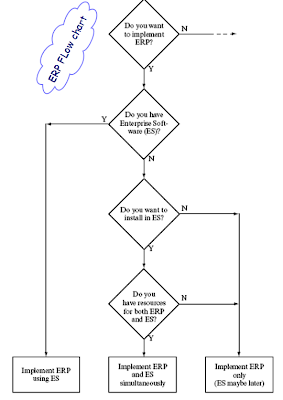
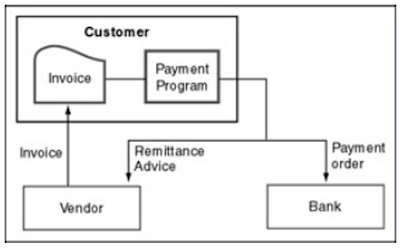
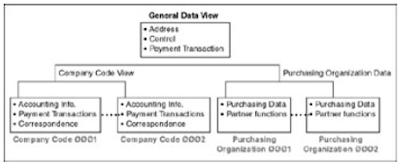
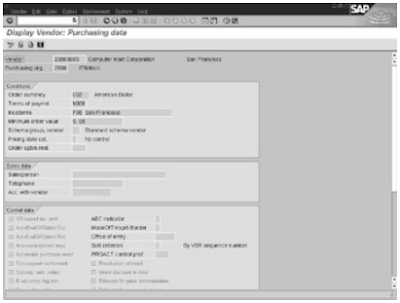
Before investing money and implementing enterprise resource planning the company shall analyze the benefits of erp .
Advantages of ERP:
1. Better sales and service is a serious gain.
2. It helps it shipping items on time to any where.
3. We can ship goods in less time.
4. Sales people can concentrate on sales rather than bothering about sales.
5. Customer service can be improved.
6. Productivity of labor increases by providing all the components at one palce .
7. Reduce purchase cost by providing the advance vision reports and procuring the data when
required over the market with best price.
8. Purchase cost will be reduced.
9. ERP reduces inventories.
10. The space available in the company will be used effectively.
11. Cash flow will be improved.
12.Productivity will be improved.
13. Employees job satisfaction will be better .
Cost and benefit analysis of Enterprise resource Planning:
Advantages of ERP:
1. Better sales and service is a serious gain.
2. It helps it shipping items on time to any where.
3. We can ship goods in less time.
4. Sales people can concentrate on sales rather than bothering about sales.
5. Customer service can be improved.
6. Productivity of labor increases by providing all the components at one palce .
7. Reduce purchase cost by providing the advance vision reports and procuring the data when
required over the market with best price.
8. Purchase cost will be reduced.
9. ERP reduces inventories.
10. The space available in the company will be used effectively.
11. Cash flow will be improved.
12.Productivity will be improved.
13. Employees job satisfaction will be better .
Cost and benefit analysis of Enterprise resource Planning:
This can be done either by top level people of the company or by the joint venture of middle level and high level people of the company.
The problem with high level committee is there won't be enough consensus among the total employees which is not desirable and joint group is advisable.
First higher level people of a module shall be educated regarding ERP and they shall do some home work and analysis regarding this implementation with number of meetings.
The cost and benefit shall be done in a conservative manner and shall not be over estimated the benefits so that people stay positive.
Having a good leader like general manager on the job through out the process of installation is a good idea and changing them will effect the process of erp implementation.
Who can be a ERP Project Leader ?
A person who is very much involved in the business shall be appointed as a project leader of erp and shall be made free from all other business jobs.
An outsider shall not be chosen like a project leader as he is not in touch with business process and people around him.To get the benifit of enterprise resource palnning the leader shall be well femilier with the business flow of the company.
The project leader of erp shall have operational knowledge of the business.Selecting a system person as head may give the disadvantage of not knowing what is the business process is exatly and the operational people won't have a good rappout which altimately effect the success of ERP project.
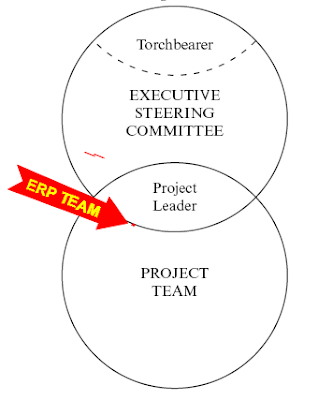
Project leader shall be the best person of the company who understand the business best.
If the operations head of a department is there in the company for more than five years with good skills he may suite to the job.
He shall have a good track record,good in managing the people and has excellent communication skills.
He shall the one who trusts and respects the peers.
Duty of ERP project leader :
Over seeing the education of erp to the entire team of company.
Follow up of the project schedule and seeing that they are as per plan.
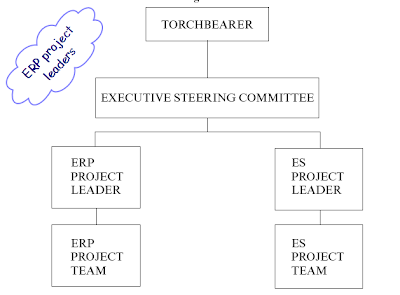
The general way that project leader work and report as shown in the figure ERP TEAM.
Any way depanding on the company each one may have different structure and for a very big business with different wings it can have project leaders both for erp wing and software implementation wing and both of them can represenet and report further to company head about the progress of the project.
Project leaders can create a speific team of experts to study a specific issue which need a deep study of understanding and they will report back to team in a specified time.This is to make sure that all functioning of erp project is good.
During the process of implementing erp the form need a professional guidenace who are all ready there in their past during the process of implementing and running business with erp and femilier with the problems that are forth coming.
These expert guide the general manager,project leader,project team about the problems and guide them about the measures to be taken. The expert will ask all critical questions about the business and its erp implementation and the top management and project team shall look after all thease matters of concern before implementing the logic of erp. The outside expert act like a adviser for the erp project and his job is very critical in the success of implementing erp .
ERP makes the operational performance of business much better and hence it leads to big financial benefits to the company and self satisfaction and carrier growth to the employees.It is like win and win situation.
So the major initial steps in erp project are
1. Making a vision statement for project implementation.
2.What is the money going to spend on this process and what are the advantages ?
3.How to organize erp project?
4.Having a set of goals for specific time and how they are performed ?
These things shall be taken care by the high level people of the company together and analyze through out the implementation process.
Related Posts
ERP implementation process and advantages
SAP CRM customer as business center
Refinance and mortgage money
The problem with high level committee is there won't be enough consensus among the total employees which is not desirable and joint group is advisable.
First higher level people of a module shall be educated regarding ERP and they shall do some home work and analysis regarding this implementation with number of meetings.
The cost and benefit shall be done in a conservative manner and shall not be over estimated the benefits so that people stay positive.
Having a good leader like general manager on the job through out the process of installation is a good idea and changing them will effect the process of erp implementation.
Who can be a ERP Project Leader ?
A person who is very much involved in the business shall be appointed as a project leader of erp and shall be made free from all other business jobs.
An outsider shall not be chosen like a project leader as he is not in touch with business process and people around him.To get the benifit of enterprise resource palnning the leader shall be well femilier with the business flow of the company.
The project leader of erp shall have operational knowledge of the business.Selecting a system person as head may give the disadvantage of not knowing what is the business process is exatly and the operational people won't have a good rappout which altimately effect the success of ERP project.

Project leader shall be the best person of the company who understand the business best.
If the operations head of a department is there in the company for more than five years with good skills he may suite to the job.
He shall have a good track record,good in managing the people and has excellent communication skills.
He shall the one who trusts and respects the peers.
Duty of ERP project leader :
Over seeing the education of erp to the entire team of company.
Follow up of the project schedule and seeing that they are as per plan.
The general way that project leader work and report as shown in the figure ERP TEAM.
Any way depanding on the company each one may have different structure and for a very big business with different wings it can have project leaders both for erp wing and software implementation wing and both of them can represenet and report further to company head about the progress of the project.
Project leaders can create a speific team of experts to study a specific issue which need a deep study of understanding and they will report back to team in a specified time.This is to make sure that all functioning of erp project is good.

During the process of implementing erp the form need a professional guidenace who are all ready there in their past during the process of implementing and running business with erp and femilier with the problems that are forth coming.
These expert guide the general manager,project leader,project team about the problems and guide them about the measures to be taken. The expert will ask all critical questions about the business and its erp implementation and the top management and project team shall look after all thease matters of concern before implementing the logic of erp. The outside expert act like a adviser for the erp project and his job is very critical in the success of implementing erp .
ERP makes the operational performance of business much better and hence it leads to big financial benefits to the company and self satisfaction and carrier growth to the employees.It is like win and win situation.
So the major initial steps in erp project are
1. Making a vision statement for project implementation.
2.What is the money going to spend on this process and what are the advantages ?
3.How to organize erp project?
4.Having a set of goals for specific time and how they are performed ?
These things shall be taken care by the high level people of the company together and analyze through out the implementation process.
Related Posts
ERP implementation process and advantages
SAP CRM customer as business center
Refinance and mortgage money