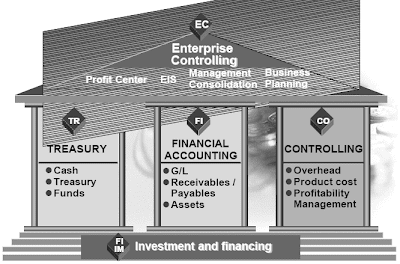
The general term “Accounting” can be used to explain numerous different capabilities and enterprise processes. The R/3 system provides an architecture of specialized accounting components to deal with these diversified functions.The Treasury component (TR) focuses on capabilities corresponding to money administration, treasury administration (including money market funds, international exchange, derivatives and securities), loans, and market danger management.The Monetary Accounting part (FI) focuses on General Ledger accounting (G/L), Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable processing, and Fixed Asset accounting.
The Funding Administration component (IM) supplies functions to help the planning,investment, and financing processes for capital investment measures.The Enterprise Controlling part (EC) consists of Profit Middle Accounting, the Govt Information System (EIS), Enterprise Planning (for group-extensive business plans at a excessive level), and EC Consolidation.The Controlling part (CO) offers a variety of instruments that can be utilized to provide operational information to the administration of an organization to help business evaluation and choice-making.
The R/3 System software part Controlling (CO) accommodates all accounting features necessary
for efficient controlling. If a corporation divides accounting into internal and exterior viewpoints, CO represents the inner accounting perspective, as a outcome of it provides data for managers those that are inside a company and are charged with directing and controlling its operations.CO includes value and revenue accounting. Along with the Enterprise Controlling (EC) software parts Profit Heart Accounting (EC-PCA) and Government Info System (EC-EIS), CO covers all facets of managerial accounting. It gives a broad selection of functional tools that could be used to provide managerial accounting data without being restricted to authorized requirements. Financial statements required for external reporting functions (e.g. steadiness sheet and P&L assertion) are created in FI. These external reporting requirements are sometimes established by general accounting requirements like GAAP or IAS, as properly as varied authorized requirements mandated by regulatory authorities.
 Reporting Requirements
Reporting Requirements
Whereas there are often completely different accounting data necessities for inner and exterior customers,a lot of the underlying data could additionally be relevant for each purposes. However that very same knowledge may be introduced in very different ways to fulfill the completely different requirements.Standardized accounting meant for exterior customers is typically termed “financial accounting”.The time period “management accounting” usually refers to the non-standardized accounting strategy that helps the management resolution-making process. Monetary accounting stories sometimes required embody the revenue assertion (or profit & loss statement), and stability sheet. Administration accounting reports may be fully uniq ue, though a
frequent instance could be departmental precise vs. plan costs for the current accounting period.
Components of Financials
External and inner accounting are separate accounting systems which can be interrelated but give consideration to totally different methods and dimensions of research to help various varieties of decision making.External accounting is known as monetary accounting. It produces the monetary statement view of the organization.Inside accounting is known as managerial accounting or controlling. It focuses on inside efficiency of the organization.
The Monetary Accounting element meets the worldwide demands of a firm's monetary accounting requirements utilizing an open, integrated data movement and simplifies monetary resolution making.l All postings between different functions in the R/3 system are made actual-time. For instance, for those who submit to the "Accounts payable" sub ledger, the system automatically makes an updating entry to the common ledger.The R/three Monetary Accounting part is split into the following areas:
- FI-GL General Ledger Accounting. The central job of G/L accounting is to provide a complete image of exterior accounting and of the accounts concerned therein.
- FI-AP Accounts Payable. A/P administers the accounting knowledge for all vendors. It is usually an integral part of the buying system.
- FI-AR Accounts Receivable. A/R administers the accounting information of customers. It is usually an integral a half of sales management.
FI-AA Asset Accounting This module encompasses your complete lifetime of assets from the preliminary acquisition as a lot as the retirement. The system calculates the values for depreciation,curiosity and different values. FI-SL Special Function Ledger offers abstract data from multiple functions at a stage of detail that is consumer defined.Funds Administration Helps monetary checking and management using budgeting techniques.Travel Administration The Travel Administration module affords a full range of procedures for processing enterprise trip information, from getting into and approving a journey request, to posting the precise trip costs. Integration with Controlling (CO) and Payroll Accounting (HR Payroll) ensures correct and efficient posting, taxation and cost of journey costs.
Treasury
The aim of the Treasury system is to make sure efficient liquidity, portfolio and threat administration for companies,from a business viewpoint.It helps processing and accounting for financial investments and borrowings.The link with external information programs (corresponding to current financial market information via an online information feed ) enables you to recognize dynamic changes in monetary markets and react to them.TR is divided into three sub-areas:
- TR-CM Money Management allows for daily money standing management and short and medium term forecasts of cash position.
- TR- Money funds management or Dedication Accounting - is a budgeting software permitting the structured administration of money budgets.
- TR-TM Treasury Management -gives management of international trade, derivatives, and different forms of securities and hedging.
Ledgers
The general ledger accommodates a file of all relevant accounting transactions from a business point of view within the G/L accounts. So as to retain a clear overview, the general ledger often comprises collective postings. In such circumstances, the knowledge posted is displayed in additional element within the subsidiary ledgers, which give their info to the general ledger in summarized type:
- Accounts Payable data all accounting transactions for dealings with suppliers. A lot of its knowledge is obtained from procurement (Supplies Management).
- Accounts Receivable data all accounting transactions for dealings with customers. Much of its information is obtained from Gross sales and Distribution. . Asset Accounting records all accounting transactions regarding the administration of assets.
- Journey Administration manages and calculates travel costs and supports journey planning and journey expenses
- Bank ledger supports the posting of cash flows.
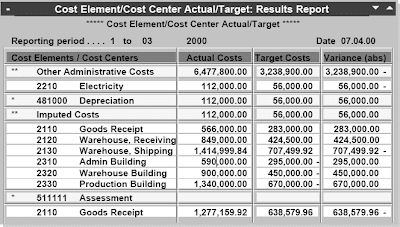
All G/L account postings that submit to business expense accounts routinely send the bills as costs to Controlling. The balances of G/L accounts are used to calculate monetary statements.
Components of Controlling
The assorted CO components can be labeled into different groups. The classification signifies the normal objective of a given component. Administration of an enterprise requires the utilization of completely different tools for different situations. If you need to research revenue, for instance, then you want a device acceptable to the view you want to take (e.g.: by product or by accountability middle). The Profitability Management component group has two tools (parts) which are out there for addressing this enterprise want (Profitability Analysis and Profit center Accounting).Equally, the Overhead Price Controlling and Product Cost Controlling component groups provide tools acceptable to different sorts of business requirements.
How can we cut back our overhead costs? Overhead Price Controlling (CO-OM) is the CO component that gives instruments to help answer that question. In lots of organizations, overhead costs have taken an enormous upward jump, together with prices which the group cannot assign directly to either merchandise or services. While manufacturing areas usually display nice progress in controlling prices and optimizing processes, overhead continues to show little cost transparency, so it's difficult to get a transparent image of why these costs are incurred.What prices happen within our organization? Value Element Accounting (CO-OMCEL) classifies the prices and revenues which are posted to CO, and provides the aptitude for reconciliation of costs in CO with the Financial Accounting (FI) module.What are the manufacturing costs of a product? Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC) has two main areas of focus. It is used to develop estimates of what it will value to supply a product (or even a service). It also has capabilities to track the precise prices of production, and provides in depth tools for value analysis.How profitable are individual market segments? Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) supplies a spotlight on the results of an organization’s doing business with the external marketplace. It supplies the ability to define which facets or segments of that market are related for analyzing working results, akin to revenue by buyer, product, geographic space, sales group, etc. And it offers multidimensional drill-down reporting, to provide extremely flexible views of working results.
How worthwhile are particular person enterprise areas? Profit Middle Accounting (EC-PCA) supplies a focus on internal areas of a company which have responsibility for reaching sure revenue or productiveness goals.Price and Income Component Accounting (CO-OM-CEL) is part of the Overhead Cost Controlling component group. It provides the structure for task of CO information via the classification of transaction line objects in response to the nature of the price or income being posted to a given controlling object (e.g. cost center, inner order, etc.).The price flows in CO can le ad to the necessity for reconciliation between inside and exterior accounting in sure cases. Price and Income Aspect Accounting is the CO part providing performance that helps this doable requirement. The Reconciliation Ledger provides reporting capabilities for figuring out the variations in prices between FI and CO, as effectively as a tool for creating reconciliation postings to FI, if desired.
Overhead Maintenance
Overhead Price Controlling has three components. Every addresses certain facets of analyzing and controlling overhead costs. Overhead prices are defined as prices that cannot be assigned directly to price objects (e.g. manufacturing orders, etc.).The percentage of overhead in complete prices has risen sharply in recent years. The number of employees employed in overhead areas grew from 25-30% within the 1950's to more than 50% today. Overhead has grown in both manufacturing and service organizations. Analysis in the United States revealed that overhead makes up approximately eighty% of the prices in the machine and electronics manufacturing industries. As overhead grows, the proportion of instantly assignable production costs shrink. Consequently, it is becoming increasingly vital to investigate and management overhead costs.Similarly, more and more subtle instruments are wanted to facilitate the applying of overhead to manufacturing orders and other price objects.
Cost Center Accounting
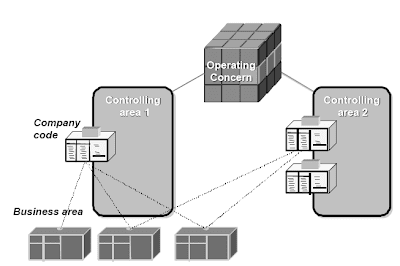
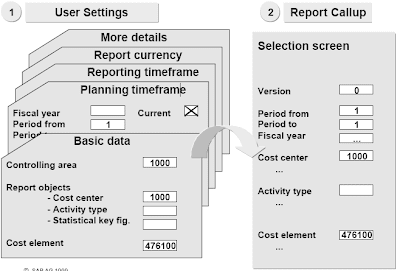
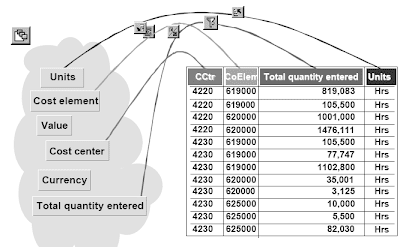
The Value Center Accounting element (CO-OM-CCA) tracks where prices happen in your organization. The cost heart is an organizational unit in a controlling area. Value centers might be defined in accordance with several completely different design approaches. A typical approach could be for an enterprise to outline a value middle for every low-stage organizational unit that has accountability for managing costs. As prices are incurred, they're assigned or posted to the suitable price center.These prices might embrace payroll costs, rent and utility costs, or every other prices assignable to a given value center.Each value center is assigned to a class, e.g. Administration value heart, manufacturing price center, etc. Every cost heart grasp report has a subject for the title of the individual answerable for the price center.The posting and task of prices to price centers not solely makes managerial accounting potential;however is a vital step for using the opposite Controlling components. As noted above, cost facilities could be set up based on completely different design approaches, including functional necessities, allocation criteria, actions or companies offered, geographic location and/or space of responsibility. However whichever approach is selected, it needs to be constant throughout the enterprise.Price facilities could be grouped together to supply abstract value information. Actually, a elementary requirement for implementing Price Center Accounting is the creation of a normal hierarchy for a controlling area. The usual hierarchy consists of all value facilities in that controlling area, and supplies the flexibility to research summary prices at every node of the structure.
Internal Orders
An Inner Order is an especially flexible CO device that can be used for a extensive variety of functions to track prices and, in some instances revenues, within a controlling area. Inner orders provide capabilities for planning, monitoring, and allocation of costs.Internal orders may be used for a wide range of functions, and could be grouped into four normal classes:
- Overhead orders: Used to watch overhead costs incurred for a specific objective, corresponding to conducting a trade fair, or monitoring prices for maintenance and restore work.
- Investment orders: Used to monitor costs incurred in the creation of a exhausting and fast asset, equivalent to building a storage facility.
- Accrual orders: Used to offset postings of accrued prices (costs calculated in CO) to price centers.
- Orders with revenue: Used to interchange the price accounting elements of SD customer orders if SD just isn't being used, so that each costs and revenues may be tracked; or to observe revenues not affecting the organization's core enterprise (equivalent to miscellaneous revenues).
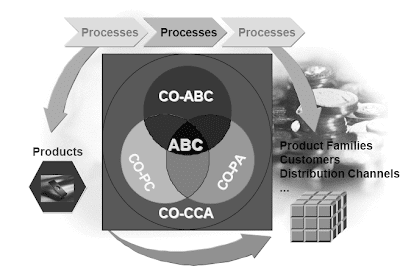
Activity Based Costing
Traditionally, overhead prices are allocated from price centers to price objects by manner of numerous strategies, reminiscent of surcharges and exercise allocations.By contrast, Activity-Primarily based Costing assigns prices to business processes, without regard for which organizational models could additionally be concerned in generating these costs. A course of is a cross-purposeful object, which can pull sources from any value heart in a controlling area.ABC has been applied in R/3 as an enhancement to the fee administration functionality. All overhead costs are still assigned to price centers. The fee facilities that make the most of resources in carrying out a process allocate the value of those sources to the process. (Instance: a Purchasing price middle would allocate prices it incurred in preparing and distributing a Request for Quotations to a Procurement business process.) The processes are then consumed by cost objects (comparable to manufacturing orders) and the related prices are allocated to those value objects. Process costs not associated to value objects are handed along to CO-PA with the intention to present a extra correct and complete accounting of overhead costs.Value Heart Accounting answers the question of the place costs occur, whereas Exercise-Based Costing solutions the question of why (for what goal) prices occur.
 Product Cost Controlling
Product Cost Controlling
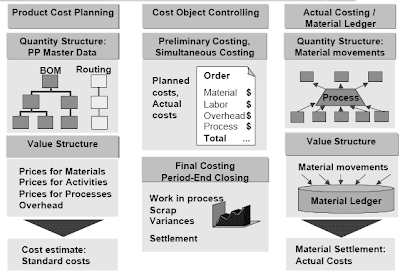
Product Cost Controlling is concerned with all features of planning the price of producing merchandise or services, in addition to monitoring and analyzing the precise prices that are incurred in the manufacturing process. Product Price Controlling consists of the following elements:
Product Price Planning is used for preliminary costing and can reply the next questions:
- What shall be the value of producing a certain services or products?
- Is external procurement inexpensive than in-house production?
- What are the prices of manufacturing, if we assume a actually perfect scenario? This estimate might then be used as a baseline towards which we are in a position to evaluate different “real world” manufacturing scenarios.
Price Object Controlling focuses on monitoring the precise direct costs of production and the interval end closing process.Precise manufacturing costs are accumulated as raw materials are issued and labor is performed. This info permits detailed comparisons between the deliberate cost and the actual cost of any given manufacturing phase.Interval end closing procedures embrace the application of overhead costs, calculation and posting of the value of products still in manufacturing (work in course of), calculation of variances between customary and actual costs, and settlement of variances to the CO-PA, EC-PCA and FI modules.Actual Costing / Material Ledger is used to calculate precise prices for each materials at the end of the period. Supplies and their actions are valued with a standard worth during the period. Any variances from this customary are collected in the materials ledger when invoices are acquired or orders settled. During interval finish closing these variances are used to calculate an actual value for the material within the closed period. Postings might be made in FI to replicate this price.
Product Cost Planning refers again to the creation of value estimates for the manufacturing of products or services. If a quantity construction (Bill of Materials and routing) is available within the PP (Production Planning) module of the R/3 system, you presumably can create a price estimate automatically utilizing the PP data.If no quantity structure is available in R/3, the price gadgets could be entered manually by the use of unit costing, or could be transferred routinely from a non-SAP system utilizing batch input.In Value Object Controlling, the prices incurred in the production of a services or products are collected on a price object (akin to a manufacturing order). Various varieties of price objects can be utilized, depending in your controlling requirements. These include production orders, sales orders, course of orders or product cost collectors. Price Object Controlling additionally gives tools for calculating Work In Process, scrap costs, and variances at interval finish close.Actual Costing is used to calculate actual product costs at period finish close. The end result may be transferred to the fabric master as a weighted common value for the closed period. The values connected with material movements are collected within the Materials Ledger. Both single-level settlement and multi-degree settlement functions can be found to calculate the actual materials prices at interval end close.
 Product Cost Planning
Product Cost Planning
There are numerous generally requested questions that Product Cost Planning may help answer. These would possibly embrace:
- How excessive are the value of goods manufactured and the value of goods sold?
- Is it currently attainable to supply at this market price in any respect? What is our value floor?
- Is it cheaper to produce giant or small tons?
- What does my cost structure seem like? How a lot of the full price is materials and how a lot is labor?
- What are the consequences of improvements within the manufacturing process?
- Which organizational unit most influences the product prices?
- Which plant has the lowest production costs?
- What is the influence of machine depreciation and energy costs on my product (primary costs)?
- A normal cost estimate can be used to valuate the fabric stock.
A Invoice Of Materials (BOM) is an entire, formally structured listing of the elements that make up a product or assembly. The record accommodates the material number of every element, together with the amount and unit of measure. The elements are often recognized as BOM items. A BOM can include materials which have their very own BOMs.The work center is the physical location at which an operation is carried out. When the master file for a piece middle is created in PP, it is linked to a cost heart, and also the varied exercise varieties produced by the cost center. This hyperlink allows access to the exercise type unit prices, that are used in valuing labor (or machine time) equipped by the associated fee facilities in a manufacturing process.The Routing lists the specific steps required to fabricate a product. These “steps” are referred to as operations. The routing specifies the next for each operation:
- the work center which carries out the operation
- the default values used for calculating dates, capacities and production costs
- whether or not the costs of an operation are taken into account for costing
- the fabric elements needed to carry out an operation
Cost Object Controlling
Value Object Controlling consists of three principal steps: preliminary costing of the fee object, simultaneous costing, and interval-finish closing.Preliminary costing refers again to the calculation of deliberate prices for a cost object, corresponding to a production order. Planning variances will be decided by comparing the outcomes of preliminary order costing with the standard price estimate for the quantity of fabric to be produced with the order.In Cost Object Controlling, as portions of uncooked materials are issued to be used in a production scenario, either from inventory or from external buy, their value is accumulated on the appropriate price object (corresponding to a production order). Equally, as an exercise type is performed in the manufacturing state of affairs (corresponding to hours of direct labor), the price of that exercise is also accrued on the price object. This process is termed simultaneous costing. It refers to the posting of value to a price object by the identical transaction that paperwork the material problem or activity completion. (The transaction that's used to document the completion of items of an exercise is called a confirmation.) The simultaneous costing idea may generally be known as valuation of amount flows to a cost object.Interval-end closing refers to a series of duties carried out on the end of every accounting period. This includes calculating relevant overhead costs, calculation of labor in course of (WIP), calculation of variances, and settlement (which passes information to Monetary Accounting, Revenue Middle Accounting, and Profitability Analysis).Varied normal reports are offered to research the costs posted to price objects.
Product Cost Control by Order
Order-associated production is lot-based production to stock. Value Object Controlling in order-associated manufacturing gives information about a production order whose prices are settled to stock. Price Object Controlling in order-related manufacturing can be used with or without the Manufacturing Planning module.For each production order, you probably can
- Calculate deliberate and actual prices
- Go on precise costs to other objects in the R/three System
- Analyze deliberate and precise costs
The functions for order-related manufacturing assist you to do the following:
- Find out which costs were incurred for manufacturing orders that haven't yet been settled, and cross on the work in course of for every order to Monetary Accounting and Revenue Center Accounting on the end of every period.
- Discover out which production variances occurred for each order and pass these values on to FI, Profitability Evaluation, and Revenue Center Accounting as costs for the period.
- Find out which prices have been incurred for scrap and go these values on to FI, Profitability Analysis, and Revenue Center Accounting as prices for the period.
- Complete the prices for all production orders with particular selection standards and display the results in a summarized form.
Product Cost Control by Period
Repetitive manufacturing refers to manufacturing planning and management utilizing run schedule headers that deliver the semifinished and finished products to stock.The planned necessities for repetitive manufacturing are usually generated automatically by material requirements planning (MRP), though they can be created manually. Production planning and management makes use of the planned orders for capacity planning and scheduling.In contrast to order-associated manufacturing, the deliberate orders are usually not converted into run schedule headers utilizing the lot size. As a substitute, the planned requirements are defined on run schedule headers.Run schedule headers are not based on lots, however exist over a time frame defined by the user.Below some circumstances this era might be the complete life cycle of the product.
Product Cost Control by Sales Order
The Product Value by Gross sales Order part is recommended for make-to-order environments. You ought to utilize the Product Cost by Gross sales Order component within the following situations:
- When you're manufacturing in-home just about a sales order.
- If you find yourself purchasing merchandise just about a sales order and reselling them to your customers.
- If you finish up providing services whose prices are assigned to a gross sales order.
This element means that you simply can do the next:
- Calculate and analyze deliberate costs and precise costs by sales order merchandise
- Calculate and analyze planned revenues and actual revenues by sales order item
- Calculate the value of your inventories of finished and unfinished products
- Create reserves mechanically
- Switch information to Monetary Accounting (FI)
- Switch data to Profitability Analysis (CO-PA)
- Switch data to Revenue Heart Accounting (EC-PCA)
Related Posts
MySAP CRM and customer as business partner
How
Customer Relationship management makes company Leader
CRM Uses and how to get best results with CRM
CRM software solutions and mysap advantage