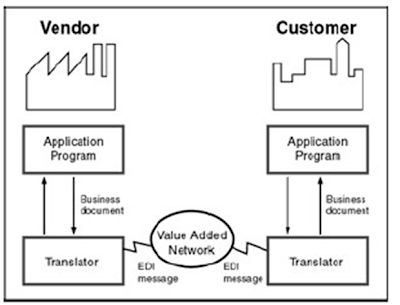
An EDI process is a transfer of one or a sequence of electronic messages.It involves senders, receivers, language, content, and a medium. In EDI, the senders and receivers are called trading partners, and the X12 or EDIFACT standards supply a common language for formatting the information content of common messages.
Software tools called translators enable trading partners to converse in a standard language, and application programs (such as SAP R/3), coupled with networking facilities such as the Internet or a commercial VAN (Value−Added Network), supply the messaging medium.
Trading Partners Parties involved in a business transaction are called trading partners. The trading partners can be any combination of organizations or business types. For example, customers and vendors are trading partners.
Business Documents A business document is a legal document that defines the transaction conducted between trading partners. The legal boundaries for these transactions are defined by trade agencies, trading partners, and the ISO (International Standards Organization). The trading partners are bound by the terms and conditions of these documents. Numerous business documents are in existence today. Examples of some typical business documents follow.
- Requests for quotes
- Purchase orders
- Purchase order changes
- Purchase order acknowledgments
- Invoices
 EDI Messages
EDI Messages - The formation of common standards has many advantages.
- Standardization allows representation that can be easily processed by a computer system.
- Standardization allows companies to exchange information that is independent from the application software.
- Third−party applications can provide EDI translation and thus relieve the application of having to keep up with evolving standards.(19.2)
Related Posts :
Business Processing using EDI
Introduction to EDI
EDI converter for SAP and EDI standards
SAP ABAP BAPI 1
SAP ABAP BAPI 2
No comments :
Post a Comment