SAP Financial Asset Allocation is having a discussion about the mixing of the subsidiary ledgers with the overall ledger is as vital as the mixing of accounting and logistics functions.Each transaction in customer and vendor accounts in Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable and in the asset accounts has a direct impact on the corresponding accounts of the overall ledgers.Thus the subsidiary ledgers are at all times in balance with their G/L reconciliation accounts.The G/L reconciliation accounts should be arrange in advance along with the Mounted Belongings department.
Asset Acquiring
The acquisition posting could be created in the division that is primarily responsible for this enterprise transaction.Acquisition of an asset from a enterprise companion => Exterior acquisition:
"Acquisition from in-house manufacturing" is the capitalization of products or services that are partially or completely produced in your individual enterprise. The costs for these in-home produced goods or services (comparable to upkeep) should be capitalized to assets. Generally, the capitalization of production costs can be achieved by creating an order/challenge in IM, after which settling this object first to an AUC and then to an asset.
Asset Explorer
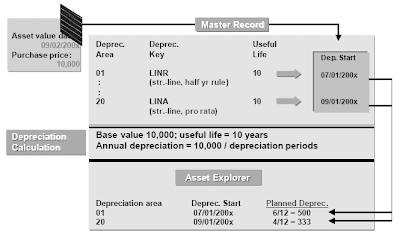
The Asset Explorer consists of crucial functions of the outdated asset worth display transaction.The main variations are: a greater overview thanks to make use of of an summary tree and tab pages, a more transparent display of the system's calculation of depreciation, and new features for printing and exporting values.Till now, you navigated between depreciation areas using push buttons. Now depreciation areas are displayed in an outline tree, from which they can be selected. Two totally different symbols allow you to right away distinguish beteween actual depreciation areas and derived depreciation areas.The field above the tree structure provides data on the selected asset: its firm code, asset predominant quantity and sub-number. You may leap from this discipline to the asset master data.Until now, you also used push buttons to achieve the next screens: plan values, book values,transactions, and simulation of depreciation terms and transactions. The Asset Explorer shows planned depreciation values for the chosen depreciation areas and transactions in one screen. Book values and depreciation parameters are on separate tab pages.You'll have the option to display planned values, book values and transactions straight within the Asset Explorer in a print preview format, as nicely as print and export this information. On the planned values tab web page,you probably can name the features for displaying the depreciation calculation and for recalculation of depreciation.
Changes to Master Data
The following data is routinely set within the asset master report on the time of the primary acquisition posting:
Value Fields
The asset value date (capitalization date) determines the depreciation start date of the asset. This date is determined for every depreciation space by the period control method of the depreciation key.The system determines the deliberate annual depreciation, and planned interest, based on the depreciation begin date and the depreciation terms.When additional transactions are posted within the current 12 months, these values are updated.The posting date and the asset worth date all the time have to be in the same fiscal year.
 Document Type
Document Type
You either use the document kind that's defaulted by the system otherwise you enter you own document type.You define the document kind in the FI implementation guide.It's a two character, alpha-numeric entry that systematizes how documents are stored.You assign exactly one number vary to every document type.You specify account varieties which may be allowed when making entries with a specific doc type.The document kind determines how the posting is processed:
Transaction Type
Transaction sorts are used with every posting. They determine acquisitions, retirements and transfers.The asset historical past sheet studies and other FI-AA studies use the transaction type to establish the totally different kinds of transactions and display them individually (for instance, the transaction sort specifies the place the value change is shown within the asset historical past sheet: as a retirement of a previous-12 months acquisition or of a present-year acquisition).The transaction type specifies which of the following are up to date:
 Each transaction kind belongs to a transaction sort group. The transaction type group defines the
Each transaction kind belongs to a transaction sort group. The transaction type group defines the
traits of the transaction type. Within the transaction sort display, select "Goto" within the menu bar to display the transaction kind group.The transaction kind groups are mounted and can't be changed.You'll have the ability to restrict specific transaction sort groups to certain asset lessons (for instance, down payments allowed only in the asset class for belongings underneath construction). All transaction varieties assigned to this transaction sort group can solely be used for property belonging to the appropriate class.There are standard reviews that can assist you show an asset portfolio divided into separate transaction types.
Posting Clearing Accounts
If asset acquisition postings aren't integrated, you would normally use a clearing account. This needs to be a common ledger account with open merchandise administration to ensure which you can clear the account.Reasons for non-built-in acquisitions:
It's now also possible to make non-integrated acquisition postings for several belongings at once.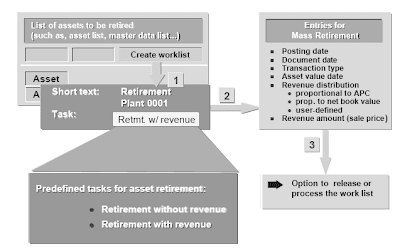 Asset Acquisition with MM Integration
Asset Acquisition with MM Integration
The instance shows an asset acquisition with MM integration. It exhibits the following activities:purchase requisition, buy order, goods receipt, bill receipt, and creation of an asset.The steps are: creation of a purchase requisition, creation of an asset master report, creation of the purchase order:
Utilizing account assignment sort A (A=asset) you can enter an asset grasp file when creating the
buy order. It is not doable yet to create an asset master file straight once you use purchase order transaction ME21N. However, it's still attainable using the "old" buy order transaction ME21.
Goods receipt: Once you enter the purchase order, you determine whether the asset is posted on to Asset Accounting, and thereby capitalized, when the goods receipt is posted (valuated good receipt), or whether or not capitalization doesn't happen till the invoice receipt is posted (non-valuated items receipt). The first possibility could be used when the goods receipt takes place earlier than the bill receipt. When the bill is acquired later, there may be variations between the invoice amount and the amount posted at the time of the products receipt. On this case, adjustment postings are made to the asset. No corrections are necessary for an non-valuated good receipt, since the asset was not but capitalized. Nonetheless, the system makes use of the date of the goods receipt because the capitalization date.
Invoice receipt:If the products receipt was non-valuated, the asset is capitalized, line objects are created and the worth fields are updated.
Retirement and G/L Accounts
There are alternative ways of posting retirements:
The system determines the reference interval for the asset retirement primarily based on the asset value date (= asset retirement date) and the interval control method (period control key) of the depreciation key.The system robotically determines the proportional worth changes (depreciation) as much as this period that apply to the part of the asset being retired, and cancels this depreciation. At the similar time, the system posts the asset retirement.The achieve or loss results as the steadiness of the follow ing: the amount of the asset retirement, the quantity of worth adjustments, and the income (that is, the sale worth) that is acquired for the asset.
Mass Retirement
Mass retirement, with or without revenue, is outlined as a regular activity in the system.To carry out a mass retirement, comply with these steps:
1. Use an asset report to create a list of the belongings to be retired.
2. Create a work list.
3. Select a purpose for the work list:
- Retirement without revenue
- Retirement sale (with revenue)
4. Enter the revenue distribution.
5. Process the work list. Or edit the work list earlier than releasing it.
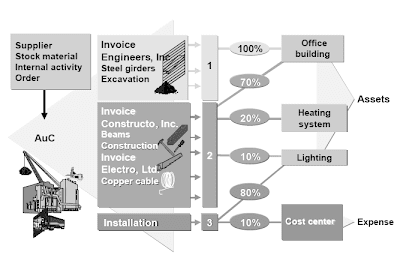
Asset Under Construction
Assets you produce yourself have two phases that are relevant to Asset Accounting:
Line Item Settlement
When performing a line item settlement of an asset under development to one or more accomplished belongings, it's greatest to proceed as follows:
Current Value Depression
In addition to the automatic calculation of depreciation using depreciation keys, you too can plan handbook depreciation for individual belongings in the FI-AA component.When you enter the transaction kind, the system acknowledges that you need to perform book depreciation (for example present-value depreciation).You probably can choose the depreciation areas, for which you wish to enter depreciation, in a dialog box. The depreciation might be current-worth depreciation, for example, that is allowed for e book depreciation however not for tax depreciation.After you've got manually planned depreciation, the system doesn't but create an FI document. This doc will not be generated till the depreciation posting program is run.Equally, you may publish write-ups or post-capitalization by selecting the appropriate transaction type and the depreciation areas you need to post.
Related Posts
CREATION OF SMART FORMS
CREATION OF SMART FORMS PART TWO
CREATION OF SMART FORMS PART THREE
Asset Acquiring
The acquisition posting could be created in the division that is primarily responsible for this enterprise transaction.Acquisition of an asset from a enterprise companion => Exterior acquisition:
- In Asset Accounting (FI-AA) integrated with Accounts Payable (incoming invoice), but without reference to a buy order order.
- In FI-AA with automatic offsetting entry, however with out link to a purchase order requisition and with out integration with Accounts Payable. This posting is generally used when the bill has not yet been received, or when the invoice was posted by the Accounts Payable division beforehand in a separate step. The offsetting account additionally has to be cleared.
- In FI-AA with automated clearing of the offsetting entry: The first posting normally is made in FIAP.
"Acquisition from in-house manufacturing" is the capitalization of products or services that are partially or completely produced in your individual enterprise. The costs for these in-home produced goods or services (comparable to upkeep) should be capitalized to assets. Generally, the capitalization of production costs can be achieved by creating an order/challenge in IM, after which settling this object first to an AUC and then to an asset.
Asset Explorer
The Asset Explorer consists of crucial functions of the outdated asset worth display transaction.The main variations are: a greater overview thanks to make use of of an summary tree and tab pages, a more transparent display of the system's calculation of depreciation, and new features for printing and exporting values.Till now, you navigated between depreciation areas using push buttons. Now depreciation areas are displayed in an outline tree, from which they can be selected. Two totally different symbols allow you to right away distinguish beteween actual depreciation areas and derived depreciation areas.The field above the tree structure provides data on the selected asset: its firm code, asset predominant quantity and sub-number. You may leap from this discipline to the asset master data.Until now, you also used push buttons to achieve the next screens: plan values, book values,transactions, and simulation of depreciation terms and transactions. The Asset Explorer shows planned depreciation values for the chosen depreciation areas and transactions in one screen. Book values and depreciation parameters are on separate tab pages.You'll have the option to display planned values, book values and transactions straight within the Asset Explorer in a print preview format, as nicely as print and export this information. On the planned values tab web page,you probably can name the features for displaying the depreciation calculation and for recalculation of depreciation.
Changes to Master Data
The following data is routinely set within the asset master report on the time of the primary acquisition posting:
- Capitalization date of the asset (derived from asset worth date)
- Date of preliminary acquisition on the asset master report (derived from asset value date)
- Acquisition yr and acquisition interval (derived from posting date)
Value Fields
The asset value date (capitalization date) determines the depreciation start date of the asset. This date is determined for every depreciation space by the period control method of the depreciation key.The system determines the deliberate annual depreciation, and planned interest, based on the depreciation begin date and the depreciation terms.When additional transactions are posted within the current 12 months, these values are updated.The posting date and the asset worth date all the time have to be in the same fiscal year.
 Document Type
Document TypeYou either use the document kind that's defaulted by the system otherwise you enter you own document type.You define the document kind in the FI implementation guide.It's a two character, alpha-numeric entry that systematizes how documents are stored.You assign exactly one number vary to every document type.You specify account varieties which may be allowed when making entries with a specific doc type.The document kind determines how the posting is processed:
- With document kind "AA" you publish gross, that's, with out deducting a discount.
- With doc kind "AN" (KN, RN), the amount capitalized to the asset is reduced by the discount net document kind).
Transaction Type
Transaction sorts are used with every posting. They determine acquisitions, retirements and transfers.The asset historical past sheet studies and other FI-AA studies use the transaction type to establish the totally different kinds of transactions and display them individually (for instance, the transaction sort specifies the place the value change is shown within the asset historical past sheet: as a retirement of a previous-12 months acquisition or of a present-year acquisition).The transaction type specifies which of the following are up to date:
- Asset balance sheet accounts
- Depreciation areas
- Worth fields
 Each transaction kind belongs to a transaction sort group. The transaction type group defines the
Each transaction kind belongs to a transaction sort group. The transaction type group defines thetraits of the transaction type. Within the transaction sort display, select "Goto" within the menu bar to display the transaction kind group.The transaction kind groups are mounted and can't be changed.You'll have the ability to restrict specific transaction sort groups to certain asset lessons (for instance, down payments allowed only in the asset class for belongings underneath construction). All transaction varieties assigned to this transaction sort group can solely be used for property belonging to the appropriate class.There are standard reviews that can assist you show an asset portfolio divided into separate transaction types.
Posting Clearing Accounts
If asset acquisition postings aren't integrated, you would normally use a clearing account. This needs to be a common ledger account with open merchandise administration to ensure which you can clear the account.Reasons for non-built-in acquisitions:
- the invoice arrived earlier than the asset.
- the asset has already been delivered however the bill has not.
It's now also possible to make non-integrated acquisition postings for several belongings at once.
 Asset Acquisition with MM Integration
Asset Acquisition with MM IntegrationThe instance shows an asset acquisition with MM integration. It exhibits the following activities:purchase requisition, buy order, goods receipt, bill receipt, and creation of an asset.The steps are: creation of a purchase requisition, creation of an asset master report, creation of the purchase order:
Utilizing account assignment sort A (A=asset) you can enter an asset grasp file when creating the
buy order. It is not doable yet to create an asset master file straight once you use purchase order transaction ME21N. However, it's still attainable using the "old" buy order transaction ME21.
Goods receipt: Once you enter the purchase order, you determine whether the asset is posted on to Asset Accounting, and thereby capitalized, when the goods receipt is posted (valuated good receipt), or whether or not capitalization doesn't happen till the invoice receipt is posted (non-valuated items receipt). The first possibility could be used when the goods receipt takes place earlier than the bill receipt. When the bill is acquired later, there may be variations between the invoice amount and the amount posted at the time of the products receipt. On this case, adjustment postings are made to the asset. No corrections are necessary for an non-valuated good receipt, since the asset was not but capitalized. Nonetheless, the system makes use of the date of the goods receipt because the capitalization date.
Invoice receipt:If the products receipt was non-valuated, the asset is capitalized, line objects are created and the worth fields are updated.
Retirement and G/L Accounts
There are alternative ways of posting retirements:
- With or without revenue (scrapping)
- With or with out customer (not built-in)
- As complete or partial retirement
- As mass retirement (utilizing a worklist)
- As retirement of a number of assets (throughout the manually posted retirement transaction)
The system determines the reference interval for the asset retirement primarily based on the asset value date (= asset retirement date) and the interval control method (period control key) of the depreciation key.The system robotically determines the proportional worth changes (depreciation) as much as this period that apply to the part of the asset being retired, and cancels this depreciation. At the similar time, the system posts the asset retirement.The achieve or loss results as the steadiness of the follow ing: the amount of the asset retirement, the quantity of worth adjustments, and the income (that is, the sale worth) that is acquired for the asset.
Mass Retirement
Mass retirement, with or without revenue, is outlined as a regular activity in the system.To carry out a mass retirement, comply with these steps:
1. Use an asset report to create a list of the belongings to be retired.
2. Create a work list.
3. Select a purpose for the work list:
- Retirement without revenue
- Retirement sale (with revenue)
4. Enter the revenue distribution.
5. Process the work list. Or edit the work list earlier than releasing it.
Asset Under Construction
Assets you produce yourself have two phases that are relevant to Asset Accounting:
- the below development phase and
- the helpful life.
- as a "normal" asset grasp record (for summary settlement)
- as an asset grasp report with line merchandise management.
Line Item Settlement
When performing a line item settlement of an asset under development to one or more accomplished belongings, it's greatest to proceed as follows:
- Select all line objects which you need to settle in the identical proportion to the identical receiver.
- Define the distribution rule for these line items.
- Post the settlement of line gadgets to the desired receivers utilizing the distribution rule.
- Observe that this posting procedure settles all line objects, to which a distribution rule is assigned.

Current Value Depression
In addition to the automatic calculation of depreciation using depreciation keys, you too can plan handbook depreciation for individual belongings in the FI-AA component.When you enter the transaction kind, the system acknowledges that you need to perform book depreciation (for example present-value depreciation).You probably can choose the depreciation areas, for which you wish to enter depreciation, in a dialog box. The depreciation might be current-worth depreciation, for example, that is allowed for e book depreciation however not for tax depreciation.After you've got manually planned depreciation, the system doesn't but create an FI document. This doc will not be generated till the depreciation posting program is run.Equally, you may publish write-ups or post-capitalization by selecting the appropriate transaction type and the depreciation areas you need to post.
Related Posts
CREATION OF SMART FORMS
CREATION OF SMART FORMS PART TWO
CREATION OF SMART FORMS PART THREE
No comments :
Post a Comment