SAP security infrastructure gives a good protection for the data that is existing and updated in the database. SAP programs safety typically is just seen as the implementation of the authorization/role concept. However, SAP options based mostly on open multi tiered client/server and Net-primarily based architecture embrace many parts that can alternate or are used for exchanging knowledge and information with other elements, applications, or systems. Each of the weather needed for the communication and change of information is a layer of the SAP safety infrastructure also identified as a safety service.Safety should be addressed in any respect of these layers. Here is an introduction to every of them, which will most likely be further covered in following sections.
Presentation level This level is represented by all types of front ends used for accessing mySAP systems. This is typically the SAPGUI for Home windows, though different options can be found, such because the SAPGUI for HTML, the short cuts, Session Managers, and other entrance ends that can be programmed with the SAP Automation and different utilities. At the presentation degree, the primary security service is the Person Authentication.
Application level This degree contains the appliance logic that is run by the ABAP programs. The position-based mostly and authorization concept is the foremost security service located at this level.
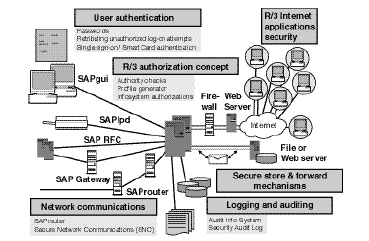
SAP databases These are the containers of all the business information, as properly as the metadata, data models, and object repository. They should be protected in opposition to unauthorized accesses, which can come from direct or remote accesses. It is extremely important to recognize and defend probably the most crucial system tables. This is the extent of information access protection.
Network The community is the defacto spine of computing, and there isn't a enterprise or collaborative utility that can work without it.mySAP techniques are a posh set of networked servers and purposes each inside and outdoors the companies. As such, the network is the enabler that have to be protected. Since SAP R/3 release 3.1G, the system contains the SNC interface that might be complemented with third-get together security merchandise to additional improve and protect the mySAP community communications. The community is situated at the entry safety level.
Distant communications The natural openness of the mySAP programs and the infinite prospects of communicating and exchanging information between them and other programs requires additionally a safety analysis from the standpoint of exterior or distant communications, mainly in the areas of the RFC and CPIC protocols which are utilized in other interfacing techniques, such because the BAPIs (business utility programming interfaces).
Internet The Web represents the biggest alternative and natural marketplace for e-business and, on the same time, the riskiest place if safety measures aren't in place. mySAP techniques are extensively based mostly on Internet know-how and are Internet enabled. Web safety is very intensive and would require a book on its own. In the case of mySAP systems, care should be particularly taken using firewalls, defending the ITS servers, and utilizing SNC and different cryptographic technologies.
Working system The mySAP answer naturally consists of a large assortment of software applications. Entry protection to SAP records data and directories and the operating system commands should even be correctly in place.Moreover, safety should additionally address the general system panorama: growth system, quality assurance system, productive system, and any linked complementary system, whether belonging to the SAP Enterprise Framework structure or not. Safety also implies the CTS.
All safety facets on mySAP methods elements are based on restricting the access to each of the system’s layers to approved customers or licensed exterior programs only. A safety infrastructure must additionally embody all of the logging and auditing possibilities because these mechanisms are required for monitoring and enforcing the safety policy.
Commonplace Safety on SAP Programs
The mySAP programs embrace many safety features, the majority of which aren't typically utilized in most customers’ installations. On one hand, it is straightforward to suppose that with a function to reach SAP techniques, you have to first leak into the network, the working system, or the database. Although generally that is true, additionally it is true that if inside threats are considered, normal security measures will definitely not be enough.
The SAP Basis Middle ware (R/3) consists of basic and generic security measures primarily based totally on passwords for person authentication, in addition to the authorization concept for person entry to enterprise information and transactions. However SAP Basis comes with other highly effective security features comparable to assist for SNC, SSF, and digital signatures, permitting using exterior security merchandise, SSO options, good playing cards, and plenty of different choices to go properly with the needs of essentially the most exigent companies and chief security officers.
Improving SAP Normal Safety
In the occasion you understand the safety elements and infrastructure, there is a lot you can do to improve the R/3 methods’ safety without compromising the conventional person’s operation. You can enhance security by:
These layers should inter operate to type a cohesive security strategy. That cannot happen except you understand what each layer is meant to do.
Security at Presentation Stage
Presentation degree security addresses all types of entrance ends used for accessing SAP systems. That is typically the SAPGUI, although other choices can be found, such because the SAPGUI for HTML, SAPGUI for Java, the short cuts, the mySAP.com Workplace, the Session Supervisor, and different front ends or log on applications that might be programmed with SAP Automation and different utilities. The primary safety service on the presentation stage is person authentication. When safety fails at this degree, it's typically because:
Because of this, you see unauthorized users logging in with privileged person accounts, many unsuccessful log on makes an attempt or users utilizing different people’s accounts. It's primarily the job of the Foundation administrators and user administrators, together with the IT division and the security manager, to define a clear authentication coverage, to set in place all the standard SAP security measures, and if wanted, to add any superior measures to protect the system at the presentation level.
Application Stage Safety
Security at this stage addresses the application logic that's run by the ABAP programs. Here the principle security service is the person authorization idea, which grants or denies entry to business objects and transactions primarily based upon a consumer’s authorization profiles.When safety fails at this degree, it's typically as a outcome of:
Because of this, you see unintentional transaction executions by unauthorized customers, efficiency problems, display or modification of confidential information by unauthorized customers, or even deletion of vital data.
Several occasions, it happened to me that a user who was not imagined to have such an authorization had unintentionally deleted or modified components of the quantity vary table (NRIV), and due to the legal implications of this, we needed to make some extent-in-time recovery of the entire system.
It's the application administrator’s job to define which users have access to what information and transactions. These definitions must later be technically implemented by the consumer and authorization administrators. It is also crucial that every developer follows a programming methodology that includes safety checks.
Security on the Database Level
The SAP methods’ databases are the containers for all the enterprise info and the metadata, data models, and object repository. They have to be protected towards unauthorized accesses. At this level, security providers should grant entry protection to R/three data.When security fails at this degree, it is usually as a consequence of:
Because of this, you see modifications on the database level that compromise system integrity and consistency, uncontrolled access to confidential information below the appliance stage, or system unavailability. In certainly one of my buyer installations, the operator began a table space reorganization instead of adding a new data file to a table space. The system was stopped for some hours. It is the job of the database administrators, together with the OS system managers and the Foundation directors, to take applicable security measures at this level. A variety of the measures are altering the passwords of privileged database users, protecting SAPDBA with expert mode, proscribing exterior distant access to learn only mode, auditing essential tables, setting the S_TABU_DIS authorization object accurately, and others.
Operating System Stage Security
Safety companies must assure entry safety to SAP information and directories, as well as the operating system instructions and programs. At this level, security providers are provided by the operating system features themselves. When safety fails at this level, it is usually as a consequence of:
Consequently, you see deletion of essential system and utility information, software program malfunctions, or experience unavailability.It's the job of the working system manager to implement security measures at the operating system and to monitor the principle log record sdata of the audit system. Some measures to incorporate: implementing a security password coverage on the person degree, not creating unnecessary users or providers, monitoring SETUID packages, setting ACLs (Entry Control Lists) in crucial records data and directories, and defending exterior instructions from being executed from SAP.
Related posts
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
MySAP environment security solutions
SAP security authentication and authorization
Marketing and erp mysap crm options
Organizational Challenges with crm and mysap crm solutions
Presentation level This level is represented by all types of front ends used for accessing mySAP systems. This is typically the SAPGUI for Home windows, though different options can be found, such because the SAPGUI for HTML, the short cuts, Session Managers, and other entrance ends that can be programmed with the SAP Automation and different utilities. At the presentation degree, the primary security service is the Person Authentication.
Application level This degree contains the appliance logic that is run by the ABAP programs. The position-based mostly and authorization concept is the foremost security service located at this level.

SAP databases These are the containers of all the business information, as properly as the metadata, data models, and object repository. They should be protected in opposition to unauthorized accesses, which can come from direct or remote accesses. It is extremely important to recognize and defend probably the most crucial system tables. This is the extent of information access protection.
Network The community is the defacto spine of computing, and there isn't a enterprise or collaborative utility that can work without it.mySAP techniques are a posh set of networked servers and purposes each inside and outdoors the companies. As such, the network is the enabler that have to be protected. Since SAP R/3 release 3.1G, the system contains the SNC interface that might be complemented with third-get together security merchandise to additional improve and protect the mySAP community communications. The community is situated at the entry safety level.
Distant communications The natural openness of the mySAP programs and the infinite prospects of communicating and exchanging information between them and other programs requires additionally a safety analysis from the standpoint of exterior or distant communications, mainly in the areas of the RFC and CPIC protocols which are utilized in other interfacing techniques, such because the BAPIs (business utility programming interfaces).
Internet The Web represents the biggest alternative and natural marketplace for e-business and, on the same time, the riskiest place if safety measures aren't in place. mySAP techniques are extensively based mostly on Internet know-how and are Internet enabled. Web safety is very intensive and would require a book on its own. In the case of mySAP systems, care should be particularly taken using firewalls, defending the ITS servers, and utilizing SNC and different cryptographic technologies.
Working system The mySAP answer naturally consists of a large assortment of software applications. Entry protection to SAP records data and directories and the operating system commands should even be correctly in place.Moreover, safety should additionally address the general system panorama: growth system, quality assurance system, productive system, and any linked complementary system, whether belonging to the SAP Enterprise Framework structure or not. Safety also implies the CTS.
All safety facets on mySAP methods elements are based on restricting the access to each of the system’s layers to approved customers or licensed exterior programs only. A safety infrastructure must additionally embody all of the logging and auditing possibilities because these mechanisms are required for monitoring and enforcing the safety policy.
Commonplace Safety on SAP Programs
The mySAP programs embrace many safety features, the majority of which aren't typically utilized in most customers’ installations. On one hand, it is straightforward to suppose that with a function to reach SAP techniques, you have to first leak into the network, the working system, or the database. Although generally that is true, additionally it is true that if inside threats are considered, normal security measures will definitely not be enough.
The SAP Basis Middle ware (R/3) consists of basic and generic security measures primarily based totally on passwords for person authentication, in addition to the authorization concept for person entry to enterprise information and transactions. However SAP Basis comes with other highly effective security features comparable to assist for SNC, SSF, and digital signatures, permitting using exterior security merchandise, SSO options, good playing cards, and plenty of different choices to go properly with the needs of essentially the most exigent companies and chief security officers.
Improving SAP Normal Safety
In the occasion you understand the safety elements and infrastructure, there is a lot you can do to improve the R/3 methods’ safety without compromising the conventional person’s operation. You can enhance security by:
- Designing and implementing a safe methods infrastructure by means of firewalls, settings, password insurance policies, and parameters
- Setting probably the most appropriate values for security-related instance profile parameters
- Using exterior safety products
- Establishing a safety policy and effectively communicating it
- Making a security guidelines that can be periodically tested both manually or routinely so you'll have the option to consider the efficiency of your safety coverage
- Enforcing the security policy by the use of logging and auditing ? Monitoring security alerts and finding threats
- Establishing a process for fixed update of the safety policies The Multilayer SAP Safety Infrastructure
These layers should inter operate to type a cohesive security strategy. That cannot happen except you understand what each layer is meant to do.
Security at Presentation Stage
Presentation degree security addresses all types of entrance ends used for accessing SAP systems. That is typically the SAPGUI, although other choices can be found, such because the SAPGUI for HTML, SAPGUI for Java, the short cuts, the mySAP.com Workplace, the Session Supervisor, and different front ends or log on applications that might be programmed with SAP Automation and different utilities. The primary safety service on the presentation stage is person authentication. When safety fails at this degree, it's typically because:
- The safety policy is weak, not effectively communicated or enforced, or not existing at all.
- The profile parameters that enforce primary safety measures aren't set.
- The passwords of standard users have not been changed.
- Primary protection measures on the workstation aren't taken.
- Superior safety methods resembling SNC, SSO, consumer certificates that allows encryption, or good log in devices have not been implemented.
- Safety auditing and monitoring is scarce.
Because of this, you see unauthorized users logging in with privileged person accounts, many unsuccessful log on makes an attempt or users utilizing different people’s accounts. It's primarily the job of the Foundation administrators and user administrators, together with the IT division and the security manager, to define a clear authentication coverage, to set in place all the standard SAP security measures, and if wanted, to add any superior measures to protect the system at the presentation level.
Application Stage Safety
Security at this stage addresses the application logic that's run by the ABAP programs. Here the principle security service is the person authorization idea, which grants or denies entry to business objects and transactions primarily based upon a consumer’s authorization profiles.When safety fails at this degree, it's typically as a outcome of:
- The authorization system has been poorly implemented.
- Crucial authorizations haven't been defined.
- Local development did not embrace appropriate authority checks.
- Administration of authorizations and profiles are not correctly distributed and protected.
- The person and authorization info system is never used.
Because of this, you see unintentional transaction executions by unauthorized customers, efficiency problems, display or modification of confidential information by unauthorized customers, or even deletion of vital data.
Several occasions, it happened to me that a user who was not imagined to have such an authorization had unintentionally deleted or modified components of the quantity vary table (NRIV), and due to the legal implications of this, we needed to make some extent-in-time recovery of the entire system.
It's the application administrator’s job to define which users have access to what information and transactions. These definitions must later be technically implemented by the consumer and authorization administrators. It is also crucial that every developer follows a programming methodology that includes safety checks.
Security on the Database Level
The SAP methods’ databases are the containers for all the enterprise info and the metadata, data models, and object repository. They have to be protected towards unauthorized accesses. At this level, security providers should grant entry protection to R/three data.When security fails at this degree, it is usually as a consequence of:
- Customary passwords have not been changed.
- Access to the operating system isn't properly protected.
- Distant entry to the database is not secure.
- Auditing has not been activated on vital tables.
- The authorization system at SAP stage is poorly implemented.
Because of this, you see modifications on the database level that compromise system integrity and consistency, uncontrolled access to confidential information below the appliance stage, or system unavailability. In certainly one of my buyer installations, the operator began a table space reorganization instead of adding a new data file to a table space. The system was stopped for some hours. It is the job of the database administrators, together with the OS system managers and the Foundation directors, to take applicable security measures at this level. A variety of the measures are altering the passwords of privileged database users, protecting SAPDBA with expert mode, proscribing exterior distant access to learn only mode, auditing essential tables, setting the S_TABU_DIS authorization object accurately, and others.
Operating System Stage Security
Safety companies must assure entry safety to SAP information and directories, as well as the operating system instructions and programs. At this level, security providers are provided by the operating system features themselves. When safety fails at this level, it is usually as a consequence of:
- Permissions on records data and directories will not be properly set.
- The password and consumer coverage at the OS stage is static and widely known.
- Logging and monitoring is scarce.
Consequently, you see deletion of essential system and utility information, software program malfunctions, or experience unavailability.It's the job of the working system manager to implement security measures at the operating system and to monitor the principle log record sdata of the audit system. Some measures to incorporate: implementing a security password coverage on the person degree, not creating unnecessary users or providers, monitoring SETUID packages, setting ACLs (Entry Control Lists) in crucial records data and directories, and defending exterior instructions from being executed from SAP.
Related posts
sap internet transaction architecture
SAP internet transaction application components
MySAP environment security solutions
SAP security authentication and authorization
Marketing and erp mysap crm options
Organizational Challenges with crm and mysap crm solutions
No comments :
Post a Comment