In standard reports, key figures comparable to the characteristics are formatted in preserving with the report request. From this display screen, you may entry additional evaluation functions or required further key figures by deciding on a subject (double -click). The information within the report listing will be displayed in an inventory or represented in a graphic.
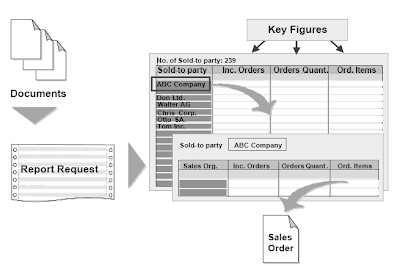
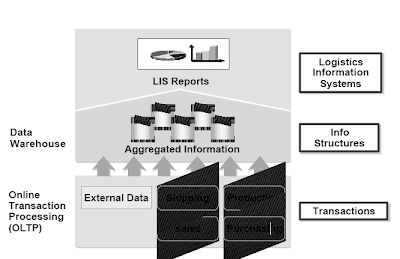
Informations System Strecture
The entire LIS data is saved in info structures.Transactions from the R/3 functions which can be performed daily are aggregated for LIS for statistical purposes. Data from other methods can additionally be utilized in LIS.The experiences most incessantly used may be accessed from the SAP normal menu.Distinction is made between different reporting types:
- Normal experiences: List of document, grasp data, etc. and combinations of those objects (characteristics) to be chosen within the report request
- Reporting via information systems within the functions: Normal analyses from FIS (Financials), LIS (Logistics), HIS (Human Assets)
- Reporting through info programs with separate databases and instruments for generating versatile report structures: EIS (Government Information System) and the Business Data Warehouse.
- The application reporting timber provide varied predefined reports. These experiences have been outlined by SAP in response to business requirements.
- The application info programs also allow you to outline your own data buildings in the SAP R/3 System to meet your enterprise’s particular person requirements.
Related Posts
MySAP CRM Marketing Introduction Marketing and Advertizing in CRM
MySAP and ERP
No comments :
Post a Comment