SAP has a good deal and methods in dealing with tax issues in different countries and there are certain rules that we need to follow to get the outputs required as per tax implications.This must be specified per company code or per the best degree of the jurisdiction code.Value-added tax is calculated as the balance between turnover tax (R/three-time period: output tax) and prior tax (R/3-time period: input tax).Output tax is calculated using the online value of merchandise and is charged to customers. The output tax is a legal responsibility which the enterprise owes to the tax authority.Enter tax is calculated utilizing the net bill amount and is charged by vendors. The paid enter tax is a receivable which the enterprise claims from the tax authority.Only the tax which is levied on the worth added to the products by the enterprise needs to be remitted to the tax authority.Tax authorities can set a nondeductible portion for enter tax which cannot then be claimed as a deduction from the the calculation of tax due. The quantity may be posted to a separate expense account, or it could be distributed to the G/L account and assets line items.
Taxes on purchases include gross sales tax and use tax. Both taxes only apply to items that are consumed by the customer. Items which can be utilized in production or for resale to a 3rd occasion remain untaxed. If a taxable good is bought, both gross sales or use tax is levied. Subsequently, every good is barely taxed once.This slide exhibits a posting of gross sales taxes. Gross sales tax is collected by a vendor on a sale and remitted to the jurisdiction of the customer. The system calculates gross sales tax based mostly on material and buyer location and posts it in Sales and Distribution (SD) and Supplies Management (MM). If customers are exempt from taxation, you can specify this of their master data by entering the suitable indicator.
SAP offers for various types of taxation programs which may be present in numerous countries
1. Taxes are levied at a country/federal level, with uniformly outlined rates.
2.Taxes are levied at a state/jurisdictional degree, with charges been defined by the state/jurisdiction.As a result of complications involved with this sort of taxation(i.e. there are over 67,000 doable jurisdictions), third party software is usually used to determine the tax allocation. SAP gives a generic interface software to support this.In some countries (e.g. Canada, India, Brazil) taxes are even levied on both levels.Sales and use taxes are typical examples of taxes below federal level.
The FI system assists with the management of taxes calculated by:
The shopper solely has to pay use tax if he was not already charged sales tax by the vendor. This can be the case if the vendor doesn't have a “presence” in the state of the customer or if the customer has a “self-assessment permit”. Use tax is self assessed by the shopper and remitted to the jurisdiction the place the products are consumed.There are basically two kinds of taxation that can be processed in the R/3 System:
Tax Calculation Procedure
Each nation wants a tax procedure (calculation process) assigned to it to perform tax calculations. R/3 is delivered with pre-configured tax procedures for many countries.The tax procedure contains:
The structure of the jurisdiction code needs to be defined by assigning the lengths of the level codes to the tax procedure. This exercise additionally automatically switches over tax processing for this tax process to the tax jurisdiction code method.
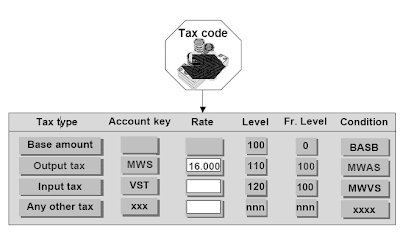
Tax Code
The tax code is entered when the document is posted and it is the primary hyperlink to the tax calculation.Depending on whether or not the country makes use of a taxation procedure with jurisdictional taxation:
. the tax code is linked to a rustic code.
. the tax code is linked to a combination of nation code and jurisdictional code.
The tax codes inside a jurisdictional taxation technique are time-dependent. You can choose in configuration if the document date or the posting date shall be legitimate for the tax calculation. n As at release 4.0 it is possible to course of tax studies of warehouses, selling agencies, or crops abroad within the home firm code with out having to create a international company code for them. If the functionality “vegetation overseas” is lively, particular tax codes could be created that are used especially for the foreign tax experiences of the crops abroad. These tax codes must have the nation entered within the subject “reporting county” and the foreign VAT numbers and other administration information should be assigned to the corporate code.
Tax rates
The tax code comprises (in addition to other information) the tax rates. Tax charges are assigned to the tax types that are included in the tax procedure. A tax code may have several tax rates entered for totally different tax sorts (if a line item shall be taxed with several tax sorts), but normally only one tax rate is entered. Instance for tax code with a couple of tax rate:
10% input tax on a line item with 40% of the tax non-deductible.Some postings to tax-related G/L accounts could have a tax rate of zero. This can be the case for:
Tax Posting
The taxes calculated by the system are usually posted via a separate line item to a particular tax
account. That is the standard scenario.Taxes with sure course of/account keys (e.g. NVV) are distributed to the relevant expense/revenue item. This is the case for gross sales tax payables or may be used for other nondeductible enter taxes.For the system to carry out automatic tax account project, the account/course of keys which generate a separate line item for the tax posting need to have the required data assigned to them. This necessary data are:
EU Market Vat Processing
Deliveries to customers in third occasion countries are tax exempt (output tax 0%). The client has to pay import tax which is usually equal to the interior-nation enter tax.Throughout the EU single market usually the country of vacation spot-precept applies. Which means that deliveries are tax exempt (output tax zero%) with acquisition tax being levied in the nation of destination.n The obstacles have been replaced by more intensive reporting for deliveries between firms in EU countries:
SAP CRM Solution Monitoring
CRM Backup Restoring System
SAP CRM Organizational Model
CRM Software Logistics and Support
MySAP CRM Marketing Introduction
CRM Marketing and lead management
Taxes on purchases include gross sales tax and use tax. Both taxes only apply to items that are consumed by the customer. Items which can be utilized in production or for resale to a 3rd occasion remain untaxed. If a taxable good is bought, both gross sales or use tax is levied. Subsequently, every good is barely taxed once.This slide exhibits a posting of gross sales taxes. Gross sales tax is collected by a vendor on a sale and remitted to the jurisdiction of the customer. The system calculates gross sales tax based mostly on material and buyer location and posts it in Sales and Distribution (SD) and Supplies Management (MM). If customers are exempt from taxation, you can specify this of their master data by entering the suitable indicator.
SAP offers for various types of taxation programs which may be present in numerous countries
- Value-added tax
- Tax on Purchases
- Extra tax (country-specific, e.g. investment tax in Norway, clearing tax in Belgium)
- Withholding tax (not taught in this course)
1. Taxes are levied at a country/federal level, with uniformly outlined rates.
2.Taxes are levied at a state/jurisdictional degree, with charges been defined by the state/jurisdiction.As a result of complications involved with this sort of taxation(i.e. there are over 67,000 doable jurisdictions), third party software is usually used to determine the tax allocation. SAP gives a generic interface software to support this.In some countries (e.g. Canada, India, Brazil) taxes are even levied on both levels.Sales and use taxes are typical examples of taxes below federal level.
The FI system assists with the management of taxes calculated by:
- Checking the tax quantity entered or automatically calculating the tax.
- Posting the tax quantity to G/L accounts.
- Performing tax adjustments for money discounts or different types of deductions
- Web (taxable expense or revenue gadgets minus money discount)
- Gross (taxable expense or revenue objects together with money low cost)

The shopper solely has to pay use tax if he was not already charged sales tax by the vendor. This can be the case if the vendor doesn't have a “presence” in the state of the customer or if the customer has a “self-assessment permit”. Use tax is self assessed by the shopper and remitted to the jurisdiction the place the products are consumed.There are basically two kinds of taxation that can be processed in the R/3 System:
- Taxes at federal level, with uniformly defined rates.
- Taxes under federal stage, with rates been outlined by jurisdictions (state, country, town, or lower) on several levels.
- Because of the problems concerned with this sort of taxation, third occasion software program is usually used to determine the tax allocation. SAP provides a generic interface software program to help this.
Tax Calculation Procedure
Each nation wants a tax procedure (calculation process) assigned to it to perform tax calculations. R/3 is delivered with pre-configured tax procedures for many countries.The tax procedure contains:
- the order of steps which must be taken within the tax calculation process (the “from step”
- signifies the place the system is to acquire the quantity worth for the “step”).
- tax types (condition varieties) which are valid for the country. The R/3 system is delivered with required situation sorts for each type of tax calculations and the tax procedures already contain the correct condition types.
- account/course of keys which include additional specifications and are used for the automatic account project for taxes of a certain type. Account keys have been predefined in R/three and it's beneficial that customary account keys be used.
- TAXUSJ Customary tax process together with dealing with of jurisdiction codes
- TAXUSX Tax process used when employing an exterior tax bundle
The structure of the jurisdiction code needs to be defined by assigning the lengths of the level codes to the tax procedure. This exercise additionally automatically switches over tax processing for this tax process to the tax jurisdiction code method.
Tax Code
The tax code is entered when the document is posted and it is the primary hyperlink to the tax calculation.Depending on whether or not the country makes use of a taxation procedure with jurisdictional taxation:
. the tax code is linked to a rustic code.
. the tax code is linked to a combination of nation code and jurisdictional code.
The tax codes inside a jurisdictional taxation technique are time-dependent. You can choose in configuration if the document date or the posting date shall be legitimate for the tax calculation. n As at release 4.0 it is possible to course of tax studies of warehouses, selling agencies, or crops abroad within the home firm code with out having to create a international company code for them. If the functionality “vegetation overseas” is lively, particular tax codes could be created that are used especially for the foreign tax experiences of the crops abroad. These tax codes must have the nation entered within the subject “reporting county” and the foreign VAT numbers and other administration information should be assigned to the corporate code.
Tax rates
The tax code comprises (in addition to other information) the tax rates. Tax charges are assigned to the tax types that are included in the tax procedure. A tax code may have several tax rates entered for totally different tax sorts (if a line item shall be taxed with several tax sorts), but normally only one tax rate is entered. Instance for tax code with a couple of tax rate:
10% input tax on a line item with 40% of the tax non-deductible.Some postings to tax-related G/L accounts could have a tax rate of zero. This can be the case for:
- gadgets which are tax-exempt however must be reported to the tax authorities. For this stuff a particular tax code with a tax price of zero is created.
- gadgets which are created by non-taxable transactions like goods challenge supply, items movement, etc. A particular tax code have to be assigned to these transactions.
Tax Posting
The taxes calculated by the system are usually posted via a separate line item to a particular tax
account. That is the standard scenario.Taxes with sure course of/account keys (e.g. NVV) are distributed to the relevant expense/revenue item. This is the case for gross sales tax payables or may be used for other nondeductible enter taxes.For the system to carry out automatic tax account project, the account/course of keys which generate a separate line item for the tax posting need to have the required data assigned to them. This necessary data are:
- the posting keys (40 and 50 are beneficial),
- guidelines which decide on which fields the account determination is predicated (account determination may be based mostly on tax code or on account key)
- the tax accounts
EU Market Vat Processing
Deliveries to customers in third occasion countries are tax exempt (output tax 0%). The client has to pay import tax which is usually equal to the interior-nation enter tax.Throughout the EU single market usually the country of vacation spot-precept applies. Which means that deliveries are tax exempt (output tax zero%) with acquisition tax being levied in the nation of destination.n The obstacles have been replaced by more intensive reporting for deliveries between firms in EU countries:
- The acquisition tax is self-assessed by the client and must be reported to the tax authorities in an prolonged advance return for tax on gross sales/purchases. In the identical report, the acquisition tax might be claimed as enter tax. So, in precise fact, the company does not need to pay any taxes for the acquisition and the acquisition tax is just a device to report the EU acquisitions to the tax authorities.
- The vendor has to report the tax-exempt deliveries/items actions to their tax authorities in an EU sales list. This sales checklist additionally contains the receivers of the goods. To identify the receivers each company is assigned a VAT registration number. This number must be specified on each bill between EU companies.
- The acquisition tax code is a tax code which generates two posting lines. It posts the acquisition tax to the credit side of the acquisition output tax account and the identical quantity to the debit facet of the acquisition input tax account.
- The output tax code for the tax exempt deliveries needs to have an EC code for goods, services, and subcontracting within the EU to extract the relevant sales for the EU gross sales list. Because of technical reasons, it's necessary to assign a tax account to the tax code although no tax is posted.
SAP CRM Solution Monitoring
CRM Backup Restoring System
SAP CRM Organizational Model
CRM Software Logistics and Support
MySAP CRM Marketing Introduction
CRM Marketing and lead management
No comments :
Post a Comment