In SAP Financial Master Data Depreciation Areas you may post each the asset steadiness sheet values and the depreciation values from the individual depreciation areas to separate steadiness sheet accounts or earnings assertion accounts within the common ledger.Usually you must post more than one depreciation space in parallel to the general ledger if you're creating completely different monetary assertion versions. You can outline any variety of financial statement variations per chart of accounts in FI (Common Ledger) for this purpose. For every stability sheet account and earnings assertion account, you specify in the monetary statement model the steadiness sheet merchandise or earnings statement item through which the account values ought to appear. You outline the monetary assertion version in FI Customizing.
Defining Poster to General Ledger
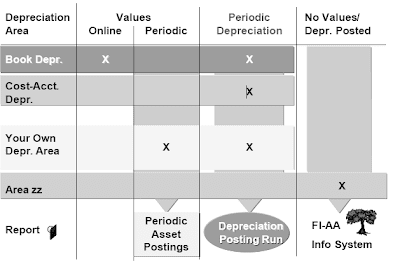
Specify how and if the values from particular person depreciation areas are to be posted to the final ledger. You would possibly have the following options:
Functions of Asset Classes
Asset lessons are an important technique of structuring fastened belongings in keeping with the necessities of your enterprise. The definitions of the asset class apply to all company codes in a client.An asset class consists of two primary sections:
An important operate of the asset class is to establish the connection between the asset grasp records and the accounts which are posted for them in the basic ledger. You employ account determination to establish this connection. (It is sometimes also referred to as account allocation.).The account dedication key may be equivalent to the account variety of the asset steadiness sheet account within the basic ledger (for a small asset class catalog). In case you have several comparable asset classes, you have to use completely different account determination keys for them, although their values are all up to date to a single asset steadiness sheet account. A number of asset courses can use the identical account willpower key if they use the same chart of accounts and put up to the identical G/L accounts.Should you use completely different charts of accounts, nonetheless, you need just one account willpower key to put up asset values of all asset lessons to different accounts in the completely different charts of accounts.
 Outline Acquisition/Retirement Accounts: In this step you enter the necessary G/L accounts for acquisition, retirement, steadiness sheet revaluation, and price amounts that are not capitalized (price component and account for nonoperationg expense or capitalization differences).Outline Depreciation Accounts: For these depreciation areas that publish depreciation to the overall ledger, you probably can assign the following G/L accounts:
Outline Acquisition/Retirement Accounts: In this step you enter the necessary G/L accounts for acquisition, retirement, steadiness sheet revaluation, and price amounts that are not capitalized (price component and account for nonoperationg expense or capitalization differences).Outline Depreciation Accounts: For these depreciation areas that publish depreciation to the overall ledger, you probably can assign the following G/L accounts:
The quantity vary controls the project of the variety of the asset master record. You outline number task as either inner or external. When inside number project is used,the system mechanically assigns the next out there quantity in the numerical sequence in the outlined quantity range interval. When exterior quantity project is used, the number is assigned explicitly
by the user or by one other system.You may assign each company code its personal quantity ranges, or firm codes can share number ranges.
Screen Layout
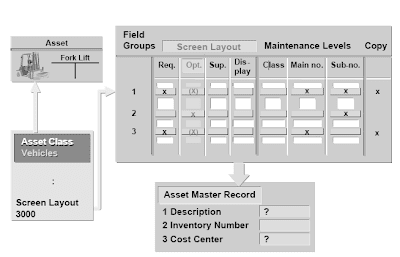
The screen layout specifies which input fields are displayed in the asset grasp document, and if they are required entry fields or non-obligatory entry fields.This lets you scale back the variety of grasp information fields to those that are particularly wanted for the given asset class, and to ensure that certain important management information is entered.In addition to the knowledge on the fields (required entry, optional entry, show, suppress), the display layout specifies the upkeep stage of master data fields. It also determines if they're allowed to be used as a reference (for copying).The maintenance level specifies the master data stage at which each area could be maintained. The potential maintenance levels are:
Screen Layout for Valuation Data
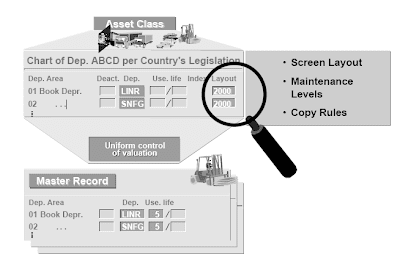
In every asset class, you enter a screen layout rule for each depreciation area. This rule applies to the valuation fields in the depreciation area.SAP supplies screen layout rules 1000 and 2000 in the usual system.These display screen format guidelines additionally include a maintenance level. The upkeep stage ensures that depreciation is managed uniformly. There are three options:
Asset class :This upkeep level ensures uniform control of valuation at the degree of the asset class. The entries made within the asset class are passed on to the asset grasp file, and you can't overwrite them.
Asset foremost number:The control of valuation is uniform at the stage of the asset grasp record. The entries made within the asset class are adopted within the asset master file, but can then be changed there. All asset sub numbers that belong to this asset master document undertake these values from the primary number, and can no longer change them.
Asset sub-quantity : There may be more freedom within the management of valuation. Asset sub-numbers can have their own completely different depreciation terms.
Implementation Guide
There is a simplified model of the Implementation Information available for FI-AA. It comprises all the steps you need for a quick minimal configuration of the Asset Accounting component. After you complete all of the actions on this simplified Implementation Guide, Asset Accounting is ready for production startup.You can use this operate to configure FI-AA in a small company that makes use of the usual asset accounting functions with a small asset class catalog.When you want any of the following features, you have to use the extra complete SAP Reference IMG for Asset Accounting:
General Asset Classes
Use this function to generate a small catalog of asset courses. Producing asset courses from G/L accounts contains the important steps for assigning the obligatory G/L accounts (account willpower). It also predefines constructions for asset grasp data (display screen format) and activates two depreciation areas with depreciation terms.These parameters are generated in a one-to-one relationship to your asset steadiness sheet accounts.Earlier than you can begin the era of asset classes, you first must process all these steps. You can perform each of these steps independently.You'll give you the chance to acquire a list of the created objects with an overview of the activities that had been performed.The record contains only these asset courses that have been created with the asset class generation function.
Protection of Existing Objects
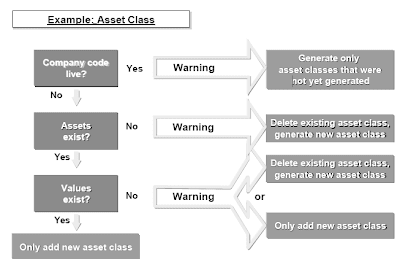
Producing asset courses from G/L accounts is dependent on the status of the company code.Company code is in production status (stay): The system creates only asset courses that weren't but created. Existing asset courses remain unchanged.Company code is in take a look at status:
Asset Classes and Additional Functions
Copy asset courses from reference:You may copy new asset courses from the asset courses that had been generated from G/L accounts. This has the advantage you can define the default values more precisely (notably for depreciation phrases) than when generating the asset classes. For instance, you ought to utilize one asset class for all property that post to the same G/L account and use the identical depreciation method.
Asset and Construction
Property under building (AuC) require a separate asset class with their very own account determination,since they must be proven separately within the stability sheet.Select depreciation key '0000' in order to make certain that depreciation is simply not calculated for belongings underneath building in depreciation areas for the steadiness sheet. Nevertheless, special tax depreciation and funding assist are attainable even on property underneath construction.It is also attainable to put up down payments on belongings under construction.Even after an asset under development has been fully capitalized, you possibly can still post credit memos to it. However, it's a should to permit unfavorable APC.To manage more extensive asset investments the part IM (Investment Administration) integrates internal orders and tasks with the AuC. You can thereby monitor the details of capital investments inside the R/3 CO module.
Low Value Assets
You may choose whether or not to handle low value assets (LVAs) utilizing particular person administration or collective management.For each sort of administration, it's a should to set up a separate asset class.In the occasion you select collective management of LVAs, it's a must to enter a base unit of quantity within the asset class.You additionally need to set up a examine of the utmost quantity in the depreciation areas of the asset class for LVAs.If you happen to copied asset courses, it's best to verify this setting in each depreciation area.You enter the utmost allowed amount for each company code in Customizing for Asset Accounting. Choose Valuation; Amount Specifications.
Creating Master Record
Whenever you create an asset grasp record, you've two choices:
Creating Multiple Records
When creating asset grasp records, you may create multiple comparable assets.This operate is helpful, for instance, if you will buy 20 PCs directly to your coaching department, or 12 desks for a new suite of offices.You'll be able to nonetheless make separate entries for each particular person asset within the following fields:
Time Dependent Data
Some info within the asset grasp record can be managed as time-dependent data. This is of specific significance for price accounting assignments (for instance, cost center, order). Shift operation and asset shutdown can have a direct effect on depreciation. Therefore you should enter them in the time-dependent data, where they can be modified on a monthly basis. Depreciation posting ought to take place on a monthly basis. In consequence, the currently valid price heart is always used for the depreciation posting run.
Depreciation Data
The default values come from the asset class.You could change or add to them within the different depreciation areas of the asset grasp record.A few of the information in depreciation areas is derived from the acquisition posting.Depreciation phrases equivalent to index, variable depreciation portion or scrap worth are extra parameters that are mainly used in the related fee-accounting depreciation area.
Changing Assets
Every time you change an asset grasp file, the system creates a change document. It contains a listing of fields that were changed and the number of adjustments to a field. As properly as, the identify of the consumer and the outdated and new contents of fields are stored.When a giant number of belongings are affected by a change, you can make a mass change. Utilizing this process, you presumably can carry out freely-definable master data modifications, mostly routinely, (for instance the change of value center project).
 Asset Sub Number
Asset Sub Number
You might also specify external or inner number assignment for the asset sub-number. You make this specification in the asset class. For instance, you could possibly use external number project during the legacy knowledge transfer after which switch over to internal quantity task after the legacy data switch is complete.If a fixed asset is made up of many part assets, it could be useful to handle these component assets as separate sub-numbers. This could be helpful for both technical and accounting reasons. Some reasons for utilizing sub-numbers in this approach embody:
selection from an inventory show of sub-numbers. You too can report individually on collected depreciation and e-book values for earlier fiscal years for particular person asset sub-numbers. Utilizing the screen layout in the asset class, you possibly can specify maintenance degree at the sub-quantity level.This allows you to change the default values for depreciation phrases on the sub-number.
Related Posts
SAP SCRIPT CONTROLS PART 5
SAP SCRIPT CONTROLS PART 6
Defining Poster to General Ledger
Specify how and if the values from particular person depreciation areas are to be posted to the final ledger. You would possibly have the following options:
- Don't publish any values for the area.
- Post APC values on-line, however depreciation periodically.
- Submit APC values and depreciation periodically.
- Submit solely depreciation, periodically.

Functions of Asset Classes
Asset lessons are an important technique of structuring fastened belongings in keeping with the necessities of your enterprise. The definitions of the asset class apply to all company codes in a client.An asset class consists of two primary sections:
- Master knowledge section with control data and default values for the general grasp information within the asset grasp record
- Depreciation area information section with management knowledge and default values for depreciation terms for every depreciation area
An important operate of the asset class is to establish the connection between the asset grasp records and the accounts which are posted for them in the basic ledger. You employ account determination to establish this connection. (It is sometimes also referred to as account allocation.).The account dedication key may be equivalent to the account variety of the asset steadiness sheet account within the basic ledger (for a small asset class catalog). In case you have several comparable asset classes, you have to use completely different account determination keys for them, although their values are all up to date to a single asset steadiness sheet account. A number of asset courses can use the identical account willpower key if they use the same chart of accounts and put up to the identical G/L accounts.Should you use completely different charts of accounts, nonetheless, you need just one account willpower key to put up asset values of all asset lessons to different accounts in the completely different charts of accounts.
 Outline Acquisition/Retirement Accounts: In this step you enter the necessary G/L accounts for acquisition, retirement, steadiness sheet revaluation, and price amounts that are not capitalized (price component and account for nonoperationg expense or capitalization differences).Outline Depreciation Accounts: For these depreciation areas that publish depreciation to the overall ledger, you probably can assign the following G/L accounts:
Outline Acquisition/Retirement Accounts: In this step you enter the necessary G/L accounts for acquisition, retirement, steadiness sheet revaluation, and price amounts that are not capitalized (price component and account for nonoperationg expense or capitalization differences).Outline Depreciation Accounts: For these depreciation areas that publish depreciation to the overall ledger, you probably can assign the following G/L accounts:The quantity vary controls the project of the variety of the asset master record. You outline number task as either inner or external. When inside number project is used,the system mechanically assigns the next out there quantity in the numerical sequence in the outlined quantity range interval. When exterior quantity project is used, the number is assigned explicitly
by the user or by one other system.You may assign each company code its personal quantity ranges, or firm codes can share number ranges.
Screen Layout
The screen layout specifies which input fields are displayed in the asset grasp document, and if they are required entry fields or non-obligatory entry fields.This lets you scale back the variety of grasp information fields to those that are particularly wanted for the given asset class, and to ensure that certain important management information is entered.In addition to the knowledge on the fields (required entry, optional entry, show, suppress), the display layout specifies the upkeep stage of master data fields. It also determines if they're allowed to be used as a reference (for copying).The maintenance level specifies the master data stage at which each area could be maintained. The potential maintenance levels are:
- Asset class
- Essential asset quantity
- Asset sub-number
Screen Layout for Valuation Data
In every asset class, you enter a screen layout rule for each depreciation area. This rule applies to the valuation fields in the depreciation area.SAP supplies screen layout rules 1000 and 2000 in the usual system.These display screen format guidelines additionally include a maintenance level. The upkeep stage ensures that depreciation is managed uniformly. There are three options:
Asset class :This upkeep level ensures uniform control of valuation at the degree of the asset class. The entries made within the asset class are passed on to the asset grasp file, and you can't overwrite them.
Asset foremost number:The control of valuation is uniform at the stage of the asset grasp record. The entries made within the asset class are adopted within the asset master file, but can then be changed there. All asset sub numbers that belong to this asset master document undertake these values from the primary number, and can no longer change them.
Asset sub-quantity : There may be more freedom within the management of valuation. Asset sub-numbers can have their own completely different depreciation terms.

Implementation Guide
There is a simplified model of the Implementation Information available for FI-AA. It comprises all the steps you need for a quick minimal configuration of the Asset Accounting component. After you complete all of the actions on this simplified Implementation Guide, Asset Accounting is ready for production startup.You can use this operate to configure FI-AA in a small company that makes use of the usual asset accounting functions with a small asset class catalog.When you want any of the following features, you have to use the extra complete SAP Reference IMG for Asset Accounting:
- Depreciation areas in foreign currency
- Necessities for consolidation of a company group
- Definition of your personal depreciation keys, transaction sorts, reviews
- Group property
General Asset Classes
Use this function to generate a small catalog of asset courses. Producing asset courses from G/L accounts contains the important steps for assigning the obligatory G/L accounts (account willpower). It also predefines constructions for asset grasp data (display screen format) and activates two depreciation areas with depreciation terms.These parameters are generated in a one-to-one relationship to your asset steadiness sheet accounts.Earlier than you can begin the era of asset classes, you first must process all these steps. You can perform each of these steps independently.You'll give you the chance to acquire a list of the created objects with an overview of the activities that had been performed.The record contains only these asset courses that have been created with the asset class generation function.
Protection of Existing Objects
Producing asset courses from G/L accounts is dependent on the status of the company code.Company code is in production status (stay): The system creates only asset courses that weren't but created. Existing asset courses remain unchanged.Company code is in take a look at status:
- If there are not any asset grasp records in an existing asset class: This asset class is deleted and generated again.
- If there are property in an current asset class, but as but no values:Both all asset lessons are deleted and generated once more, or only new asset classes are added.
- If transactions exist for the assets: You possibly can solely add new asset classes.

Asset Classes and Additional Functions
Copy asset courses from reference:You may copy new asset courses from the asset courses that had been generated from G/L accounts. This has the advantage you can define the default values more precisely (notably for depreciation phrases) than when generating the asset classes. For instance, you ought to utilize one asset class for all property that post to the same G/L account and use the identical depreciation method.
- Specify required entry fields for asset master knowledge:On this step, you'll give you the chance to enter further particulars for the display format of asset grasp records. You may specify, for instance, which fields are required entry fields.
- Define allowed entries for person fields:Analysis groups: These are asset master knowledge fields for which the consumer can specify their use and meaning.
- Environmental protection indicator: Here you may enter a measure taken to comply with environmental protection laws.
- Cause for investment: On this subject you can enter an explanation for a capital investment.You can use these fields as choice criteria in reporting (select Dynamic picks within the report choice display screen, or within the definition of type versions).
- Enter/change default values in asset courses: Right here you'll be able to enter default values for depreciation phrases, web value tax, insurance coverage, leasing, and consumer fields.
Asset and Construction
Property under building (AuC) require a separate asset class with their very own account determination,since they must be proven separately within the stability sheet.Select depreciation key '0000' in order to make certain that depreciation is simply not calculated for belongings underneath building in depreciation areas for the steadiness sheet. Nevertheless, special tax depreciation and funding assist are attainable even on property underneath construction.It is also attainable to put up down payments on belongings under construction.Even after an asset under development has been fully capitalized, you possibly can still post credit memos to it. However, it's a should to permit unfavorable APC.To manage more extensive asset investments the part IM (Investment Administration) integrates internal orders and tasks with the AuC. You can thereby monitor the details of capital investments inside the R/3 CO module.
Low Value Assets
You may choose whether or not to handle low value assets (LVAs) utilizing particular person administration or collective management.For each sort of administration, it's a should to set up a separate asset class.In the occasion you select collective management of LVAs, it's a must to enter a base unit of quantity within the asset class.You additionally need to set up a examine of the utmost quantity in the depreciation areas of the asset class for LVAs.If you happen to copied asset courses, it's best to verify this setting in each depreciation area.You enter the utmost allowed amount for each company code in Customizing for Asset Accounting. Choose Valuation; Amount Specifications.
Creating Master Record
Whenever you create an asset grasp record, you've two choices:
- You enter the corporate code and asset class for the model new asset grasp record. The asset class offers an important default values to the asset master record.
- You employ an present asset grasp file as a reference. (The reference asset may supply better default values than an asset class alone.) Make certain that you don't copy undesirable data from the reference asset (for instance, the capitalization date).
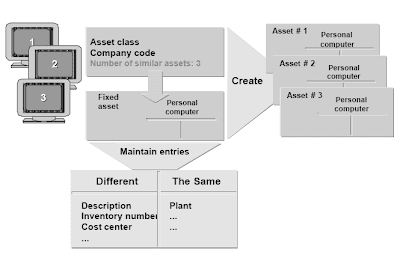
Creating Multiple Records
When creating asset grasp records, you may create multiple comparable assets.This operate is helpful, for instance, if you will buy 20 PCs directly to your coaching department, or 12 desks for a new suite of offices.You'll be able to nonetheless make separate entries for each particular person asset within the following fields:
- Inventory quantity
- Business area
- Price center
- Analysis teams 1 to five

Time Dependent Data
Some info within the asset grasp record can be managed as time-dependent data. This is of specific significance for price accounting assignments (for instance, cost center, order). Shift operation and asset shutdown can have a direct effect on depreciation. Therefore you should enter them in the time-dependent data, where they can be modified on a monthly basis. Depreciation posting ought to take place on a monthly basis. In consequence, the currently valid price heart is always used for the depreciation posting run.
Depreciation Data
The default values come from the asset class.You could change or add to them within the different depreciation areas of the asset grasp record.A few of the information in depreciation areas is derived from the acquisition posting.Depreciation phrases equivalent to index, variable depreciation portion or scrap worth are extra parameters that are mainly used in the related fee-accounting depreciation area.
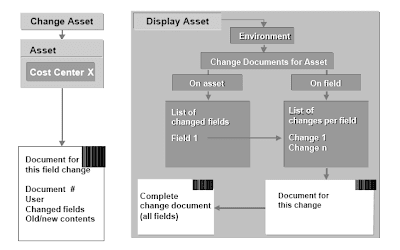
Changing Assets
Every time you change an asset grasp file, the system creates a change document. It contains a listing of fields that were changed and the number of adjustments to a field. As properly as, the identify of the consumer and the outdated and new contents of fields are stored.When a giant number of belongings are affected by a change, you can make a mass change. Utilizing this process, you presumably can carry out freely-definable master data modifications, mostly routinely, (for instance the change of value center project).
 Asset Sub Number
Asset Sub NumberYou might also specify external or inner number assignment for the asset sub-number. You make this specification in the asset class. For instance, you could possibly use external number project during the legacy knowledge transfer after which switch over to internal quantity task after the legacy data switch is complete.If a fixed asset is made up of many part assets, it could be useful to handle these component assets as separate sub-numbers. This could be helpful for both technical and accounting reasons. Some reasons for utilizing sub-numbers in this approach embody:
- You wish to handle the values for subsequent acquisitions individually (for instance, for buildings).
- You want to handle the values for particular person elements of property separately.
- You want to cut up up the asset based on varied technical aspects.
selection from an inventory show of sub-numbers. You too can report individually on collected depreciation and e-book values for earlier fiscal years for particular person asset sub-numbers. Utilizing the screen layout in the asset class, you possibly can specify maintenance degree at the sub-quantity level.This allows you to change the default values for depreciation phrases on the sub-number.
Related Posts
SAP SCRIPT CONTROLS PART 5
SAP SCRIPT CONTROLS PART 6
No comments :
Post a Comment