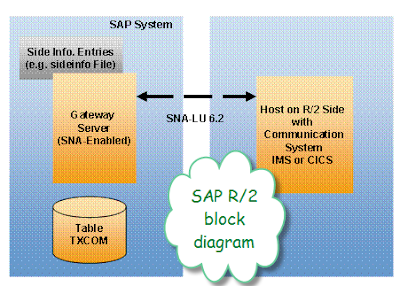
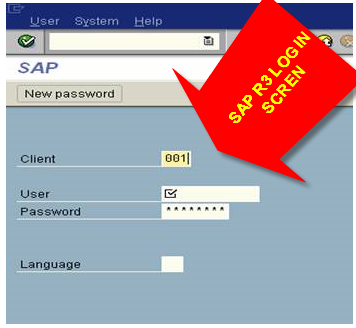
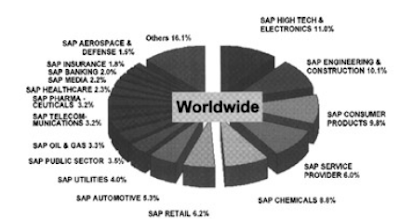
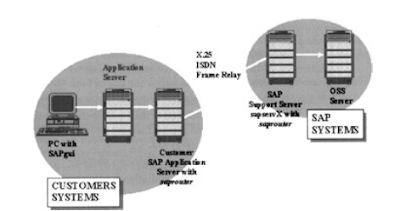
The worlds best erp provides software for all most all regularly happening business scenarios as mentioned here at MySAP CRM Business Scenarios and SAP Solutions and here we are going to discuss this topic further.
Business view of erp software provides information on the business partners involved and offers an outlook of the extent and the flow of the collaboration between the participants. The business view documents the business arguments and the value potential that can be realized by the participants. This basic information gives the idea for the basis for calculating the investment and the rate of return.
Figure shown below describes the business relationship between the participants within the collaborative business scenario Campaign Management using a correlation. The scenario shows how three potential participants in marketing campaigns an external data provider, a manufacturer, and a mailing provider can work together to execute a marketing campaign jointly and successfully.
Figure shown below describes the business relationship between the participants within the collaborative business scenario Campaign Management using a correlation. The scenario shows how three potential participants in marketing campaigns an external data provider, a manufacturer, and a mailing provider can work together to execute a marketing campaign jointly and successfully.
 The marketing manager first will have the overview of the current sales figures using SAP Business Information Warehouse (SAP BW). Keeping in mind the market development, the marketing requirements, and the potential competitor behavior, the marketing manager identifies the products whose turnover will be increased by a marketing campaign.
The marketing manager first will have the overview of the current sales figures using SAP Business Information Warehouse (SAP BW). Keeping in mind the market development, the marketing requirements, and the potential competitor behavior, the marketing manager identifies the products whose turnover will be increased by a marketing campaign.The marketing manager defines the campaign name and outlines its start and end dates. Like the marketing manager, the sales manager defines the campaign target group by selecting customers or prospects.
Marketing and sales managers check and discuss the campaign and its target group once again and confirm the start of the campaign. After this effort, the mailing activities are generated and forwarded, using an external mail shot provider . The marketing manager monitors the status and execution of individual mail shots. At the end of the campaign cycle, the marketing and sales managers can evaluate the effectiveness of the campaign and use this experience in the next campaign.
Qualitative and quantitative improvements occur during the course of business are:
- Improved quality of data through data consistency
- Reduced transaction costs through improved collaboration
- Integration of external and internal analysis data
- Use of external market know-how
- Lean campaign planning and execution
- Concentration on core business tasks by outsourcing the campaign execution
The component view unifies the IT application landscapes of business scenario participants in one consistent display. It describes the application components that are required to support the business process. The activities are divided up into relevant individual steps that are executed within the appropriate applications. Moreover, the component view contains information on release requirements and is the basis for the subsequent technical implementation .
The different views which are customized to meet the information requirements of various recipients (management, specialist department, IT specialists ensures that there is a consistent transition from business context to component implementation in an IT application landscape.
 The advantages of integrated common business processes are documented as business benefits and as value potential on both pages of the business view of a C-Business Map. For example, up to 3 0 % reduced transaction costs are estimated for the business scenario Campaign Management. Savings are measured as a percentage.
The advantages of integrated common business processes are documented as business benefits and as value potential on both pages of the business view of a C-Business Map. For example, up to 3 0 % reduced transaction costs are estimated for the business scenario Campaign Management. Savings are measured as a percentage.SAP Business Case Builder
To enable a quantitative calculation of the expected customer-specific value from using mySAP Business Suite solutions. SAP has developed SAP Business Case Builder. As part of a profitability analysis (a business case) for a planned software solution, SAP Business Case Builder offers a structured procedure for calculating ROI. taking the customer-specific situation into account.
SAP Business Case Builder is structured in three parts:
1• Industry analysis .
2• Identification of a software solution for a customer-specific situation.
3• Creation of an investment appraisal as part of a business case With SAP Business Case Builder, companies can analyze and document their specific situations and compare their requirements with the solution portfolio of mySAP Business Suite. Companies can also create investment appraisals for the selected solutions using SAP Business Case Builder.
Advantages of Business Scenarios
Companies always pursue one or more of the following goals, which must also be the focus of optimization and software support of business processes:
- Increase turnover and market share
- Increase profitability and lower costs
- Satisfy customers to generate business advantages
Various business scenarios can help to facilitate your reaching these goals Therefore, at the end of the detailed descriptions of the individual applications of mySAP CRM. we have included a useful overview that does the following: lists the important business scenarios of the affected sub applications, succinctly outlines their functionality, and breaks down existing potential benefits into turnover, profitability, and customer satisfaction .
Related Posts:
SAP R/3 Introduction to best ERP Mysap
Challenges in implementing ERP
ERP implementation practices