The mySAP Market is a crucial element inside the world mySAP.com e-business platform, as a outcome of it is the main participant within the collaborative business-to-business area, offering a set of advanced companies that can be utilized by many other mySAP solutions..The need for collaboration and cooperation among the many information methods of different corporations has at all times existed. But the large infrastructure supplied right this moment by the Internet and Internet protocols has enabled collaboration amongst companies like never before. Virtual marketplaces, also identified as e-marketplaces, are in the current day the utmost expression of that collaboration.
An e-marketplace is a concentrator for inter enterprise communication. Via an e-market, the paperwork generated by the data systems of different firms are exchanged. The e-marketplaces also provide added worth services for businesses, comparable to shopping for and selling, bidding, news, financial institution providers, logistic operators, and so on.
There are horizontal digital marketplaces wherein corporations from completely different trade sectors do business. And there are vertical ones, by which solely firms from the identical business collaborate. There are also non-public marketplaces the place only an organization and its business companions (suppliers, most important clients, and so forth) do business together.
In Might 2000, SAP created a model new firm with the mission of promoting market software program and projects. This company is SAPMarkets, dedicated to spearheading all market efforts of the SAP Group. One month later, in June 2000, SAPMarkets reached an settlement with the company CommerceOne for the joint improvement, help, and sale of the software program for the creation and operation of digital marketplaces. As a outcome of this joint venture, SAPMarkets launched its software solution for e-marketplaces known as MarketSet.
MarketSet Overview
MarketSet is the SAPMarkets open solution for horizontal, vertical, and personal e-marketplaces. As such, MarketSet is the main utility resolution for the mySAP Market component.
MarketSet can be used for designing, implementing, and managing virtual marketplaces that doubtlessly ship added value to companies and enterprise partners. Examples of added worth companies include the likelihood for decreasing inventories’ cycle instances and bettering an efficient communication channel between patrons and suppliers in order that the availability chain becomes built-in into a fast and efficient collaboration process.
The virtual market can be a place where there's a higher transparency between enterprise companions, allowing for simultaneous interactions, the publication of requests for proposals, or demand planning. Due to this fact, suppliers taking part inside marketplaces can respond faster to purchaser needs in contrast with different competitors outside the marketplace.
E-marketplaces could be one of the environment friendly collaboration resources for enterprise and buying and selling partners. The exchange of information in real time allows for a terrific optimization potential for saving costs and for streamlining the availability chain and thus the time to market or the product or service availability. Therefore, e-marketplaces will directly benefit companies and end customers, and corporations can successfully turn this collaborative relationship into an amazing alternative for generating revenues and profit.
With the aim and focus of getting that efficiency out of collaborative communities, SAPMarkets created the MarketSet platform. It's a collaboration platform that may present these added worth companies by additionally joining processes and exchanging paperwork throughout a number of information systems. The MarketSet is therefore a step ahead in the traditional procurement processes and purposes and can deal with each direct procurement and sophisticated provide chain management.
From a software standpoint, the MarketSet supplies all the wanted items to design and construct a virtual market that can provide collaborative business companies such as selling and buying, auctions, catalogs, planning, and so on. As an open platform, e-market operators can develop their service offerings by incorporating additional services by different providers.
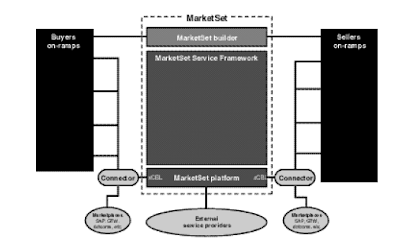
MarketSet Inside BlocksWithin the inside parts of the MarketSet, the very first thing you should look at is the MarketSet Service Framework. This is the part in command of holding the totally different companies supported by the MarketSet. The Service Framework is a collection of rules, strategies, APIs (utility program interfaces), and tools, that are answerable for managing and controlling the way in which wherein those companies must be placed throughout the e-marketplace.
MarketSet Service Framework is a very open surroundings, and subsequently it might actually contain two kinds of companies: these included inside the MarketSet or from third parties.The companies of release 2.zero of MarketSet embrace:
Some sorts of third-party services embrace:
The MarketSet Builder, also referred to as the User Interface Builder, is the element accountable for generating the HTML interface for the users. It is technically based on an open source solution that features position and personalization capabilities, as effectively as help for doc alternate based on both XML and xCBL. For directors, it also includes a framework for handling transformations, styles, and other administration tools.
From a useful viewpoint, the MarketSet Builder is in control of offering a standard look, personalization companies, and the consumer interface framework for the integration of the MarketSet services. To facilitate the creation of e-marketplaces for market makers, the MarketSet Builder consists of:
MarketSet Platform
The MarketSet Platform supplies the know-how basis for the MarketSet. The performance might be divided into three important elements: security, connectivity, and management. Concerning security, the MarketSet Platform gives the single logon functionality for all the companies integrated throughout the MarketSet: function-based mostly access management by means of the user administration interface Netegrity, PKI (public key infrastructure)- primarily based authentication assist with x.509 CA both for person and XPC authentication, and multilevel person and role administration by way of consumer administration interface.

The connectivity part is in command of managing all the communication with the buying and selling companions, the integration with their purposes, EDI (Digital Knowledge Interchange) communications, and assist for the RosettaNet standards. The principle element for the reference to the buying and selling companions is the MarketSet Connector, which is a part of the MarketSet Platform layer. This piece allows for the mapping and transformation of knowledge, in addition to the connection of virtually any system. Regarding SAP environments, the MarketSet Connector is prepared to translate classical SAP interface mechanisms, similar to RFC (Distant Perform Calls), IDOC (intermediate paperwork), or BAPIs (enterprise software programming interfaces), to xCBL.
The MarketSet Connector is predicated on the classical Enterprise Connector with XPC (XML Portal Connector) add-ons, an XML integration software program supplied to virtual marketplaces by CommerceOne and totally integrated within the MarketSet. The MarketSet Connector uses protocols equivalent to HTTPS (HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer) or more normally SonicMQ, which is an implementation of a queue system that makes use of SSL (Safe Sockets Layer) over TCP/IP and permits such characteristics as excessive availability, load balancing, and scalability.
Finally, the management components embrace options for performance tuning of every of the providers, offering with an administration console for the complete management of the marketplace.
All these systems behind the firewalls of the companies that function in the e-marketplace are often called On-Ramps systems. These programs can be both classical ERPs (enterprise resource planning) akin to SAP R/three or different buying and promoting functions, from any software vendor or developed in-house. In any case and whichever kind of system, it will seemingly be in a place to communicate with the MarketSet utilizing the MarketSet Connector. As an illustration, procurement systems will be in a position to access catalog providers, planning instruments will be ready to collaborate with different purposes via the marketplace providers, selling functions will be in a position to obtain orders, and so on. In abstract, any sort of system within the firms that function in the e-market will be in a position to combine into the MarketSet.

MarketSet Business Framework
The MarketSet Enterprise Framework hosts all of the different services that could be supported by the MarketSet 2.0. A service is a selected software that gives added value to the trading partners that use it. A person from a company could be subscribed to at the least one, a number of, or all the services offered throughout the MarketSet.
MarketSet Procurement
One of the most typical providers offered by the MarketSet is buying or procurement, which enables customers to create buy requisitions and automate the buying processes, such as the order or the approval. One of many further benefits for firms is the likelihood for consolidating the procurement wants across a number of divisions, departments, plants, or geographies, and all without needing to install or configure any additional applications.With the opportunity of linking environment friendly procurement processes primarily based on an e-market with the planning and design strategy of direct items, firms have a wonderful atmosphere for improving the availability chain by exchanging paperwork and information with business partners.
The MarketSet Procurement, as one of the services of the MarketSet, is a Web based application answerable for offering procurement providers to these firms that take part of the e-marketplace. The procurement services are supreme not solely for giant firms, but also for small and medium-sized companies, which can participate in a solid procurement solution with out the need to install and configure their own hardware and software.
Related posts
SAP internet transaction application components
SAP authorization and client administration in mysap.com
SAP Authorization and ALE
Authorization and implementation of SAP
An e-marketplace is a concentrator for inter enterprise communication. Via an e-market, the paperwork generated by the data systems of different firms are exchanged. The e-marketplaces also provide added worth services for businesses, comparable to shopping for and selling, bidding, news, financial institution providers, logistic operators, and so on.
There are horizontal digital marketplaces wherein corporations from completely different trade sectors do business. And there are vertical ones, by which solely firms from the identical business collaborate. There are also non-public marketplaces the place only an organization and its business companions (suppliers, most important clients, and so forth) do business together.
In Might 2000, SAP created a model new firm with the mission of promoting market software program and projects. This company is SAPMarkets, dedicated to spearheading all market efforts of the SAP Group. One month later, in June 2000, SAPMarkets reached an settlement with the company CommerceOne for the joint improvement, help, and sale of the software program for the creation and operation of digital marketplaces. As a outcome of this joint venture, SAPMarkets launched its software solution for e-marketplaces known as MarketSet.
MarketSet Overview
MarketSet is the SAPMarkets open solution for horizontal, vertical, and personal e-marketplaces. As such, MarketSet is the main utility resolution for the mySAP Market component.
MarketSet can be used for designing, implementing, and managing virtual marketplaces that doubtlessly ship added value to companies and enterprise partners. Examples of added worth companies include the likelihood for decreasing inventories’ cycle instances and bettering an efficient communication channel between patrons and suppliers in order that the availability chain becomes built-in into a fast and efficient collaboration process.
The virtual market can be a place where there's a higher transparency between enterprise companions, allowing for simultaneous interactions, the publication of requests for proposals, or demand planning. Due to this fact, suppliers taking part inside marketplaces can respond faster to purchaser needs in contrast with different competitors outside the marketplace.
E-marketplaces could be one of the environment friendly collaboration resources for enterprise and buying and selling partners. The exchange of information in real time allows for a terrific optimization potential for saving costs and for streamlining the availability chain and thus the time to market or the product or service availability. Therefore, e-marketplaces will directly benefit companies and end customers, and corporations can successfully turn this collaborative relationship into an amazing alternative for generating revenues and profit.
With the aim and focus of getting that efficiency out of collaborative communities, SAPMarkets created the MarketSet platform. It's a collaboration platform that may present these added worth companies by additionally joining processes and exchanging paperwork throughout a number of information systems. The MarketSet is therefore a step ahead in the traditional procurement processes and purposes and can deal with each direct procurement and sophisticated provide chain management.
From a software standpoint, the MarketSet supplies all the wanted items to design and construct a virtual market that can provide collaborative business companies such as selling and buying, auctions, catalogs, planning, and so on. As an open platform, e-market operators can develop their service offerings by incorporating additional services by different providers.

MarketSet Inside BlocksWithin the inside parts of the MarketSet, the very first thing you should look at is the MarketSet Service Framework. This is the part in command of holding the totally different companies supported by the MarketSet. The Service Framework is a collection of rules, strategies, APIs (utility program interfaces), and tools, that are answerable for managing and controlling the way in which wherein those companies must be placed throughout the e-marketplace.
MarketSet Service Framework is a very open surroundings, and subsequently it might actually contain two kinds of companies: these included inside the MarketSet or from third parties.The companies of release 2.zero of MarketSet embrace:
- MarketSet Procurement
- MarketSet Order Management
- MarketSet Dynamic Pricing
- MarketSet Catalog
- MarketSet Analytics
- MarketSet Bulletin Board
- MarketSet Life-Cycle Collaboration
- MarketSet Provide Chain Collaboration
Some sorts of third-party services embrace:
- Logistic Providers
- Transport Association
- Transport Settlement
- Legal Companies
- Foreign Commerce Atrium
- Import/Export Control
- Sanctioned Party Record Screening
- Customs Willpower
- Export Paperwork
- Financial Providers
- E-fee
- Escrow
- Obtain Credit score
- Credit Threat Analysis
- Factoring (Promoting of Debts)
- Purchasing Cards
- Credit Risk Insurance
- Security Providers
- Personal Identification
- Content material Setup Providers
- Public sale Execution Providers
The MarketSet Builder, also referred to as the User Interface Builder, is the element accountable for generating the HTML interface for the users. It is technically based on an open source solution that features position and personalization capabilities, as effectively as help for doc alternate based on both XML and xCBL. For directors, it also includes a framework for handling transformations, styles, and other administration tools.
From a useful viewpoint, the MarketSet Builder is in control of offering a standard look, personalization companies, and the consumer interface framework for the integration of the MarketSet services. To facilitate the creation of e-marketplaces for market makers, the MarketSet Builder consists of:
- Templates
- System for person/policy management
- Function-based mostly and user-based personalization
- Methods for trading associate registration and person login
MarketSet Platform
The MarketSet Platform supplies the know-how basis for the MarketSet. The performance might be divided into three important elements: security, connectivity, and management. Concerning security, the MarketSet Platform gives the single logon functionality for all the companies integrated throughout the MarketSet: function-based mostly access management by means of the user administration interface Netegrity, PKI (public key infrastructure)- primarily based authentication assist with x.509 CA both for person and XPC authentication, and multilevel person and role administration by way of consumer administration interface.

The connectivity part is in command of managing all the communication with the buying and selling companions, the integration with their purposes, EDI (Digital Knowledge Interchange) communications, and assist for the RosettaNet standards. The principle element for the reference to the buying and selling companions is the MarketSet Connector, which is a part of the MarketSet Platform layer. This piece allows for the mapping and transformation of knowledge, in addition to the connection of virtually any system. Regarding SAP environments, the MarketSet Connector is prepared to translate classical SAP interface mechanisms, similar to RFC (Distant Perform Calls), IDOC (intermediate paperwork), or BAPIs (enterprise software programming interfaces), to xCBL.
The MarketSet Connector is predicated on the classical Enterprise Connector with XPC (XML Portal Connector) add-ons, an XML integration software program supplied to virtual marketplaces by CommerceOne and totally integrated within the MarketSet. The MarketSet Connector uses protocols equivalent to HTTPS (HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer) or more normally SonicMQ, which is an implementation of a queue system that makes use of SSL (Safe Sockets Layer) over TCP/IP and permits such characteristics as excessive availability, load balancing, and scalability.
Finally, the management components embrace options for performance tuning of every of the providers, offering with an administration console for the complete management of the marketplace.
All these systems behind the firewalls of the companies that function in the e-marketplace are often called On-Ramps systems. These programs can be both classical ERPs (enterprise resource planning) akin to SAP R/three or different buying and promoting functions, from any software vendor or developed in-house. In any case and whichever kind of system, it will seemingly be in a place to communicate with the MarketSet utilizing the MarketSet Connector. As an illustration, procurement systems will be in a position to access catalog providers, planning instruments will be ready to collaborate with different purposes via the marketplace providers, selling functions will be in a position to obtain orders, and so on. In abstract, any sort of system within the firms that function in the e-market will be in a position to combine into the MarketSet.

MarketSet Business Framework
The MarketSet Enterprise Framework hosts all of the different services that could be supported by the MarketSet 2.0. A service is a selected software that gives added value to the trading partners that use it. A person from a company could be subscribed to at the least one, a number of, or all the services offered throughout the MarketSet.
MarketSet Procurement
One of the most typical providers offered by the MarketSet is buying or procurement, which enables customers to create buy requisitions and automate the buying processes, such as the order or the approval. One of many further benefits for firms is the likelihood for consolidating the procurement wants across a number of divisions, departments, plants, or geographies, and all without needing to install or configure any additional applications.With the opportunity of linking environment friendly procurement processes primarily based on an e-market with the planning and design strategy of direct items, firms have a wonderful atmosphere for improving the availability chain by exchanging paperwork and information with business partners.
The MarketSet Procurement, as one of the services of the MarketSet, is a Web based application answerable for offering procurement providers to these firms that take part of the e-marketplace. The procurement services are supreme not solely for giant firms, but also for small and medium-sized companies, which can participate in a solid procurement solution with out the need to install and configure their own hardware and software.
Related posts
SAP internet transaction application components
SAP authorization and client administration in mysap.com
SAP Authorization and ALE
Authorization and implementation of SAP