SAP Project Migration to mySAP is not truly a technical process of operating a certain upgrade program. It's largely a concept of evolving ERP business processes into collaborative e-business processes and making probably the most of the potential markets created in the Internet economy. Subsequently, a migration to mySAP.com is extra of a conceptual course of, where ERP remains to be the again-workplace and important enterprise software, and new solutions are added and built-in to get better enterprise worth in a extra world economy. There's, nevertheless, the idea of migrating to mySAP.com in terms of licensing, however this process can be better addressed by the SAP gross sales representatives.
The primary query that arises is where SAP R/3 stands in this picture. Taking a look at the evolution of SAP software solutions, it was already 1998 when the New Dimension merchandise had been launched as predecessors to the more comprehensive platform represented by mySAP.com solutions. SAP developed from a single product company (producing R/3) to a world resolution one, but it was still R/3 at the coronary heart and heart of the picture.According to SAP, R/3 is now one very important piece of the mySAP options and is being further enhanced and developed. The result is SAP R/3 Enterprise, as the new version of SAP R/3.
There are heaps of reasons for “migrating” to a mySAP.com platform. A few of these reasons are:
Introduction to ASAP
ASAP is the normal framework for SAP’s implementation of R/3 tasks and has been extended to cowl not only R/three, however other mySAP solutions, reminiscent of CRM (Customer Relationship Management), APO, or e-procurement (BBP). Within the context of the answer life cycle management, ASAP is the basic and more vital methodology for the implementation of advanced projects. Nevertheless, ASAP goes past just a methodology and supplies a giant quantity of its personal tools and utilities for simplifying the implementation process. ASAP can traditionally be complemented with SAP and SAP partners’ implementation services, comparable to coaching, support, consulting, and so on.
Though there are different ASAPs for the mySAP options, the final phases are fairly frequent to all of them, the main difference being the actions and duties for constructing the enterprise course of maps and the configuration options. So within the following sections, the generic ASAP is essentially introduced, with R/3 implementations as the core for the work packages and actions explained.The path proposed by SAP to succeed in the aim of getting a quick return on funding-that's, accomplishing a fast and price-effective implementation-is based on the idea of facilitating a quick implementation of mySAP purposes and guaranteeing the quality. To achieve a each quick and quality implementation, ASAP is predicated on the following issues:
The main tools supplied by ASAP are:
The ASAP solution set is delivered in a CD-ROM that is put in independently of SAP techniques, though it can be linked with them and might be available from the Solution Architect Portal. ASAP is launch-dependent and is consistently updated. SAP supplies periodic updates within the SAP Service Market, and in the newest releases, it is included inside ValueSAP.
Consistent with SAP strategy, the ASAP technique of implementation is positioned in conserving with the next aims and methods:
The ASAP Road map is the challenge plan of the methodology. It’s a effectively-outlined and clear process-oriented mission plan, providing a step-by-step guide during the life of the implementation project. The Road map is made up of five main phases, each describing the principle work packages, activities, and tasks to achieve the anticipated results. Together with the activities and tasks, ASAP supplies all the process descriptions, instruments, training, services, and documentation that shall be useful for finishing up these activities. The next sections briefly introduce the frequent Road map phases.
Venture Preparation
At this primary section, mission preparation, the challenge mission and scope are defined. Some key problems with this section are:
ASAP offers instruments, such because the Undertaking Estimator, which helps and guides the project staff utilizing predefined questionnaires geared toward firm upper management. Using the outcomes of those questions, consultants can consider the answers and supply a excessive-stage evaluation of the undertaking scope, in addition to an preliminary estimation of required resources and planning. That is the undertaking beginning point.
The finish result of this section consists of two essential documents in the implementation, the project charter and the detailed undertaking plan. The management crew or steering committee is answerable for evaluating such a plan and approving it if no objections are found. This may set off the beginning for the subsequent phase. ASAP pays specific attention to ensure the quality in the whole mission process and selections taken throughout the execution of this phase. Any error or wrong choices can negatively have an effect on the subsequent stream of the project and might produce delays, which suggests longer mission time and better costs.Thus Project Migration to mySAP is going to help us to do the job in a better way.
Related posts
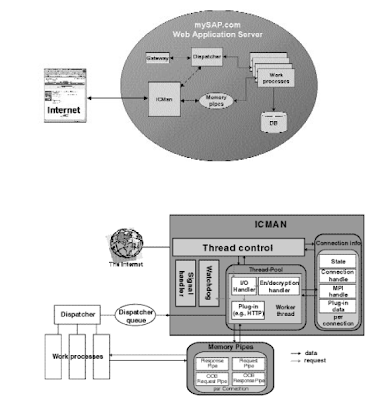
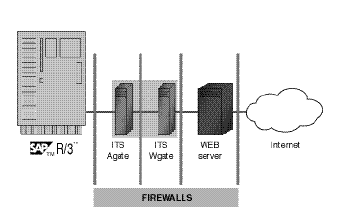
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
Mysap market place introduction
Customer interface in mysap market place
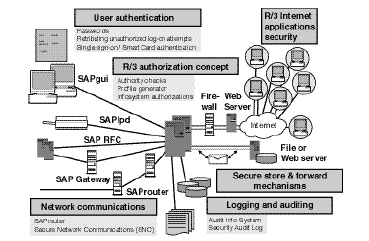
MySAP environment security solutions
CALL FUNCTION PART FIVE
CALL METHOD
The primary query that arises is where SAP R/3 stands in this picture. Taking a look at the evolution of SAP software solutions, it was already 1998 when the New Dimension merchandise had been launched as predecessors to the more comprehensive platform represented by mySAP.com solutions. SAP developed from a single product company (producing R/3) to a world resolution one, but it was still R/3 at the coronary heart and heart of the picture.According to SAP, R/3 is now one very important piece of the mySAP options and is being further enhanced and developed. The result is SAP R/3 Enterprise, as the new version of SAP R/3.
There are heaps of reasons for “migrating” to a mySAP.com platform. A few of these reasons are:
- Create value in the new economic system wherein electronic commerce has an important function
- Effective and price discount in the relationships with enterprise partners
- Creating new enterprise lines
- Common access, with out set up to enterprise portals
- Implementing real and collaborative e-business
- Easy contracts, all accessible software can be utilized if wanted
- If it’s not already there, migrate SAP R/3 to a minimum of release 3.1I or higher, to latest releases equivalent to 4.6C.
- Build an idea for an Enterprise Portal (using, as an illustration, mySAP Workplace solutions).
- Build a concept and implement one or more of the Customer Relationship Administration solutions, as an illustration, Internet Gross sales, Mobile Sales, Buyer Interplay Center, or all of them.
- Implement a Data Warehouse solution (Enterprise Warehouse), which will be wanted to investigate information and feedback the the rest of e-enterprise solutions and therefore incorporate Enterprise Intelligence.
- Build a concept and implement one or more of the Provide Chain Administration solutions, for instance, the APO (Advanced Planner and Optimizer).
- Construct an idea and implement an e-procurement solution to streamline the buying and procurement processes. Take into account also the implementation or integration inside an e-marketplace.
- Integrate the parts carried out with the back-finish (ERP) systems.
- Construct the function idea for customers and business partners.
- Implement the Enterprise Portal and combine all implemented components.
- Provide customers and business companions with the data wanted for performing their jobs or their relationships.
Introduction to ASAP
ASAP is the normal framework for SAP’s implementation of R/3 tasks and has been extended to cowl not only R/three, however other mySAP solutions, reminiscent of CRM (Customer Relationship Management), APO, or e-procurement (BBP). Within the context of the answer life cycle management, ASAP is the basic and more vital methodology for the implementation of advanced projects. Nevertheless, ASAP goes past just a methodology and supplies a giant quantity of its personal tools and utilities for simplifying the implementation process. ASAP can traditionally be complemented with SAP and SAP partners’ implementation services, comparable to coaching, support, consulting, and so on.
Though there are different ASAPs for the mySAP options, the final phases are fairly frequent to all of them, the main difference being the actions and duties for constructing the enterprise course of maps and the configuration options. So within the following sections, the generic ASAP is essentially introduced, with R/3 implementations as the core for the work packages and actions explained.The path proposed by SAP to succeed in the aim of getting a quick return on funding-that's, accomplishing a fast and price-effective implementation-is based on the idea of facilitating a quick implementation of mySAP purposes and guaranteeing the quality. To achieve a each quick and quality implementation, ASAP is predicated on the following issues:
- Clear definition of the mission, goals, and the scope of the project.
- A clearly defined venture scope is vital to adjust time planning and to strategy mission cost plans to actual costs.
- Enhance the feasibility of realizing an in depth planning at first of the project.
- Standardizing and establishing a single challenge or implementation methodology, as defined by ASAP itself.
- Making a homogeneous mission environment.
The main tools supplied by ASAP are:
- Implementation Assistant
- World Question and Answer Database
- Business Engineer
- Data Corner
The ASAP solution set is delivered in a CD-ROM that is put in independently of SAP techniques, though it can be linked with them and might be available from the Solution Architect Portal. ASAP is launch-dependent and is consistently updated. SAP supplies periodic updates within the SAP Service Market, and in the newest releases, it is included inside ValueSAP.
Consistent with SAP strategy, the ASAP technique of implementation is positioned in conserving with the next aims and methods:
- ASAP is the mySAP implementation resolution straight developed and supported by SAP and partners.
- ASAP presents a preliminary planning of the resource needs-time, prices,individuals-based mostly on the initial buyer information and requirements.
- ASAP gives an optimum setting for quite a bit of totally different mySAP tasks, even improve projects.
- ASAP is aimed at and particularly fitted to those implementation initiatives the place the variety of changes to standard SAP purposes is reduced to a minimum.
The ASAP Road map is the challenge plan of the methodology. It’s a effectively-outlined and clear process-oriented mission plan, providing a step-by-step guide during the life of the implementation project. The Road map is made up of five main phases, each describing the principle work packages, activities, and tasks to achieve the anticipated results. Together with the activities and tasks, ASAP supplies all the process descriptions, instruments, training, services, and documentation that shall be useful for finishing up these activities. The next sections briefly introduce the frequent Road map phases.
Venture Preparation
At this primary section, mission preparation, the challenge mission and scope are defined. Some key problems with this section are:
- Define clear challenge objectives.
- Reach total settlement on challenge issues amongst concerned parties.
- Set up an environment friendly course of for making choices and resolving conflicts.
- Prepare the company for accepting cultural and process changes.
ASAP offers instruments, such because the Undertaking Estimator, which helps and guides the project staff utilizing predefined questionnaires geared toward firm upper management. Using the outcomes of those questions, consultants can consider the answers and supply a excessive-stage evaluation of the undertaking scope, in addition to an preliminary estimation of required resources and planning. That is the undertaking beginning point.
The finish result of this section consists of two essential documents in the implementation, the project charter and the detailed undertaking plan. The management crew or steering committee is answerable for evaluating such a plan and approving it if no objections are found. This may set off the beginning for the subsequent phase. ASAP pays specific attention to ensure the quality in the whole mission process and selections taken throughout the execution of this phase. Any error or wrong choices can negatively have an effect on the subsequent stream of the project and might produce delays, which suggests longer mission time and better costs.Thus Project Migration to mySAP is going to help us to do the job in a better way.
Related posts
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
Mysap market place introduction
Customer interface in mysap market place
MySAP environment security solutions
CALL FUNCTION PART FIVE
CALL METHOD