ERP has some basic data called master data and here in this post we are also going to discuss about data warehouse concept and what are the organization levels.On master data other dependent data will be available and it is called master data.
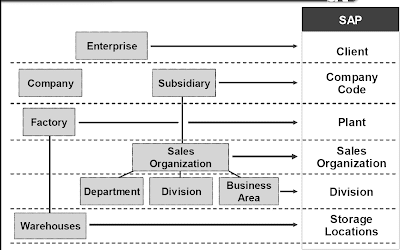
Organizational Parts : A company’s enterprise structure is mapped to SAP purposes using organizational elements. They are used to represent the enterprise construction by way of legal and enterprise-associated purposes. Organizational parts embrace authorized firm entities, crops, storage areas, gross sales workplaces, and profit centers. The simple examples are :
1.The highest-degree factor of all organizational components is the Client. The Consumer represents the enterprise orheadquarters group.
2. A Company Code is a unit included within the balance sheet of a legally-independent enterprise and is the central organizational aspect of Financial Accounting.
3. In the context of Sales and Distribution, the Sales Organization is the central organizational element that controls the terms of sale to the customer. Division is normally used to symbolize product line.
4. In the context of Production Planning, Plant is the central organizational unit. A Plant can manufacture product, distribute product, or provide a service.
5.In Inventory Administration, materials stocks could be differentiated inside one plant in response to Storage Location.
6.Organizational components may be assigned to a single software equivalent to Sales Organization assigned to Sales and Distribution, or to a number of purposes comparable to Plant assigned to Supplies Administration and Production Planning.
The highest-degree component of all organizational elements is the client. The shopper could be an enterprise group with several subsidiaries. All the enterprise knowledge in an SAP System implementation is break up into at least the consumer area, and often into decrease stage organizational constructions as well.
7.Versatile organizational elements in the SAP System allow extra complicated enterprise constructions to be represented. If there are rather a lot of organizational components, the authorized and organizational structure of an enterprise may be introduced in different views.
8.By linking the organizational elements, the separate enterprise areas will be integrated and the
construction of the entire enterprise represented in the SAP System. This links are outlined in Customizing.
9.When defining the organizational elements, bear in mind that they outline the construction for how data is to be entered, tracked, and extracted from the SAP system.
ERP Master Data: Knowledge which is used lengthy-time period within the SAP System for several business processes.Grasp information is created centrally and can be utilized by all functions and all approved users. Examples of master information in SAP embrace prospects, materials, and vendors.
1. A customer grasp comprises key data that defines the business relationship between a company and its customer. The master data is used to assist execution of key enterprise processes corresponding to customer requests, deliveries, invoices, and payments.
2. Master information additionally has an organizational side as the data is organized into views that are assigned to organizational elements.The customer master is organized into three views which are every situated at a unique organizational stage: Basic Data (Client), Monetary Accounting Information (Firm Code), and Sales Data (Sales Space).
3.Information on the shopper level can be utilized by all firm codes. The customer account number is assigned on this level. Meaning the same customer has an express accounts receivable number in all firm codes from a monetary view.
4.Transactions: Utility applications which execute business processes in the SAP System comparable to making a buyer order, posting an incoming cost, or approving a leave request.
5.Doc: A data document that is generated when a transaction is carried out.
6.When creating an order for a buyer, you need to take transport agreements, delivery and payment conditions, and so on, with business companions into consideration. To avoid re-entering this information every time for every activity associated to these business partners, relevant information for the activity from the master document of the enterprise companion is simply copied.
7.In the same method, the material grasp document stores info, such as the price per unit of amount, and inventory per storage location that is processed during order entry. This idea is legitimate for processing information for each master document included within the activity.
8. When performing each transaction, applicable organizational components should be assigned. Assignments to the enterprise construction within the doc are generated in addition to the information stored for the customer and material.
9.The doc generated by the transaction comprises all relevant pre-outlined data from the master knowledge and organizational elements.
10. A doc is generated for every transaction carried out within the SAP System.
DATA WAREHOUSE CONCEPT
1. While you are using the transactions within the Logistics purposes, the Logistics Information System (LIS) updates related information. You might also update information from other techniques in the LIS.
2.The LIS aggregates and shops this info within the knowledge warehouse. Data could be aggregated on a qualitative as well as on a quantitative foundation:
3. quantitative discount by aggregating on period level
4. qualitative reduction by selecting particular key figures
5.You'll have the opportunity to then use the tools in the Sales Information System (SIS) to investigate this aggregated information. The aggregation results in an improvement of the response occasions and of the quality of the ensuing reports.
SAP BW permits the evaluation of data from operative SAP functions as properly as all different business purposes and external data sources reminiscent of databases, online companies, and the Internet.
1.Administrator Workbench (AWB) functions allow you to control, monitor, and maintain all knowledge procurement processes.
2.SAP BW enables Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) for staging information from large quantities of operative and historical data. OLAP expertise permits multi-dimensional analyses in accordance with various business perspectives.
3.The BW server, which is preconfigured by Business Content material for core areas and processes, allows you to examine the relationships in every space within your company. Business Content material gives focused info to firms, divided into roles. This helps your workers to hold out their tasks. In addition to roles, Enterprise Content contains other preconfigured objects such as InfoCubes,queries, key figures, and characteristics. These objects facilitate the implementation of SAP BW.
4.The Business Explorer (BEx) part gives users with in depth analysis options.
5.BEx is the SAP BW part that provides versatile reporting and evaluation tools that you should utilize for strategic evaluation and supporting the choice-making process in your company. Workers with access authorization can analyze historic and present information at differing levels of element and from completely different perspectives.
6.BEx permits a wide spectrum of customers to access info in SAP BW. This could be done in Enterprise Portal from an iView that you can name alongside the functions where you extract the data, within the Internet or Intranet (Net Application Design), or utilizing a cell system. Internet Utility Design permits you to implement generic OLAP navigation in Web purposes and in Business Intelligence cockpits for both easy and extremely-individual scenarios. Highly individual scenarios with customerdefined user interface components could be realized using normal markup languages (HTML) for example. Net Utility Design encompasses a wide spectrum of interactive Internet-based Business Intelligence scenarios you could modify to fit your requirements using commonplace Net technology.
7. Portal Integration consists of
(1) single level of entry
(2) position-primarily based staging of knowledge,
(3) personalization,
(4) publication of iViews, and
(5) integration of unstructured data.
Query,Reporting, and Analysis include
(1) query design utilizing the BEx Analyzer,
(2) multi-dimensional (OLAP) evaluation,
(3) geographical analysis,
(4) advert-hoc reporting, and
(5) alerts.
Internet Utility Design contains
(1) interactive analytical content,
(2) data cockpits and dashboards,
(3) basis for creating analytical functions,
(4) creation of iViews for a portal, and
(5) wizard-help.
ERP basis and sap netweaver overview
MYSAP ERP advantages and main features
No comments :
Post a Comment