SAP Financial and General Ledger Accounts has the chart of accounts is a variant which contains the construction and the fundamental details about normal ledger accounts.You outline the chart of accounts with a 4 character identifier. You outline the components of the chart of account, e.g. language, length of the G/L account number, group chart of accounts, status.The chart of accounts has to be assigned to each firm code which wish to create accounts based on the defined structure.The maintenance language is the language through which account descriptions are maintained.A group account quantity might be entered right into a G/L-account. This group account quantity is used for reporting throughout company codes which use completely different charts of accounts. If a group chart of accounts is entered into the chart of accounts, the system makes this area a required entry within the G/L master account and verifies that the group account number entered exists in the group chart of accounts.A chart of accounts which is not yet completed can be blocked so that no company code can use it until ready.The length of the G/L account quantity may be from 1 to 10 digits.
Chart of Accounts Segment
The chart of accounts comprises primary details about the accounts. Information per account is bundled into what known as the chart of account-segment.It incorporates the:
Company Code Segments
To use one of the accounts from the assigned chart of accounts in your company code, a “company code-phase” needs to be created. This “company code-section” is added to the chart of account segment,and together they type the account.Data within the company code section is restricted for this company code. This info controls entry of accounting documents and management of accounting data.
Fields in Company Code Segments
The Firm Code section for a similar G/L account could be different relying on the needs of the corporate code. For instance, one company code could gather tax when utilizing expense accounts and would flag the tax category subject, whereas one other firm code could not.You outline the information that is pertinent to each firm code:
Balance Sheets and P and L Accounts
In the chart of accounts-phase, it's obligatory to indicate whether or not the account will most likely be a stability sheet or a profit+loss assertion account.These two forms of accounts are treated otherwise within the closing procedure.For stability sheet accounts, the stability is carried forward to the same account.For P+L assertion accounts, the stability is carried forward to a retained earnings account and the P+L assertion account is about to zero. The account to which the steadiness is carried ahead is assigned to a key (e.g. x) and this key is entered within the subject ”P+L statement account kind” within the chart of accounts-segment.In customizing, users define the retained earnings account and during G/L master report creation, it is assigned to expense accounts. If there is just one retained earnings account, R/three will routinely use the one outlined in customizing. If there are multiple retained earnings account, during grasp report creation, the user could have the choice to resolve on the retained earnings account per P+L account.
Since a chart of accounts incorporates many various sorts of accounts, they are often bundled into completely different “account groups ”. Normally one account group bundles accounts with the identical duties inside the final ledger, e. g. money accounts, material accounts, asset accounts, revenue and loss accounts.By assigning a quantity vary to an account group, you'll give you the chance to be certain that accounts of the identical sort are throughout the identical quantity range. Number intervals for G/L account grasp records can overlap.The account group needs to be entered in the chart of accounts-segment and controls the looks of the corporate code section of a G/L account. For instance, for all of your money accounts, you wish to have the ability to view the entire detailed line items. In customizing, for your “Cash Accounts” account group, you'll alter the sector status to make “line merchandise show” a required entry.
R/3 delivers predefined account groups.The sector status makes it doable to influence the looks of an account's grasp data.Fields which are not used will be suppressed.Fields which have an entry that shouldn't be changed might be set to display only (even in change mode)
Master Data Field Status
The fields displayed on the general ledger grasp document aren't only controlled by the account group, but in addition by the master knowledge transaction that you are using (transaction dependent control) i.e. create, change, display. As quickly as the master record is created and you don't want delicate fields modified, on the master document change transaction in customizing, you specify that a certain area is not changeable. For example, you need the forex of your money account to be GBP and you don't want it to be changed, customise the grasp file change transaction to have the field be display only.For every field, the sector standing definitions from the account group and the transaction are taken into consideration and the one with larger priority is used. The priorities are (starting with the highest):
Reconciliation Accounts
Reconciliation accounts are common ledger accounts assigned to the business partner master information to report all transactions within the sub-ledger.Any postings to the sub-ledger accounts robotically updates the balances of the assigned reconciliation accounts. In this approach, the general ledger is all the time up-to-date.You define a G/L-account as a reconciliation account by coming into the form of reconciliation account that it's into the sphere ”Recon.account for acct kind”.
D for customers
K for vendors
The reconciliation account is then only valid for the desired account type.Typical reconciliation accounts are the accounts “Commerce Receivables” and ”Trade Payables”.It isn't possible to publish to reconciliation accounts directly.
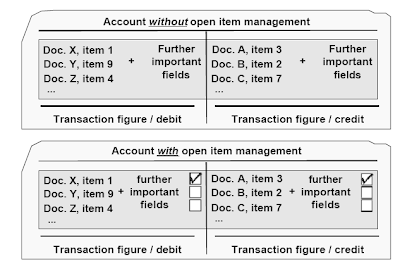
Line Item Display
Transaction figures are the sums of line items on the debit or credit score side. The balance is the
distinction between the debit and the credit score transaction figure.The sphere “line item display” is a control area within the company code section of an account.For accounts with out “line merchandise display” only the transaction figures are up to date when a document is posted to this account. When a user desires to have a look at this account on-line, they'll solely find a way to view the balance.For accounts with “line merchandise display” a very powerful knowledge from the posted line gadgets is stored in a particular index table. Because this knowledge can be saved within the paperwork, it's redundant and desires further storage and system time. When a consumer wants to have a look at this account on-line, they will be able to view both the balance and the individual line item details.Because of system sources that are wanted by the road merchandise show, it shouldn't be used for accounts the place the line merchandise information might be extra simply accessed in another method,
e.g.
Gadgets in accounts with open merchandise administration are specified as open or cleared.Accounts with open merchandise management will need to have line item show activated.Normal ledger accounts ought to be administered with open merchandise management when you must verify whether there is an offsetting posting for a given enterprise transaction. Open and cleared objects may be displayed individually, and due to this fact it's straightforward to see which business transactions nonetheless need to be cleared.It's finest to use open merchandise management for:
Only Balance in Local Currency
If the field “Solely balances in native forex” is marked within the master information report, solely transaction figures for amounts transferred to native forex are managed.This indicator ought to be set for clearing accounts from which you want to give you the option to clear objects simply by zero-balancing the amounts in local currency. Then no difference postings brought on by change fee differences have to be made.The indicator needs to be set in money discount and GR/IR clearing accounts.It should not be set in reconciliation accounts for patrons or vendors.The indicator is usually set in balance sheet accounts which are not saved in foreign forex echange and never managed on an open merchandise basis.
Methods in Creating G L Accounts
With the two step method, the chart of accounts segment is created separately from the corporate code segment. This permits for creating the GL account only in the chart of accounts or in a quantity of firm codes.Use the one step technique to create a GL account in a specified firm code. Repeat step 2 of the two step method, create in the company code segment, to create the GL account in additional company codes as needed.
Creating GL accounts by copying :
Collective Processing
The SAP R/3 System gives collective processing capabilities for the G/L account master.You can change the grasp knowledge within the chart of accounts area, company code specific information or the names of a number of G/L accounts at the same time. The G/L accounts may be from different charts of accounts.You can make modifications to the displayed G/L accounts:
Group of Chart Accounts
For internal purposes, reporting over several company codes could additionally be desirable, e.g a balance sheet shall be generated which incorporates the financial positions of several firm codes.That is no problem as lengthy as all firm codes use the identical chart of accounts. However, some company codes may have to use particular charts of accounts due to legal requirements. If this is the case for inside reporting, then:
Country Chart of Accounts
A substitute for using a gaggle chart of accounts is to use a rustic charts of accounts. While every company code makes use of the same operational chart of accounts, the company codes which require a different chart of accounts for external reporting can have a country chart of accounts assigned and have the country chart of account number (alternative quantity) entered in each company code segment. Every nation account number can solely be used once.Since all firm codes post into the identical operational chart of accounts, cross-company code controlling is possible. Accounting clerks who could also be familiar with the country charts of accounts may have to get used to using the operational chart of accounts.
Bank Master Data
Every bank which is used in the system (e.g. as a home bank or as a customer/vendor financial institution) must have a bank grasp record.Financial institution grasp information are stored centrally in the bank directory. Each report is recognized by the financial institution country and the financial institution key. Financial institution master records include bank deal with information and control data resembling the SWIFT Code, postal giro data, and financial institution group (for fee optimization).Financial institution grasp data might be created four ways:
Related Posts
Chart of Accounts Segment
The chart of accounts comprises primary details about the accounts. Information per account is bundled into what known as the chart of account-segment.It incorporates the:
- Account quantity
- Title of the account (as short and as long text)
- Control fields (mentioned on the following slides)
- Consolidation fields
Company Code Segments
To use one of the accounts from the assigned chart of accounts in your company code, a “company code-phase” needs to be created. This “company code-section” is added to the chart of account segment,and together they type the account.Data within the company code section is restricted for this company code. This info controls entry of accounting documents and management of accounting data.
Fields in Company Code Segments
The Firm Code section for a similar G/L account could be different relying on the needs of the corporate code. For instance, one company code could gather tax when utilizing expense accounts and would flag the tax category subject, whereas one other firm code could not.You outline the information that is pertinent to each firm code:
- Forex
- Tax
- Reconciliation account
- Line merchandise display
- Sort key
- Field standing group
- House bank
- Interest calculation data
Balance Sheets and P and L Accounts
In the chart of accounts-phase, it's obligatory to indicate whether or not the account will most likely be a stability sheet or a profit+loss assertion account.These two forms of accounts are treated otherwise within the closing procedure.For stability sheet accounts, the stability is carried forward to the same account.For P+L assertion accounts, the stability is carried forward to a retained earnings account and the P+L assertion account is about to zero. The account to which the steadiness is carried ahead is assigned to a key (e.g. x) and this key is entered within the subject ”P+L statement account kind” within the chart of accounts-segment.In customizing, users define the retained earnings account and during G/L master report creation, it is assigned to expense accounts. If there is just one retained earnings account, R/three will routinely use the one outlined in customizing. If there are multiple retained earnings account, during grasp report creation, the user could have the choice to resolve on the retained earnings account per P+L account.
Since a chart of accounts incorporates many various sorts of accounts, they are often bundled into completely different “account groups ”. Normally one account group bundles accounts with the identical duties inside the final ledger, e. g. money accounts, material accounts, asset accounts, revenue and loss accounts.By assigning a quantity vary to an account group, you'll give you the chance to be certain that accounts of the identical sort are throughout the identical quantity range. Number intervals for G/L account grasp records can overlap.The account group needs to be entered in the chart of accounts-segment and controls the looks of the corporate code section of a G/L account. For instance, for all of your money accounts, you wish to have the ability to view the entire detailed line items. In customizing, for your “Cash Accounts” account group, you'll alter the sector status to make “line merchandise show” a required entry.
R/3 delivers predefined account groups.The sector status makes it doable to influence the looks of an account's grasp data.Fields which are not used will be suppressed.Fields which have an entry that shouldn't be changed might be set to display only (even in change mode)
- Fields which must have an entry might be made required fields.
- Fields that might be entered, but are not required, will be set to optionally available entry.
Master Data Field Status
The fields displayed on the general ledger grasp document aren't only controlled by the account group, but in addition by the master knowledge transaction that you are using (transaction dependent control) i.e. create, change, display. As quickly as the master record is created and you don't want delicate fields modified, on the master document change transaction in customizing, you specify that a certain area is not changeable. For example, you need the forex of your money account to be GBP and you don't want it to be changed, customise the grasp file change transaction to have the field be display only.For every field, the sector standing definitions from the account group and the transaction are taken into consideration and the one with larger priority is used. The priorities are (starting with the highest):
- suppress
- show
- required entry
- optional entry
Reconciliation Accounts
Reconciliation accounts are common ledger accounts assigned to the business partner master information to report all transactions within the sub-ledger.Any postings to the sub-ledger accounts robotically updates the balances of the assigned reconciliation accounts. In this approach, the general ledger is all the time up-to-date.You define a G/L-account as a reconciliation account by coming into the form of reconciliation account that it's into the sphere ”Recon.account for acct kind”.
D for customers
K for vendors
The reconciliation account is then only valid for the desired account type.Typical reconciliation accounts are the accounts “Commerce Receivables” and ”Trade Payables”.It isn't possible to publish to reconciliation accounts directly.
Line Item Display
Transaction figures are the sums of line items on the debit or credit score side. The balance is the
distinction between the debit and the credit score transaction figure.The sphere “line item display” is a control area within the company code section of an account.For accounts with out “line merchandise display” only the transaction figures are up to date when a document is posted to this account. When a user desires to have a look at this account on-line, they'll solely find a way to view the balance.For accounts with “line merchandise display” a very powerful knowledge from the posted line gadgets is stored in a particular index table. Because this knowledge can be saved within the paperwork, it's redundant and desires further storage and system time. When a consumer wants to have a look at this account on-line, they will be able to view both the balance and the individual line item details.Because of system sources that are wanted by the road merchandise show, it shouldn't be used for accounts the place the line merchandise information might be extra simply accessed in another method,
e.g.
- Reconciliation accounts (line objects are managed in the sub-ledgers)
- Gross sales income accounts (line gadgets are managed by the SD-application)
- Material stock accounts (line items are managed by the MM-application)
- Tax accounts (Tax items make sense solely in connection with the document; the tax amounts were already checked when the doc was posted.)
Gadgets in accounts with open merchandise administration are specified as open or cleared.Accounts with open merchandise management will need to have line item show activated.Normal ledger accounts ought to be administered with open merchandise management when you must verify whether there is an offsetting posting for a given enterprise transaction. Open and cleared objects may be displayed individually, and due to this fact it's straightforward to see which business transactions nonetheless need to be cleared.It's finest to use open merchandise management for:
- financial institution clearing accounts,
- clearing accounts for items receipt/bill receipt, and
- salary clearing accounts.

Only Balance in Local Currency
If the field “Solely balances in native forex” is marked within the master information report, solely transaction figures for amounts transferred to native forex are managed.This indicator ought to be set for clearing accounts from which you want to give you the option to clear objects simply by zero-balancing the amounts in local currency. Then no difference postings brought on by change fee differences have to be made.The indicator needs to be set in money discount and GR/IR clearing accounts.It should not be set in reconciliation accounts for patrons or vendors.The indicator is usually set in balance sheet accounts which are not saved in foreign forex echange and never managed on an open merchandise basis.
Methods in Creating G L Accounts
With the two step method, the chart of accounts segment is created separately from the corporate code segment. This permits for creating the GL account only in the chart of accounts or in a quantity of firm codes.Use the one step technique to create a GL account in a specified firm code. Repeat step 2 of the two step method, create in the company code segment, to create the GL account in additional company codes as needed.
Creating GL accounts by copying :
- To create an account that has the same properties as an present account, i.e. one other money account, create the brand new account with reference to the prevailing account and alter the account title accordingly.
- If all the GL accounts in an existing firm code are required in one other firm code, the entire firm code section can be copied to the new company code.
- The entire chart of accounts may be copied into a brand new chart of accounts as well, together with account determination. The monetary statement version can be copied.
Collective Processing
The SAP R/3 System gives collective processing capabilities for the G/L account master.You can change the grasp knowledge within the chart of accounts area, company code specific information or the names of a number of G/L accounts at the same time. The G/L accounts may be from different charts of accounts.You can make modifications to the displayed G/L accounts:
- You presumably can choose the fields to be changed
- You may change the values of the fields displayed. Enter the model new values within the header New to replace the prevailing values. For all G/L accounts chosen, the old worth is replaced with the new value
Group of Chart Accounts
For internal purposes, reporting over several company codes could additionally be desirable, e.g a balance sheet shall be generated which incorporates the financial positions of several firm codes.That is no problem as lengthy as all firm codes use the identical chart of accounts. However, some company codes may have to use particular charts of accounts due to legal requirements. If this is the case for inside reporting, then:
- a group chart of accounts might be used. This chart has to contain all of the group accounts.
- the group chart of accounts has to be assigned to each operational chart of accounts. If that is accomplished,the sector ”group account quantity” in the chart of account segments of the operational charts of accounts becomes a required entry field.
- in the chart of account-phase of each operational account, the group account quantity has to be entered. Totally different accounts of 1 operational chart of accounts can point to the same group account.
- a monetary statement model, for the group chart of account, must be used.
Country Chart of Accounts
A substitute for using a gaggle chart of accounts is to use a rustic charts of accounts. While every company code makes use of the same operational chart of accounts, the company codes which require a different chart of accounts for external reporting can have a country chart of accounts assigned and have the country chart of account number (alternative quantity) entered in each company code segment. Every nation account number can solely be used once.Since all firm codes post into the identical operational chart of accounts, cross-company code controlling is possible. Accounting clerks who could also be familiar with the country charts of accounts may have to get used to using the operational chart of accounts.
Bank Master Data
Every bank which is used in the system (e.g. as a home bank or as a customer/vendor financial institution) must have a bank grasp record.Financial institution grasp information are stored centrally in the bank directory. Each report is recognized by the financial institution country and the financial institution key. Financial institution master records include bank deal with information and control data resembling the SWIFT Code, postal giro data, and financial institution group (for fee optimization).Financial institution grasp data might be created four ways:
- When entering financial institution data within the buyer or vendor master report, or in the home financial institution configuration: Using the Create Bank transaction within the Accounts Receivable/Payable master file menu or The bank listing can be imported from disk or tape using program RFBVALL_0, Nation Specific Transfer of Financial institution Data. The disk with the bank listing might be obtained from one of the country’s banking organizations. It must be updated regularly or For customers utilizing the lockbox performance, a batch input session might be created that mechanically updates customer banking data within the master record.
- Banks which are utilized by your enterprise are outlined as Home Banks. Home banks are created in configuration and are composed of the financial institution grasp information, digital banking information, bank accounts per financial institution and basic ledger accounts per financial institution account.
- Within the customer/vendor master document, the sphere “Financial institution Sort” is used to differentiate between different banks. When processing invoices, if the client/vendor has multiple financial institution, the consumer can choose from the totally different banks through the use of the match code in the associate bank field.
- The house financial institution-Ids and the financial institution types can be utilized by the cost program to determine the banks to be used.
Related Posts
No comments :
Post a Comment