SAP Network Level Security gives enough protection for your network and data that is there in the world best ERP.Networks are the de facto backbones of computing. There is not any enterprise or collaborative software that may work without one. SAP programs based mostly on a client/server architecture aren't any exception. Starting with release 3.1G, SAP Foundation (R/3) systems now include the SNC interface, which may and, most often,ought to be complemented with third-party security products to additional protect community communications.When security fails at this degree, it is typically as a consequence of:
Consequently, you see users, like hackers, or applications attempting to go browsing to unauthorized systems, users logging on to the improper servers, unbalanced system hundreds, or even sniffing. One instance of security violations in the community atmosphere is when end users go browsing on to the database server when it has an administrative instance. Another one is when the rlogin service is utterly unprotected and customers have logged on by way of the community and stopped the fallacious servers.It's the network directors’ duty to design and implement a safety community topology that takes into consideration an computerized monitoring and intrusion detection system.
Transport System Level Security
SAP has provided the CTS as an environment for coordinated customizing and group growth that protects the modification of objects and settings throughout an SAP landscape. Sadly, CTS is a facet of the SAP enterprise that is often under secured.When safety fails at this stage, it is typically because:
Because of this, you see software failures, transport of copied packages without safety checks, or problems when upgrading your system.It's the process of the Foundation administrator, together with customers in charge of customizing and developers, to correctly set the system to primary security requirements and to define a safety policy that makes certain that there is some sort of filtering and monitoring throughout the CTS.
Secure Network Communications (SNC)
SAP’s standard SNC supplies safety for the communication links between the distributed elements of an R/3 system. SNC is built on the R/3 kernel primarily based on standard GSS API V2 and allows you to improve the level of your SAP security with external security merchandise: for instance, SSO, good card authentication,and encrypted communications. SNC can elevate your system to high security standards as a consequence of it may possibly cowl a number of layers, such because the presentation (authentication and SSO) layer, the distant communications layer, the community layer, and even the Web layer.
Distant Communications Level Security
The natural openness of the SAP methods and the limitless potentialities of speaking with and exchanging data between SAP and other programs requires stringent security evaluation from the viewpoint of exterior or remote communications primarily in the areas of the RFC and CPIC protocols, which are used in other interfacing strategies comparable to ALE (Software Link Enabled) or BAPIs. When safety fails at this degree, it is typically as a consequence of:
Consequently, you see surprising connections or program executions from different programs,software program failures, or entry to confidential information.It is the job of Foundation directors, together with network directors and builders, to implement normal security measures to keep away from leaving holes on the remote communication level.
Some commonplace measures embrace: don't create more RFC destinations than those mandatory, include AUTHORITY-CHECK within the programs that can be remotely known as, protect desk RFCDES, use customary interface strategies, periodically monitor the gateway server, be sure that the secinfo file exists, and others.
Document Transfer Level Safety
SAP security providers must assure the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of any sort of business documents corresponding to digital information, mail messages, and others. At this degree, SAP gives SSF mechanisms, which embody digital signatures and digital envelopes based mostly on public key technology. These mechanisms could be deployed using external security providers like digital certificates and digital envelopes.
When safety fails at this degree, it's usually because:
In consequence, you see paperwork intercepted by unauthorized persons or access to confidential information.It is the job of the Foundation administrators and knowledgeable security consultants with the help of the authorized division to define and implement secure mechanisms, like encryption strategies for protecting the safe transfer of documents.
Introduction to SSF
SAP’s commonplace SSF supplies the required help to protect R/three knowledge and paperwork as unbiased knowledge units. You need to use the SSF functions to “wrap” R/3 data in secure formats earlier than the info is transmitted over insecure communication inks. These safe formats are based on public and private keys using cryptographic algorithms.
Though SAP offers a Safety Library (SAPSECULIB) as a software program answer for digital signatures, in addition to commonplace support for SSF in sure software modules such as PDM or ArchiveLink, a high degree of safety is achieved solely when non-public keys are secured utilizing hardware units such as sensible cards.
Even supposing the communication infrastructure is perhaps well protected,additionally it is necessary to guard the non-public keys that are used in digital signatures and envelopes, because if this info is intercepted, the cryptographically strategy might be useless. This contains SAP components similar to the appliance servers when these act as the senders of the messages and therefore maintain the non-public keys.
In addition to the chance that exists in case the private key's identified to get into the fallacious fingers, it must even be considered that criminals will be focused on sabotaging the communications and could modify the public keys repository for the partners with whom the company programs communicates.
Defending Private Keys
There are two most important methods for storing and defending non-public keys:
Hardware The perfect answer for safeguarding SAP customers’ personal keys is the utilization of a person smart card for each user.With individual sensible playing cards, there is not any approach to reveal the non-public key that it holds. Additionally,the customers must identify in their sensible playing cards utilizing biometric means (such as a fingerprint, the attention print, and so forth ) or by means of a secret quantity similar to a PIN, a password, a query that only the user is conscious of, and so on. Users are accountable for securely preserving their playing cards and avoiding shedding them.
If this technique of defending private keys is selected, the businesses should develop a communication campaign so that users are informed of the importance of not sharing or letting others use their good cards. From the perspective of the server and as a means to improve performance, the advice is the use of a crypto box as a substitute of a sensible card.
Software The software resolution is not as protected as when particular hardware is used. If a file holding the keys is used, it is vitally important to guard this file from unauthorized accesses.
Defending Public Keys
If the safety products use an deal with book for holding the public keys, just as in the case of the personal keys, securely defending the information to avoid unauthorized entry or modifications is required. An alternate is to use certificates which can be issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA) to grant the authenticity of these certificates.
There are already several countries that have regulated the use of cryptography and digital signatures. Nevertheless, these rules or legal guidelines generated an enormous amount of controversy and even change frequently. Some countries already accept the digital signatures as a valid proof of obligation and due to this fact they can be used for secure business.
Web Level Security
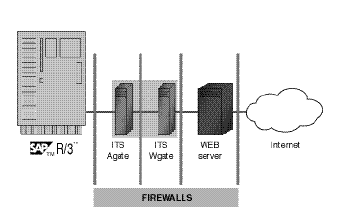
When safety fails at this stage, it is sometimes as a end result of:
Consequently, you see many varieties of attacks on Internet servers which may make methods unavailable or compromise essential information.It is the job of the Foundation administrator, network administrator, and Net administrator to set in place a system design for implementing the best security measures to guard towards attacks to the SAP techniques that are tightly related to the Internet.
A comprehensive security technique limits entry at each of these security layers to only approved customers or licensed exterior systems. It additionally accounts for the overall system panorama: growth methods, the quality assurance system, the productive system, and the CTS that operates between them, along with any connected complementary programs, whether or not they belong to the SAP Business Framework (or Web Enterprise Framework) structure or not. You want to be positive that certain protective procedures are set in place to protect in opposition to insecure packages or Trojan horses which will journey from one system to another.
Logging and Auditing
Finally, a safety infrastructure must include sturdy logging and auditing capabilities,the mechanisms you will want to monitor and enforce your safety policies.Logging and auditing deal with the efficiency of the safety measures and the capacities of the system for detecting weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and some other security problems. There are logging and auditing services in the SAP security infrastructure at each level. These amenities are applied primarily in the Security Audit Log, the AIS (Audit Data System), the safety alerts inside CCMS, and the Customers and Authorization Data System (SUIM). These tools are complemented by other logging services like those obtainable on the operating system level, database auditing statements, network and Web monitoring and management, and others.
The issue of monitoring the entire SAP safety infrastructure is that there is no single instrument for doing it automatically, although the evolution of the CCMS and the AIS tools make us think that it'd happen.Thus SAP Network Level Security gives enough safety for the data and people,companies that are connected through worlds best ERP.
Related posts
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
SAP security authentication and authorization
SAP security infrastructure for data productionSAP safety infrastructure
Outbound process with out message control with scenario
With out message control edi with example
EDI with message control scenario with purchase order and part two
- There are too many unprotected network services.
- Network topology is poorly designed.
- There's little or no community monitoring.
- Routers, filters, or firewalls aren't appropriately configured.
- SAP router configuration isn't properly set.
- There is no automatic intrusion detection system.
- Data is simply not traveling in encrypted form.
Consequently, you see users, like hackers, or applications attempting to go browsing to unauthorized systems, users logging on to the improper servers, unbalanced system hundreds, or even sniffing. One instance of security violations in the community atmosphere is when end users go browsing on to the database server when it has an administrative instance. Another one is when the rlogin service is utterly unprotected and customers have logged on by way of the community and stopped the fallacious servers.It's the network directors’ duty to design and implement a safety community topology that takes into consideration an computerized monitoring and intrusion detection system.
Transport System Level Security
SAP has provided the CTS as an environment for coordinated customizing and group growth that protects the modification of objects and settings throughout an SAP landscape. Sadly, CTS is a facet of the SAP enterprise that is often under secured.When safety fails at this stage, it is typically because:
- System landscape settings aren't correctly configured.
- Repairs are freely allowed.
- There are no filters that management which objects are being transported.
- Authorizations aren't utterly implemented.
- Transport monitoring is simply not a periodic task.
Because of this, you see software failures, transport of copied packages without safety checks, or problems when upgrading your system.It's the process of the Foundation administrator, together with customers in charge of customizing and developers, to correctly set the system to primary security requirements and to define a safety policy that makes certain that there is some sort of filtering and monitoring throughout the CTS.
Secure Network Communications (SNC)
SAP’s standard SNC supplies safety for the communication links between the distributed elements of an R/3 system. SNC is built on the R/3 kernel primarily based on standard GSS API V2 and allows you to improve the level of your SAP security with external security merchandise: for instance, SSO, good card authentication,and encrypted communications. SNC can elevate your system to high security standards as a consequence of it may possibly cowl a number of layers, such because the presentation (authentication and SSO) layer, the distant communications layer, the community layer, and even the Web layer.
Distant Communications Level Security
The natural openness of the SAP methods and the limitless potentialities of speaking with and exchanging data between SAP and other programs requires stringent security evaluation from the viewpoint of exterior or remote communications primarily in the areas of the RFC and CPIC protocols, which are used in other interfacing strategies comparable to ALE (Software Link Enabled) or BAPIs. When safety fails at this degree, it is typically as a consequence of:
- The authorization system is poorly implemented for distant communications.
- RFC communications embrace the passwords in their definitions.
- There's scarce monitoring at the gateways.
- OS and community security is also weak.
- No encryption software has been used.
Consequently, you see surprising connections or program executions from different programs,software program failures, or entry to confidential information.It is the job of Foundation directors, together with network directors and builders, to implement normal security measures to keep away from leaving holes on the remote communication level.
Some commonplace measures embrace: don't create more RFC destinations than those mandatory, include AUTHORITY-CHECK within the programs that can be remotely known as, protect desk RFCDES, use customary interface strategies, periodically monitor the gateway server, be sure that the secinfo file exists, and others.
Document Transfer Level Safety
SAP security providers must assure the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of any sort of business documents corresponding to digital information, mail messages, and others. At this degree, SAP gives SSF mechanisms, which embody digital signatures and digital envelopes based mostly on public key technology. These mechanisms could be deployed using external security providers like digital certificates and digital envelopes.
When safety fails at this degree, it's usually because:
- Certificates and encryption aren't used or implemented.
- Non-public keys usually are not properly protected.
- There is scarce tracing and monitoring.
In consequence, you see paperwork intercepted by unauthorized persons or access to confidential information.It is the job of the Foundation administrators and knowledgeable security consultants with the help of the authorized division to define and implement secure mechanisms, like encryption strategies for protecting the safe transfer of documents.
Introduction to SSF
SAP’s commonplace SSF supplies the required help to protect R/three knowledge and paperwork as unbiased knowledge units. You need to use the SSF functions to “wrap” R/3 data in secure formats earlier than the info is transmitted over insecure communication inks. These safe formats are based on public and private keys using cryptographic algorithms.
Though SAP offers a Safety Library (SAPSECULIB) as a software program answer for digital signatures, in addition to commonplace support for SSF in sure software modules such as PDM or ArchiveLink, a high degree of safety is achieved solely when non-public keys are secured utilizing hardware units such as sensible cards.
Even supposing the communication infrastructure is perhaps well protected,additionally it is necessary to guard the non-public keys that are used in digital signatures and envelopes, because if this info is intercepted, the cryptographically strategy might be useless. This contains SAP components similar to the appliance servers when these act as the senders of the messages and therefore maintain the non-public keys.
In addition to the chance that exists in case the private key's identified to get into the fallacious fingers, it must even be considered that criminals will be focused on sabotaging the communications and could modify the public keys repository for the partners with whom the company programs communicates.
Defending Private Keys
There are two most important methods for storing and defending non-public keys:
Hardware The perfect answer for safeguarding SAP customers’ personal keys is the utilization of a person smart card for each user.With individual sensible playing cards, there is not any approach to reveal the non-public key that it holds. Additionally,the customers must identify in their sensible playing cards utilizing biometric means (such as a fingerprint, the attention print, and so forth ) or by means of a secret quantity similar to a PIN, a password, a query that only the user is conscious of, and so on. Users are accountable for securely preserving their playing cards and avoiding shedding them.
If this technique of defending private keys is selected, the businesses should develop a communication campaign so that users are informed of the importance of not sharing or letting others use their good cards. From the perspective of the server and as a means to improve performance, the advice is the use of a crypto box as a substitute of a sensible card.
Software The software resolution is not as protected as when particular hardware is used. If a file holding the keys is used, it is vitally important to guard this file from unauthorized accesses.
Defending Public Keys
If the safety products use an deal with book for holding the public keys, just as in the case of the personal keys, securely defending the information to avoid unauthorized entry or modifications is required. An alternate is to use certificates which can be issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA) to grant the authenticity of these certificates.
There are already several countries that have regulated the use of cryptography and digital signatures. Nevertheless, these rules or legal guidelines generated an enormous amount of controversy and even change frequently. Some countries already accept the digital signatures as a valid proof of obligation and due to this fact they can be used for secure business.
Web Level Security

When safety fails at this stage, it is sometimes as a end result of:
- Safe protocols should not properly set.
- Encryption and certificates will not be used.
- Remote debugging of ITS will not be disabled.
- Service information are not protected.
- Firewalls and authentication might not be correctly configured.
- Security measures at Internet servers are weak.
- Monitoring is scarce.
Consequently, you see many varieties of attacks on Internet servers which may make methods unavailable or compromise essential information.It is the job of the Foundation administrator, network administrator, and Net administrator to set in place a system design for implementing the best security measures to guard towards attacks to the SAP techniques that are tightly related to the Internet.
A comprehensive security technique limits entry at each of these security layers to only approved customers or licensed exterior systems. It additionally accounts for the overall system panorama: growth methods, the quality assurance system, the productive system, and the CTS that operates between them, along with any connected complementary programs, whether or not they belong to the SAP Business Framework (or Web Enterprise Framework) structure or not. You want to be positive that certain protective procedures are set in place to protect in opposition to insecure packages or Trojan horses which will journey from one system to another.
Logging and Auditing
Finally, a safety infrastructure must include sturdy logging and auditing capabilities,the mechanisms you will want to monitor and enforce your safety policies.Logging and auditing deal with the efficiency of the safety measures and the capacities of the system for detecting weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and some other security problems. There are logging and auditing services in the SAP security infrastructure at each level. These amenities are applied primarily in the Security Audit Log, the AIS (Audit Data System), the safety alerts inside CCMS, and the Customers and Authorization Data System (SUIM). These tools are complemented by other logging services like those obtainable on the operating system level, database auditing statements, network and Web monitoring and management, and others.
The issue of monitoring the entire SAP safety infrastructure is that there is no single instrument for doing it automatically, although the evolution of the CCMS and the AIS tools make us think that it'd happen.Thus SAP Network Level Security gives enough safety for the data and people,companies that are connected through worlds best ERP.
Related posts
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
SAP security authentication and authorization
SAP security infrastructure for data productionSAP safety infrastructure
Outbound process with out message control with scenario
With out message control edi with example
EDI with message control scenario with purchase order and part two
No comments :
Post a Comment