SAP Financial Periodic Processing comprises these tasks in Asset Accounting which have to be performed at periodic intervals.If you need to plan main prices on a cost center foundation, you may periodically decide planned depreciation and curiosity and pass these on to major cost planning in the CO system via a report.Investment assist is a subsidy which an organization has received for certain asset investments. Assets which are eligible for such a subsidy are marked within the asset master information with an investment help key. All specifications for claiming the investment support are stored within the definition of this key. You'll have the opportunity to publish the declare manually or in a mass procedure.Inflation administration is required in nations with excessive charges of inflation or deflation.You can now additionally use the Schedule Manager in FI-AA to define, schedule, process, and management periodically recurring processes.
Valuation
Depreciation areas are recognized within the system by a two-character numeric key.Please keep in mind: You also outline per depreciation area the finest method to publish the asset stability sheet values(APC, proportional value adjustment) and depreciation to the overall ledger accounts. You can also define depreciation areas for reporting reasons solely: They may show values and calculate depreciation, however won't post any values to G/L accounts.You can calculate completely different values in a depreciation space for a particular purpose (for instance, for the balance sheet, for price accounting, for taxes).You additionally define per depreciation space which values must be managed (for instance, APC or positive/negative web book value).You also define for each depreciation space how posting values and depreciation phrases should be transferred to different areas.For every area you also must enter data (frequency, process, and CO account task) for depreciation posting.
Depreciation
You'll give you the option to outline which types of depreciation should be used for each depreciation area (that's atypical, particular, or unplanned depreciation).The system helps the following direct varieties of depreciation:
Specs and parameters that the system requires to calculate depreciation amounts are entered in calculation methods. Calculation methods substitute the internal calculation key of the depreciation key.The person calculation strategies:
Imputed Interest
For value accounting, you might have to calculate imputed interest on the capital tied up in assets.Specify the next settings:
If revaluation (indexing) is planned for a depreciation space, you'll find a way to specify an index series for calculating the substitute value. You enter the index series within the asset or in the asset class.The index series have to be assigned to an index class. This class contains the important control parameters for the index series. 12 months-dependent index lessons are also used.For each fiscal 12 months, you need to specify index figures for the index series. If they're missing, the system switches to the simulated annual rate of revaluation.An indexed revaluation can be calculated for the accumulated depreciation and the imputed interest (if the interest calculation secret's based on substitute worth).You specify within the depreciation area the posting to general ledger, indicating whether you need to submit revaluation of APC and/or of depreciation/interest.
You can calculate the present substitute value in two other ways:
Depreciation Posting Program
The calculation and planning of depreciation, interest, and revaluation is controlled by transaction varieties in the Asset Accounting system.They will additionally be entered manually using a special posting transaction (for more information, see present-value depreciation). In each instances, these planned values in Asset Accounting should be periodically posted to the corresponding expense and asset balance sheet accounts within the normal ledger.The depreciation posting program RABUCH00 updates the asset values and generates a batch-enter
session for the replace of the overall ledger.The posting session also posts the totally different depreciation varieties, curiosity, and revaluation, in addition to the writing-off and allocation of particular reserves. The system doesn't create particular person documents, solely summarized posting paperwork (per enterprise area and per account dedication).The depreciation posting program RAPOST00 can be used to put up depreciation for more than 100,000 assets. In distinction to the ordinary depreciation posting program RABUCH00 depreciation is posted on to the general ledger.There are specific restrictions to be taken into mind. For extra details see the documentation of this report.
For each depreciation area and company code, specify for posting depreciation:
n You additionally have to specify the accounts for posting. (Account willpower).To ensure consistency between Asset Accounting and Monetary Accounting, it's important to course of the batch enter session created by the posting report.If you happen to fail to process the batch enter session, an error message will seem at the subsequent posting run.
Setting for Posting General Ledger
For every depreciation space, specify whether you need to:
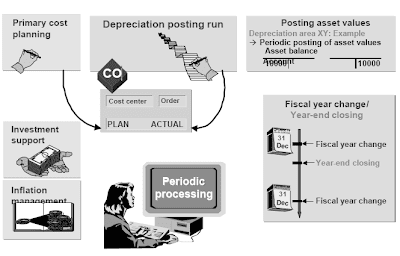
 Fiscal Year Change
Fiscal Year Change
The fiscal year change program opens new annual value fields for each asset.The earliest you can start this program is within the final posting interval of the present year.You want to run the fiscal year change program on your whole firm code.You can only process a fiscal yr change in a subsequent yr if the previous year has already been closed for business.Take care to not confuse the fiscal yr change program with 12 months-end closing for accounting purposes.
Year End Closing
Preparation for year-finish closing:
Related Posts
CODE MULTIPLE INTERACTIVE REPORT TWO
alv report with double click event
alv block list reporting for sap abap
alv hierarchical report
Programming report sample code
abap programming for mm module

Valuation
Depreciation areas are recognized within the system by a two-character numeric key.Please keep in mind: You also outline per depreciation area the finest method to publish the asset stability sheet values(APC, proportional value adjustment) and depreciation to the overall ledger accounts. You can also define depreciation areas for reporting reasons solely: They may show values and calculate depreciation, however won't post any values to G/L accounts.You can calculate completely different values in a depreciation space for a particular purpose (for instance, for the balance sheet, for price accounting, for taxes).You additionally define per depreciation space which values must be managed (for instance, APC or positive/negative web book value).You also define for each depreciation space how posting values and depreciation phrases should be transferred to different areas.For every area you also must enter data (frequency, process, and CO account task) for depreciation posting.
Depreciation
You'll give you the option to outline which types of depreciation should be used for each depreciation area (that's atypical, particular, or unplanned depreciation).The system helps the following direct varieties of depreciation:
- Strange depreciation
- Special depreciation
- Unplanned depreciation.
- Strange depreciation: This is the deliberate reduction in asset worth because of regular put on and tear.
- Particular depreciation: This represents a purely tax-primarily based kind of depreciation for wear and tear. This type of depreciation usually allows for depreciating a percentage of the asset value, and this proportion may be staggered within a tax concession period, without taking the actual put on and tear on the asset into consideration.
- Unplanned depreciation: That is involved with unusual circumstances, similar to injury to the asset,that result in a everlasting reduction in its value.
- Unit-of-production depreciation: This allows you to take fluctuations in activity into consideration for the depreciation calculation. It makes the quantity of depreciation dependent upon seasonal usage of the asset. Example: Variety of miles traveled or items produced.
Specs and parameters that the system requires to calculate depreciation amounts are entered in calculation methods. Calculation methods substitute the internal calculation key of the depreciation key.The person calculation strategies:
- Fundamental strategies
- Declining-steadiness strategies
- Most amount methods
- Multilevel methods
- Period control strategies can then be assigned to a depreciation key.
- Country-particular necessities are represented by methods particular to a selected chart of accounts
- They keep away from the utilization of an ever-growing number of inside calculation keys
- You can enter a depreciation key because the default worth for a particular company code or depreciation area.
Imputed Interest
For value accounting, you might have to calculate imputed interest on the capital tied up in assets.Specify the next settings:
- Enable the calculation of imputed interest for the depreciation area.
- Determine that curiosity should be posted for the corporate code and the corresponding depreciation area.
- Use a depreciation key to which calculation strategies for the depreciation kind "Interest" are assigned, or define such a key yourself.
- If the calculation of the curiosity is based on substitute value, the system calculates indexed interest.
- Depreciation method: Acknowledged proportion (10%)
- Base worth: Half of acquisition value
- Finish remedy: Depreciation after deliberate life finish
If revaluation (indexing) is planned for a depreciation space, you'll find a way to specify an index series for calculating the substitute value. You enter the index series within the asset or in the asset class.The index series have to be assigned to an index class. This class contains the important control parameters for the index series. 12 months-dependent index lessons are also used.For each fiscal 12 months, you need to specify index figures for the index series. If they're missing, the system switches to the simulated annual rate of revaluation.An indexed revaluation can be calculated for the accumulated depreciation and the imputed interest (if the interest calculation secret's based on substitute worth).You specify within the depreciation area the posting to general ledger, indicating whether you need to submit revaluation of APC and/or of depreciation/interest.
You can calculate the present substitute value in two other ways:
- Historical calculation: The substitute worth is calculated from the APC of a historic acquisition year.
- Normal calculation: The current replacement value is calculated based on the alternative worth of the previous year.
Depreciation Posting Program
The calculation and planning of depreciation, interest, and revaluation is controlled by transaction varieties in the Asset Accounting system.They will additionally be entered manually using a special posting transaction (for more information, see present-value depreciation). In each instances, these planned values in Asset Accounting should be periodically posted to the corresponding expense and asset balance sheet accounts within the normal ledger.The depreciation posting program RABUCH00 updates the asset values and generates a batch-enter
session for the replace of the overall ledger.The posting session also posts the totally different depreciation varieties, curiosity, and revaluation, in addition to the writing-off and allocation of particular reserves. The system doesn't create particular person documents, solely summarized posting paperwork (per enterprise area and per account dedication).The depreciation posting program RAPOST00 can be used to put up depreciation for more than 100,000 assets. In distinction to the ordinary depreciation posting program RABUCH00 depreciation is posted on to the general ledger.There are specific restrictions to be taken into mind. For extra details see the documentation of this report.
For each depreciation area and company code, specify for posting depreciation:
- the frequency
- the distribution technique
- CO account task
- different posting settings
n You additionally have to specify the accounts for posting. (Account willpower).To ensure consistency between Asset Accounting and Monetary Accounting, it's important to course of the batch enter session created by the posting report.If you happen to fail to process the batch enter session, an error message will seem at the subsequent posting run.
Setting for Posting General Ledger
For every depreciation space, specify whether you need to:
- Mechanically submit asset values online (solely possible for one depreciation area)
- Put up asset values at periodic intervals, (for instance, customer-outlined depreciation area or derived depreciation area)
- Put up depreciation at periodic intervals to the overall ledger.
 Fiscal Year Change
Fiscal Year ChangeThe fiscal year change program opens new annual value fields for each asset.The earliest you can start this program is within the final posting interval of the present year.You want to run the fiscal year change program on your whole firm code.You can only process a fiscal yr change in a subsequent yr if the previous year has already been closed for business.Take care to not confuse the fiscal yr change program with 12 months-end closing for accounting purposes.
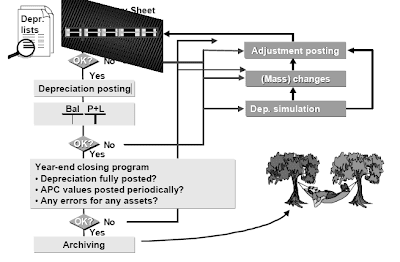
Year End Closing
Preparation for year-finish closing:
- After the depreciation lists and asset historical past sheet have been checked, depreciation is posted.
- If an area posts APC values to the overall ledger periodically, you have to to run the report
- RAPERP00 for periodic posting.
- If the ultimate end result is not satisfactory, you'll give you the chance to perform depreciation simulation or bulk changes, or make adjustment postings.
- If you change any depreciation values, you will need to run depreciation posting again.
- Once depreciation has been posted in FI-AA and FI, a steadiness sheet and revenue and loss assertion might be created.
- Depreciation was totally posted
- Errors or incomplete entries exist for any assets.

Related Posts
CODE MULTIPLE INTERACTIVE REPORT TWO
alv report with double click event
alv block list reporting for sap abap
alv hierarchical report
Programming report sample code
abap programming for mm module
No comments :
Post a Comment