SAP Controlling has one of the major job of Creating General Ledger accounts which involves certain steps.Here in this post we are going to explain them in detail with required screen shots. The accounting department makes use of some information which remains unchanged for lengthy periods of time and which is commonly referred to by different data. This data is named master data. In FI, master data contains basic ledger and sub ledger accounts, as nicely as bank master records.The pinnacle accountant wishes to know the way accounts are structured, how they are often influenced, and the way they might relate to every other.
The chart of accounts comprises fundamental details about the accounts. Info per account is bundled into what is recognized as the chart of account-segment.It contains the:
Fields in the Chart of Account
The data entered in the Chart of Account section is unique whether or not users have one or a quantity of company codes. That is how the identify stays the identical and is consistent throughout firm codes.The knowledge is entered once. Every time you enter information for an organization code for an account quantity, the data from the Chart of Account segment is accessed automatically, so you don't have to enter it again.Texts entered for the Chart of Account segment are managed by textual content ID and language.Texts could be displayed by the report “Account assignment manual”.The Key Words facilitate the search on an account number.
To make use of one of the accounts from the assigned chart of accounts in your organization code, a “company code-section” must be created. This “firm code-segment” is added to the chart of account segment,and together they type the account.Info within the company code segment is restricted for this company code. This info controls entry of accounting paperwork and management of accounting data.
Fields in the Company Code
The Company Code segment for the same G/L account can be completely different relying on the needs of the company code. For example, one firm code could collect tax when utilizing expense accounts and would flag the tax category subject, whereas another company code might not.You outline the data that's pertinent to every firm code:
In the chart of accounts-section, it's vital to indicate whether or not the account shall be a steadiness sheet or a profit+loss assertion account.These two sorts of accounts are treated in another way within the closing procedure.For stability sheet accounts, the balance is carried forward to the same account.For P+L assertion accounts, the stability is carried ahead to a retained earnings account and the P+L assertion account is about to zero. The account to which the steadiness is carried forward is assigned to a key (e.g. x) and this secret's entered within the area ”P+L statement account kind” in the chart of accounts-segment.In customizing, customers define the retained earnings account and during G/L grasp document creation, it is assigned to expense accounts. If there is simply one retained earnings account, R/3 will mechanically use the one defined in customizing. If there are a couple of retained earnings account, during grasp file creation, the consumer may have the choice to determine on the retained earnings account per P+L
account.
Account Groups
Since a chart of accounts accommodates many various sorts of accounts, they can be bundled into completely different “account teams ”. Often one account group bundles accounts with the identical tasks inside the general ledger, e. g. money accounts, material accounts, asset accounts, revenue and loss accounts,...By assigning a quantity vary to an account group, you may be certain that accounts of the identical type are inside the same quantity range. Quantity intervals for G/L account grasp information can overlap.
The account group must be entered in the chart of accounts-phase and controls the looks of the corporate code phase of a G/L account. For instance, for your entire cash accounts, you want to be succesful of view all of the detailed line items. In customizing, on your “Cash Accounts” account group, you'd alter the field status to make “line item display” a required entry.R/3 delivers predefined account groups.
Field Status
Word: Fields which are suppressed might comprise values and these values still take effect!
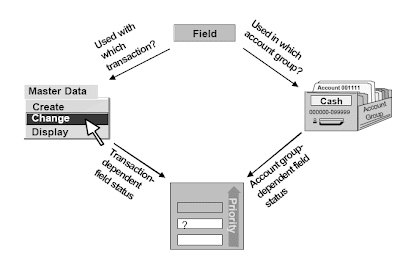
The fields displayed on the general ledger master record should not solely managed by the account
group, but also by the grasp information transaction that you are utilizing (transaction dependent control) i.e. create, change, display. Once the master document is created and you don't want delicate fields changed, on the master report change transaction in customizing, you specify that a certain field is not changeable. For example, you want the forex of your money account to be GBP and you do not want it to be modified, customize the grasp document change transaction to have the field be display only.For every area, the sphere status definitions from the account group and the transaction are taken into consideration and the one with higher priority is used. The priorities are (starting with the highest):
Reconciliation Accounts
Reconciliation accounts are basic ledger accounts assigned to the business associate master information to file all transactions in the sub-ledger.Any postings to the sub-ledger accounts routinely updates the balances of the assigned reconciliation accounts. On this method, the overall ledger is all the time up-to-date.You outline a G/L-account as a reconciliation account by coming into the type of reconciliation account that it is into the field ”Recon.account for acct kind”.
Line Item Display
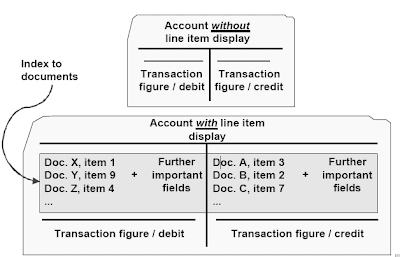
Transaction figures are the sums of line objects on the debit or credit side. The steadiness is the distinction between the debit and the credit transaction figure.The sphere “line merchandise display” is a control field in the company code segment of an account.For accounts without “line merchandise display” only the transaction figures are updated when a document is posted to this account. When a person needs to take a look at this account on-line, they will only give you the option to view the balance.For accounts with “line merchandise display” a very powerful knowledge from the posted line objects is stored in a special index table. As a outcome of this data can additionally be stored within the paperwork, it is redundant and needs additional storage and system time. When a person wants to have a look at this account on-line, they will be capable of view both the steadiness and the person line item details.
Due to system sources that are needed by the road item show, it shouldn't be used for accounts where the line item data will be more simply accessed in one other means, e.g.Reconciliation accounts (line items are managed in the sub-ledgers) . Sales income accounts (line objects are managed by the SD-application)
Open Item Management
Gadgets in accounts with open merchandise management are specified as open or cleared. Accounts with open merchandise administration should have line item show activated.Basic ledger accounts needs to be administered with open merchandise administration when you'll want to verify whether or not there is an offsetting posting for a given enterprise transaction. Open and cleared objects may be displayed separately, and due to this fact it's simple to see which enterprise transactions still must be cleared.It is best to use open merchandise management for:
Accounts in local currency
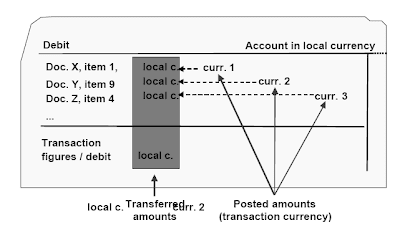
The account foreign money may be either the native foreign money, or a foreign currency.The native currency is defaulted as the account foreign money when a G/L account is created.If the account foreign money is the native foreign money, the account might be posted to in any currency. In the line item, the amount is transferred into the native currency.Transaction figures are kept per foreign money, i.e.local foreign money (sum of all amounts transferred to local currency)
Only balance in local currency
If the box “Only balances in local forex” is marked in the master information record, only transaction figures for quantities transferred to local currency are managed.This indicator should be set for clearing accounts from which you want to have the flexibility to clear objects simply by zero-balancing the quantities in local currency. Then no difference postings caused by alternate price variations must be made.The indicator needs to be set in cash low cost and GR/IR clearing accounts.It should not be set in reconciliation accounts for purchasers or vendors.The indicator is normally set in steadiness sheet accounts which are not kept in foreign exchange and never managed on an open item basis.
 Parallel accounting methods
Parallel accounting methods
For so much of companies, it may be necessary to create additional monetary statements primarily based on standards aside from nation-specific requirements, such as IAS or US-GAAP. Reasons for this could be:
Manual Creation:
With the two step method, the chart of accounts section is created individually from the company
code segment. This allows for creating the GL account only in the chart of accounts or in a number of firm codes.Use the one step technique to create a GL account in a specified firm code. Repeat step 2 of the two step technique, create within the firm code phase, to create the GL account in further firm codes as needed.
Creating GL accounts by copying :
To create an account that has the same properties as an current account, i.e. another cash account,
create the model new account on the topic of the existing account and alter the account title accordingly.If the entire GL accounts in an current firm code are required in another firm code, thetotal company code section can be copied to the model new company code.The entire chart of accounts will be copied into a model new chart of accounts as nicely, including account determination. The monetary statement model can be copied.
Data Transfer:
To reduce information entry, packages like RFBISA00, Batch Input Interface for G/L Account Master Data, can be modified by the ABAP crew to accommodate uploading new chart of accounts
information.
Collective processing
The SAP R/3 System offers collective processing functions for the G/L account master.You can change the grasp information within the chart of accounts space, firm code specific data or the names of several G/L accounts on the similar time. The G/L accounts can be from totally different charts of accounts.You may also make changes to the displayed G/L accounts:
Related Posts
SAP project introduction in the best ERPSAP project migration
SAP Project blueprint
SAP project go live and supportSAP mini applications programming and setup
SAP Project design look and feel
My SAP Project safety and security
The chart of accounts comprises fundamental details about the accounts. Info per account is bundled into what is recognized as the chart of account-segment.It contains the:
- Account quantity
- Name of the account (as brief and as long textual content)
- Control fields (discussed on the following slides)
- Consolidation fields
Fields in the Chart of Account
The data entered in the Chart of Account section is unique whether or not users have one or a quantity of company codes. That is how the identify stays the identical and is consistent throughout firm codes.The knowledge is entered once. Every time you enter information for an organization code for an account quantity, the data from the Chart of Account segment is accessed automatically, so you don't have to enter it again.Texts entered for the Chart of Account segment are managed by textual content ID and language.Texts could be displayed by the report “Account assignment manual”.The Key Words facilitate the search on an account number.
To make use of one of the accounts from the assigned chart of accounts in your organization code, a “company code-section” must be created. This “firm code-segment” is added to the chart of account segment,and together they type the account.Info within the company code segment is restricted for this company code. This info controls entry of accounting paperwork and management of accounting data.
Fields in the Company Code
The Company Code segment for the same G/L account can be completely different relying on the needs of the company code. For example, one firm code could collect tax when utilizing expense accounts and would flag the tax category subject, whereas another company code might not.You outline the data that's pertinent to every firm code:
- Foreign money
- Tax
- Reconciliation account
- Line merchandise display
- Sort key
- Discipline status group
- Home financial institution
- Interest calculation info
In the chart of accounts-section, it's vital to indicate whether or not the account shall be a steadiness sheet or a profit+loss assertion account.These two sorts of accounts are treated in another way within the closing procedure.For stability sheet accounts, the balance is carried forward to the same account.For P+L assertion accounts, the stability is carried ahead to a retained earnings account and the P+L assertion account is about to zero. The account to which the steadiness is carried forward is assigned to a key (e.g. x) and this secret's entered within the area ”P+L statement account kind” in the chart of accounts-segment.In customizing, customers define the retained earnings account and during G/L grasp document creation, it is assigned to expense accounts. If there is simply one retained earnings account, R/3 will mechanically use the one defined in customizing. If there are a couple of retained earnings account, during grasp file creation, the consumer may have the choice to determine on the retained earnings account per P+L
account.
Account Groups
Since a chart of accounts accommodates many various sorts of accounts, they can be bundled into completely different “account teams ”. Often one account group bundles accounts with the identical tasks inside the general ledger, e. g. money accounts, material accounts, asset accounts, revenue and loss accounts,...By assigning a quantity vary to an account group, you may be certain that accounts of the identical type are inside the same quantity range. Quantity intervals for G/L account grasp information can overlap.
The account group must be entered in the chart of accounts-phase and controls the looks of the corporate code phase of a G/L account. For instance, for your entire cash accounts, you want to be succesful of view all of the detailed line items. In customizing, on your “Cash Accounts” account group, you'd alter the field status to make “line item display” a required entry.R/3 delivers predefined account groups.
Field Status
- The sphere standing makes it possible to affect the appearance of an account's grasp data.Fields which aren't used could be suppressed.Fields which have an entry that should not be modified will be set to show solely (even in change mode)
- Fields which should have an entry can be made required fields.
- Fields that can be entered, but should not required, might be set to optional entry.
Word: Fields which are suppressed might comprise values and these values still take effect!
The fields displayed on the general ledger master record should not solely managed by the account
group, but also by the grasp information transaction that you are utilizing (transaction dependent control) i.e. create, change, display. Once the master document is created and you don't want delicate fields changed, on the master report change transaction in customizing, you specify that a certain field is not changeable. For example, you want the forex of your money account to be GBP and you do not want it to be modified, customize the grasp document change transaction to have the field be display only.For every area, the sphere status definitions from the account group and the transaction are taken into consideration and the one with higher priority is used. The priorities are (starting with the highest):
- suppress
- show
- required entry
- non-obligatory entry

Reconciliation Accounts
Reconciliation accounts are basic ledger accounts assigned to the business associate master information to file all transactions in the sub-ledger.Any postings to the sub-ledger accounts routinely updates the balances of the assigned reconciliation accounts. On this method, the overall ledger is all the time up-to-date.You outline a G/L-account as a reconciliation account by coming into the type of reconciliation account that it is into the field ”Recon.account for acct kind”.
- D for purchasers
- K for vendors
Line Item Display
Transaction figures are the sums of line objects on the debit or credit side. The steadiness is the distinction between the debit and the credit transaction figure.The sphere “line merchandise display” is a control field in the company code segment of an account.For accounts without “line merchandise display” only the transaction figures are updated when a document is posted to this account. When a person needs to take a look at this account on-line, they will only give you the option to view the balance.For accounts with “line merchandise display” a very powerful knowledge from the posted line objects is stored in a special index table. As a outcome of this data can additionally be stored within the paperwork, it is redundant and needs additional storage and system time. When a person wants to have a look at this account on-line, they will be capable of view both the steadiness and the person line item details.
Due to system sources that are needed by the road item show, it shouldn't be used for accounts where the line item data will be more simply accessed in one other means, e.g.Reconciliation accounts (line items are managed in the sub-ledgers) . Sales income accounts (line objects are managed by the SD-application)
- Material stock accounts (line objects are managed by the MM-software)
- Tax accounts (Tax objects make sense solely in connection with the doc; the tax quantities had been already checked when the document was posted.)

Open Item Management
Gadgets in accounts with open merchandise management are specified as open or cleared. Accounts with open merchandise administration should have line item show activated.Basic ledger accounts needs to be administered with open merchandise administration when you'll want to verify whether or not there is an offsetting posting for a given enterprise transaction. Open and cleared objects may be displayed separately, and due to this fact it's simple to see which enterprise transactions still must be cleared.It is best to use open merchandise management for:
- financial institution clearing accounts,
- clearing accounts for items receipt/invoice receipt, and
- salary clearing accounts.
Accounts in local currency
The account foreign money may be either the native foreign money, or a foreign currency.The native currency is defaulted as the account foreign money when a G/L account is created.If the account foreign money is the native foreign money, the account might be posted to in any currency. In the line item, the amount is transferred into the native currency.Transaction figures are kept per foreign money, i.e.local foreign money (sum of all amounts transferred to local currency)
- forex 1 (sum of all amounts posted in foreign money 1, would be the local currency)
- foreign money 2 (sum of all quantities posted in currency 2)
- forex 3 (sum of all amounts posted in currency 3) . etc.
Only balance in local currency
If the box “Only balances in local forex” is marked in the master information record, only transaction figures for quantities transferred to local currency are managed.This indicator should be set for clearing accounts from which you want to have the flexibility to clear objects simply by zero-balancing the quantities in local currency. Then no difference postings caused by alternate price variations must be made.The indicator needs to be set in cash low cost and GR/IR clearing accounts.It should not be set in reconciliation accounts for purchasers or vendors.The indicator is normally set in steadiness sheet accounts which are not kept in foreign exchange and never managed on an open item basis.
 Parallel accounting methods
Parallel accounting methodsFor so much of companies, it may be necessary to create additional monetary statements primarily based on standards aside from nation-specific requirements, such as IAS or US-GAAP. Reasons for this could be:
- To gain entry to worldwide capital markets
- To fulfill the needs of overseas traders
- To accommodate international restructuring and acquisitions
- To provide a greater overview of the company’s position
- Utilizing different valuation methods with put up to different G/L accounts
- Using these G/L accounts in varied financial statement variations
Manual Creation:
With the two step method, the chart of accounts section is created individually from the company
code segment. This allows for creating the GL account only in the chart of accounts or in a number of firm codes.Use the one step technique to create a GL account in a specified firm code. Repeat step 2 of the two step technique, create within the firm code phase, to create the GL account in further firm codes as needed.
Creating GL accounts by copying :
To create an account that has the same properties as an current account, i.e. another cash account,
create the model new account on the topic of the existing account and alter the account title accordingly.If the entire GL accounts in an current firm code are required in another firm code, thetotal company code section can be copied to the model new company code.The entire chart of accounts will be copied into a model new chart of accounts as nicely, including account determination. The monetary statement model can be copied.
Data Transfer:
To reduce information entry, packages like RFBISA00, Batch Input Interface for G/L Account Master Data, can be modified by the ABAP crew to accommodate uploading new chart of accounts
information.
Collective processing
The SAP R/3 System offers collective processing functions for the G/L account master.You can change the grasp information within the chart of accounts space, firm code specific data or the names of several G/L accounts on the similar time. The G/L accounts can be from totally different charts of accounts.You may also make changes to the displayed G/L accounts:
- You'll have the option to choose the fields to be modified
- You'll have the opportunity to change the values of the fields displayed. Enter the new values within the header New to replace the prevailing values. For all G/L accounts chosen, the previous value is changed with the brand new value.
- Modifications to existing G/L accounts are effective as soon as saved and will have in depth consequences. You should thus verify your adjustments before saving.
Related Posts
SAP project introduction in the best ERPSAP project migration
SAP Project blueprint
SAP project go live and supportSAP mini applications programming and setup
SAP Project design look and feel
My SAP Project safety and security